Understanding shared modules in Angular4
This article will take you through the shared modules in Angular4. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Related tutorial recommendations: "angular Tutorial"
1. AppModule
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
exports: [ AppComponent ],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }imports Other modules where the classes required by the component template declared in this module are located.
providers The creator of the service and added to the global service list, which can be used in any part of the application.
declarations declares the view classes owned in this module. Angular has three view classes: components, directives, and pipes.
Exports A subset of declarations that can be used in component templates of other modules.
bootstrap specifies the main view of the application (called the root component), which is the host for all other views. Only the root module can set the bootstrap attribute.
2. CommonModule
First take a look at what is in CommonModule .
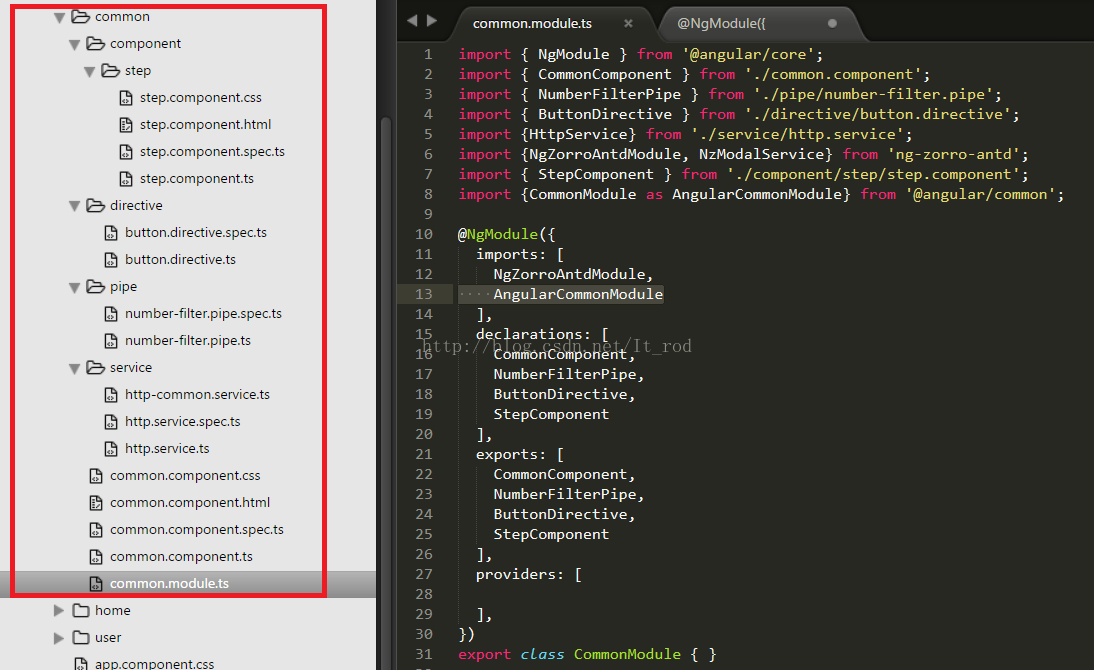
##common.module.ts code
@NgModule({
imports: [
NgZorroAntdModule,
AngularCommonModule
],
declarations: [
CommonComponent,
NumberFilterPipe,
ButtonDirective,
StepComponent
],
exports: [
CommonComponent,
NumberFilterPipe,
ButtonDirective,
StepComponent
],
providers: [
],
})pipe, component, directive so that other modules can use it.
3. AngularModule
Then we need to use this module in other modules , you need to import it.
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AngularComponent } from './angular.component';
import {RouterModule, Routes} from '@angular/router';
import {CommonModule as CommonPrivateModule} from '../../common/common.module';
import {CommonModule} from '@angular/common';
import {HttpService} from '../../common/service/http.service';
import {HttpCommonService} from '../../common/service/http-common.service';
import {BrowserModule} from '@angular/platform-browser';
const routes: Routes = [
{path: '', component: AngularComponent}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
CommonModule,
RouterModule.forChild(routes),
CommonPrivateModule
],
declarations: [AngularComponent],
providers: []
})
export class AngularModule { }angular.component.html
##<p>
<app-step [stepString]="['common component']"></app-step>
<button appButton> common directive</button> <br>
common pipe: {{1 | numberFilter}}
</p>
ButtonDirective.
4. Service
service is added in front of the Common file, but not in the CommonModule provide . Why is this? Because service is implemented by Angular's dependency injection system, not the module system. If we provide in CommonModule, then the service we use in each module is not one instance, but multiple instances. Let's test it below.
