How to clean up resources occupied by docker

Foreword:
Friends who often use docker know that docker occupies resources very quickly. The most obvious and easiest to detect is the occupation of disk space. So how do we clean up the system resources occupied by docker?
(Learning video sharing: Introduction to Programming)
The method is as follows:
View the resources occupied by docker
is cleaning up resources Before we need to figure out what system resources docker occupies. This requires a combination of different commands to accomplish.
docker container ls: By default, only running containers are listed. The -a option will list all containers including stopped ones.
docker image ls: List image information. The -a option will list intermediate images (which are the layers that other images depend on).
docker volume ls: List data volumes.
docker network ls: List network.
docker info: Displays system-level information, such as the number of containers and images, etc.
After checking the resources used by docker through these commands, I believe you have decided to clean up some resources occupied by docker! Let's start with those resources that are not being used.
Only delete those unused resources
Docker provides the convenient docker system prune command to delete stopped containers, dangling images, networks not referenced by containers, and during the build process cache:
$ docker system prune
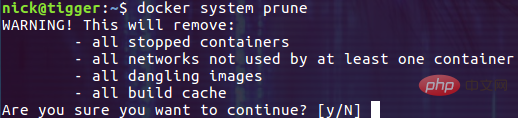
For security reasons, this command will not delete data volumes that are not referenced by any container by default. If you need to delete these data volumes at the same time, you need to explicitly Specify the --volumns parameter. For example, you may want to execute the following command:
$ docker system prune --all --force --volumes
Not only will the data volume be deleted this time, but there will not even be a confirmation process! Note that using the --all parameter will delete all unreferenced images, not just dangling images.
It is necessary to explain here what dangling images are. In fact, they can be simply understood as images that are not referenced by any image. For example, after you rebuild the image, those previously built image layers that are no longer referenced become dangling images:
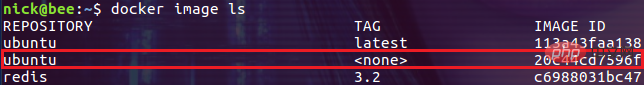
After the local image is updated, An image similar to the
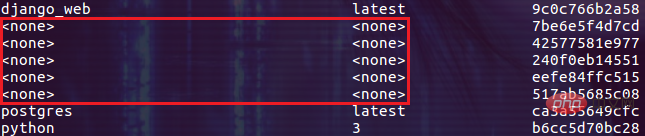
docker container prune # 删除所有退出状态的容器 docker volume prune # 删除未被使用的数据卷 docker image prune # 删除 dangling 或所有未被使用的镜像
Recall the docker system prune --all --force --volumns command we introduced earlier. If all containers in the system have been stopped before executing this command, then this command will remove all resources! Okay, now let's figure out how to stop all the containers in the system.
$ docker container ls -a -q
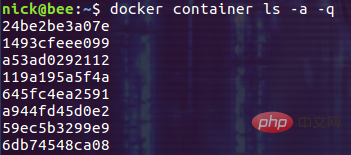
Then use the execution result of this command as the parameter of the docker container stop command:
$ docker container stop $(docker container ls -a -q)
$ docker container stop $(docker container ls -a -q) && docker system prune --all --force --volumns
Delete container: docker container rm $(docker container ls -a -q)
Delete image: docker image rm $(docker image ls -a -q)
Delete data Volume: docker volume rm $(docker volume ls -q)
Delete network: docker network rm $(docker network ls -q)
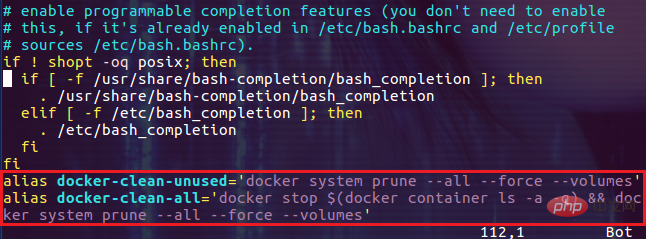
alias docker-clean-unused='docker system prune --all --force --volumes'alias docker-clean-all='docker stop $(docker container ls -a -q) && docker system prune --all --force --volumes'
把上面的命令写入到用户的 ~/.bashrc 文件中就可以了!
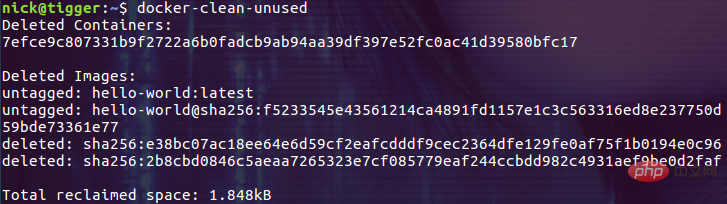
执行一次清理任务:
总结
经常清理系统资源不仅能够让系统运行的更流畅,也利于我们把精力集中在相关的重点资源上面。所以建议大家能够使用相关的资源清理命令,让 docker 保持清爽和高效。
相关推荐:docker入门教程
The above is the detailed content of How to clean up resources occupied by docker. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart the Docker container: get the container ID (docker ps); stop the container (docker stop <container_id>); start the container (docker start <container_id>); verify that the restart is successful (docker ps). Other methods: Docker Compose (docker-compose restart) or Docker API (see Docker documentation).
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]






