Syntax comparison between access and sql server

This article briefly summarizes the syntactic differences between access and sql server. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.
1. Differentiated functions and solutions
The functions in the solution shown below are defined in the method of the TAdoConn class in the untDataBase unit.
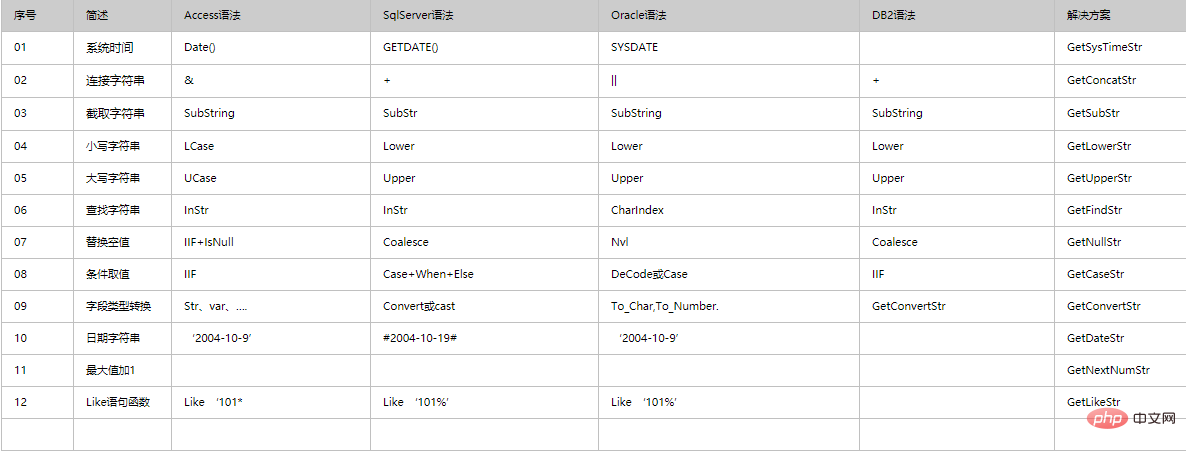
2. Database functions and keyword lists that are partially the same between Access and SQLSERVER
1. Functions
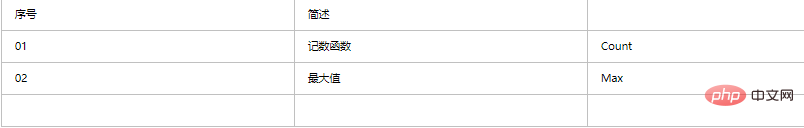
2. Keywords

3. The difference in statement syntax between Access and statement SqlServer
1. Inser Into…..Select…From statement:
The following statement in ACCESS
Insert INTO
PubSubJectAccCopys(Copy_id,Acc_id,Acc_Pid,Acc_name,acc_short,Acc_Comment,Acc_Pro,acc_type,Sub_id_flag,acc_index) (Select 200201, Acc_id,Acc_Pid,Acc_name,acc_short,Acc_Comment,Acc_Pro,acc_type,Sub_id_flag,acc_index FROM PubSubJectAcc Where PubSubJectAcc.co_type='03')
中后"(select 200201******.co_Type=' 03')" must be removed to execute, as follows:
Insert INTO
PubSubJectAccCopys(Copy_id,Acc_id,Acc_Pid,Acc_name,acc_short, Acc_Comment,Acc_Pro,acc_type,Sub_id_flag,acc_index) Select 200201,Acc_id,Acc_Pid,Acc_name,acc_short,Acc_Comment,Acc_Pro,acc_type,Sub_id_flag,acc_index FROM PubSubJectAcc Where PubSubJectAcc.co_type='03'
In SQL SERVER Medium All are OK
2. Inner Join statement 1
StrSql:='select a.user_id,a.user_opcode,b.copy_name from sysuser a inner join (syscopysuser c inner join syscopys b on c .copy_id=c.copy_id) on a.user_id=c.user_id where
a.user_opcode=''' EdtUserOpCode.text ''' And copy_name=''' Tmpcopyname '''';
should be changed to
StrSql:='select a.user_id,a.user_opcode,b.copy_name from sysuser a inner join (syscopysuser c inner join syscopys b on c.copy_id=d.copy_id) on a.user_id=c.user_id where
a.user_opcode=''' EdtUserOpCode.text ''' And copy_name=''' Tmpcopyname '''';
Retrieval of this line of code Condition error: C.copy_id=C.Copy_id should be changed to c.copy_id=d.copy_id
Note: Both writing methods can run in SQL-SERVER, but c.copy_id=C.copy_id is Cannot run in ACCESS
3. Inner Join statement 2
StrSql:='select copy_year,copy_name,a.copy_id from SysCopys a inner join SysCopysUser b on a.curcopy_flag=1 and a. copy_id=b.copy_id where b.user_id=' '''' TmpPubUserID '''';
This is
StrSql:='select copy_year,copy_name,a.copy_id from SysCopys a inner join SysCopysUser b on a.copy_id=b.copy_id where a.curcopy_flag=''1'' and b.user_id=' '''' TmpPubUserID '''';
Note: Both writing methods are It can run in SQL-SERVER, but the first one cannot run in ACCESS
4. Inner Join statement 3
The following statement can be executed in SQl server
'Select distinct sysoption.opti_id,sysoption.opti_name,sysoption.opti_code,sysroleoption.opti_sort From sysoption inner join sysroleoption ON sysoption.opti_id=sysroleoption.opti_id AND sysroleoption.role_id=:roleid'
But not in ACCESS, only
'Select distinct sysoption.opti_id,sysoption.opti_name,sysoption.opti_code,sysroleoption.opti_sort From sysoption inner join sysroleoption ON sysoption.opti_id=sysroleoption.opti_id Where sysroleoption.role_id=:roleid'
5. Update statement
Can be executed in Sql SerVer but not in Access
'Update sysuserrole SET sysuserrole.role_sort = (Select sysrole.role_sort FROM sysrole Where sysuserrole.role_id = sysrole.role_id and sysuserrole.user_id='01')'
6. Date comparison
Used in SQL SERVER
StrSql:='select copy_year,Start_month,Cur_month,Start_Flag,Start_date, End_date '
'From SysCopys '
'where copy_id=''' LoginCopyID ''' '
'and start_date
'and end_date>=''' datetostr(LoginDate) '''';
Used in ACCESS
StrSql:='select copy_year,Start_month,Cur_month ,Start_Flag,Start_date,End_date '
'From SysCopys '
'where copy_id=''' LoginCopyID ''' '
'and start_date
'and end_date>=#' datetostr(LoginDate) '#'
Refer to the 10th function "GetDateStr" above
7. Maximum value acquisition statement
StrSql:='insert into sysRoleOption '
'select ''' fidRoleId ''' as Role_ID,opti_id,'
'convert(numeric,opti_id)-(convert(numeric,opti_parentid)*100) ' MaxOptiSort
' as opti_Sort from sysoption where opti_parentid= '''
PCoTypeID(self.trvRoles.Selected.data)^.StrCoTypeID
''' and opti_bottom=''1' '''';
Change for
StrSql:='insert into sysRoleOption '
'select ''' fidRoleId ''' as Role_ID,opti_id,'
'opti_id-opti_parentid*100 ' MaxOptiSort
' as opti_sort from sysoption where opti_parentid='''
PCoTypeID(self.trvRoles.Selected.data)^.StrCoTypeID
''' and opti_bottom='' 1' ''''
Note: Both writing methods can be run in SQL-SERVER, but the first one cannot be run in ACCESS
But consider that Null values and statements will appear For versatility, you can use the 07th function "GetNullStr" and the 09th function "GetConvertStr" above to complete the conversion of strings to numbers, null values and 0 numbers: refer to the GetNextNumStr code.
1. As cannot be omitted in Sql
2. Only one Sql can be executed at a time
3. There are no substring, cast and other functions
4. Strictly distinguish between integer and character types in SQL
5. No stored procedures or triggers
6.! = is replaced with
7. Add # signs on both sides of the time string
8. In the sql statement with parameters, replace @ with ? sign
Related recommendations: access database tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Syntax comparison between access and sql server. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use sql if statement
Apr 09, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
How to use sql if statement
Apr 09, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
SQL IF statements are used to conditionally execute SQL statements, with the syntax as: IF (condition) THEN {statement} ELSE {statement} END IF;. The condition can be any valid SQL expression, and if the condition is true, execute the THEN clause; if the condition is false, execute the ELSE clause. IF statements can be nested, allowing for more complex conditional checks.
 How to configure zend for apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure zend for apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Zend in Apache? The steps to configure Zend Framework in an Apache Web Server are as follows: Install Zend Framework and extract it into the Web Server directory. Create a .htaccess file. Create the Zend application directory and add the index.php file. Configure the Zend application (application.ini). Restart the Apache Web server.
 How to solve the 'Network Error' caused by Vue Axios across domains
Apr 07, 2025 pm 10:27 PM
How to solve the 'Network Error' caused by Vue Axios across domains
Apr 07, 2025 pm 10:27 PM
Methods to solve the cross-domain problem of Vue Axios include: Configuring the CORS header on the server side using the Axios proxy using JSONP using WebSocket using the CORS plug-in
 What are the benefits of multithreading in c#?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:51 PM
What are the benefits of multithreading in c#?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:51 PM
The advantage of multithreading is that it can improve performance and resource utilization, especially for processing large amounts of data or performing time-consuming operations. It allows multiple tasks to be performed simultaneously, improving efficiency. However, too many threads can lead to performance degradation, so you need to carefully select the number of threads based on the number of CPU cores and task characteristics. In addition, multi-threaded programming involves challenges such as deadlock and race conditions, which need to be solved using synchronization mechanisms, and requires solid knowledge of concurrent programming, weighing the pros and cons and using them with caution.
 Unable to log in to mysql as root
Apr 08, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
Unable to log in to mysql as root
Apr 08, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
The main reasons why you cannot log in to MySQL as root are permission problems, configuration file errors, password inconsistent, socket file problems, or firewall interception. The solution includes: check whether the bind-address parameter in the configuration file is configured correctly. Check whether the root user permissions have been modified or deleted and reset. Verify that the password is accurate, including case and special characters. Check socket file permission settings and paths. Check that the firewall blocks connections to the MySQL server.
 Summary of phpmyadmin vulnerabilities
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:24 PM
Summary of phpmyadmin vulnerabilities
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:24 PM
The key to PHPMyAdmin security defense strategy is: 1. Use the latest version of PHPMyAdmin and regularly update PHP and MySQL; 2. Strictly control access rights, use .htaccess or web server access control; 3. Enable strong password and two-factor authentication; 4. Back up the database regularly; 5. Carefully check the configuration files to avoid exposing sensitive information; 6. Use Web Application Firewall (WAF); 7. Carry out security audits. These measures can effectively reduce the security risks caused by PHPMyAdmin due to improper configuration, over-old version or environmental security risks, and ensure the security of the database.
 How to monitor Nginx SSL performance on Debian
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to monitor Nginx SSL performance on Debian
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
This article describes how to effectively monitor the SSL performance of Nginx servers on Debian systems. We will use NginxExporter to export Nginx status data to Prometheus and then visually display it through Grafana. Step 1: Configuring Nginx First, we need to enable the stub_status module in the Nginx configuration file to obtain the status information of Nginx. Add the following snippet in your Nginx configuration file (usually located in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf or its include file): location/nginx_status{stub_status
 What is apache server? What is apache server for?
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:57 AM
What is apache server? What is apache server for?
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Apache server is a powerful web server software that acts as a bridge between browsers and website servers. 1. It handles HTTP requests and returns web page content based on requests; 2. Modular design allows extended functions, such as support for SSL encryption and dynamic web pages; 3. Configuration files (such as virtual host configurations) need to be carefully set to avoid security vulnerabilities, and optimize performance parameters, such as thread count and timeout time, in order to build high-performance and secure web applications.