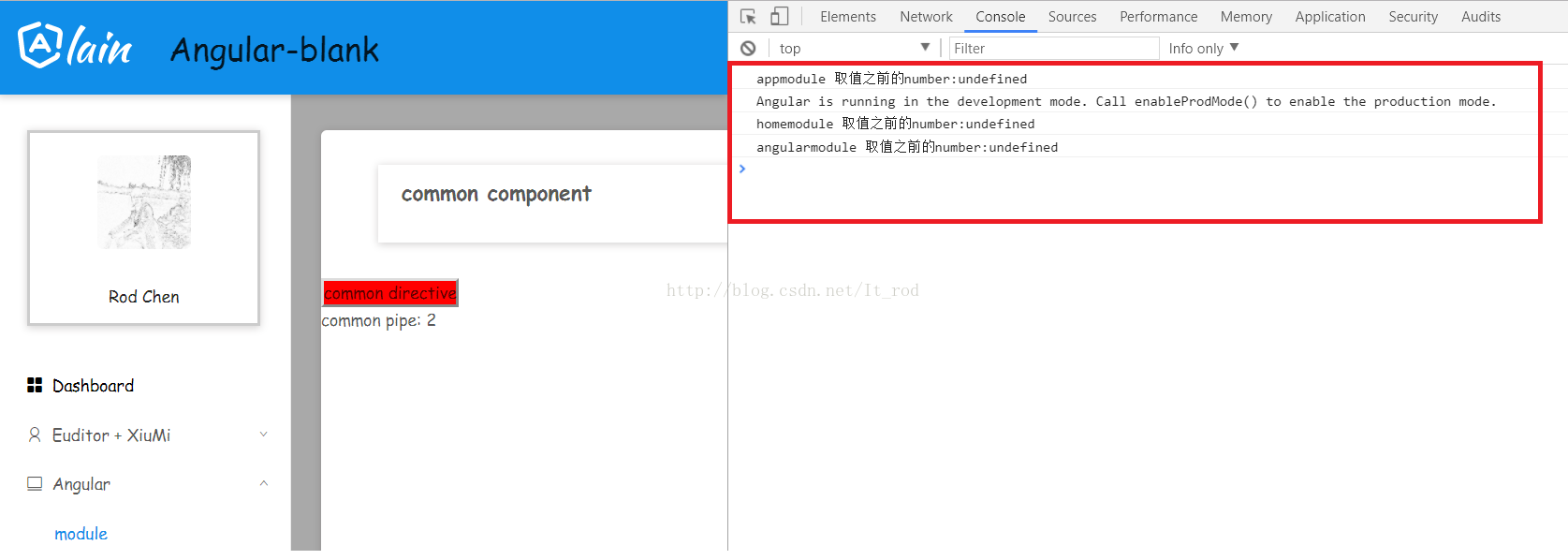
Let’s talk about the module structure of the example first, AppModule, HomeModule (submodule of AppModule), AngularModule (submodule of HomeModule). Then introduce CommonModule in the three modules respectively. 修改一下上面的CommonModule,将HttpCommonService 提供出去。
HttpCommonService
这里在service内部有两个方法,一个用于设置变量testService,一个用于取这个变量。 AppComponent
HomeCompoent
AngularComponent
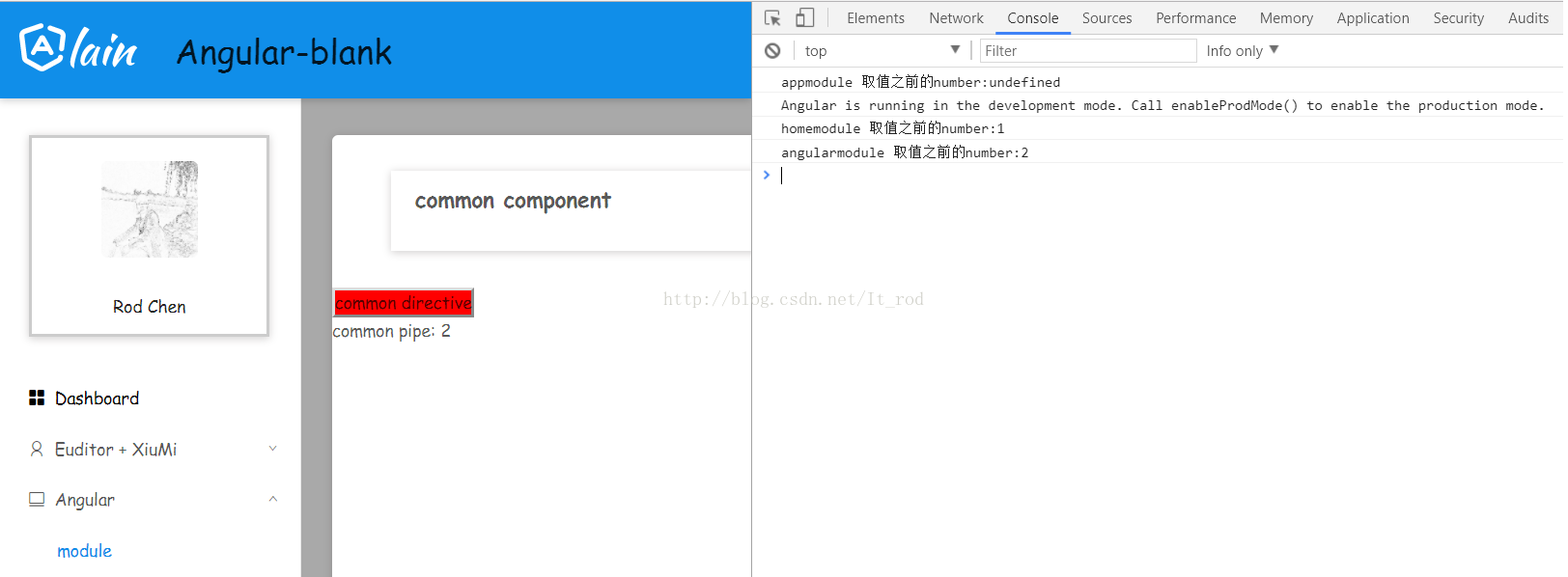
最后看一下控制台的输出: 可以看到service内部的变量每一次都是一个新值。 然后我们在将CommonModule中的service去掉,就是这个公共模块不提供service。然后在将AppModule修改一下,提供HttpCommonService。 我们再看一下页面控制台的输出。 可以看到现在是一个实例,而且service内部的变量也是缓存起来的。 所以对于service我们还是放在模块中去提供,不要放在共享模块中了。 至于页面的模板可以访问angular - blank . 更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!!@NgModule({
imports: [
NgZorroAntdModule,
AngularCommonModule
],
declarations: [
CommonComponent,
NumberFilterPipe,
ButtonDirective,
StepComponent
],
exports: [
CommonComponent,
NumberFilterPipe,
ButtonDirective,
StepComponent
],
providers: [
HttpCommonService
],
})import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import {Http, Request, RequestOptions} from '@angular/http';
import {Observable} from 'rxjs/Observable';
import {NzMessageService} from 'ng-zorro-antd';
@Injectable()
export class HttpCommonService {
private testService: number;
constructor(public httpService: Http, private _message: NzMessageService) {
}
set(number) {
this.testService = number;
}
get() {
return this.testService;
}
}export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
title = 'app';
constructor(private httpCommonService: HttpCommonService) {}
ngOnInit(): void {
console.log('appmodule 取值之前的number:' + this.httpCommonService.get());
this.httpCommonService.set(1);
}
}export class HomeComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(private httpCommonService: HttpCommonService) { }
ngOnInit() {
console.log('homemodule 取值之前的number:' + this.httpCommonService.get());
this.httpCommonService.set(2);
}
}export class AngularComponent implements OnInit {
firstString: string;
constructor(private httpCommonService: HttpCommonService) { }
ngOnInit() {
console.log('angularmodule 取值之前的number:' + this.httpCommonService.get());
}
}
The above is the detailed content of Understanding shared modules in Angular4. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1653
1653
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1304
1304
 25
25
 1251
1251
 29
29
 1224
1224
 24
24
 What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Frequently Asked Questions and Solutions for Front-end Thermal Paper Ticket Printing In Front-end Development, Ticket Printing is a common requirement. However, many developers are implementing...
 Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript is the cornerstone of modern web development, and its main functions include event-driven programming, dynamic content generation and asynchronous programming. 1) Event-driven programming allows web pages to change dynamically according to user operations. 2) Dynamic content generation allows page content to be adjusted according to conditions. 3) Asynchronous programming ensures that the user interface is not blocked. JavaScript is widely used in web interaction, single-page application and server-side development, greatly improving the flexibility of user experience and cross-platform development.
 Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
There is no absolute salary for Python and JavaScript developers, depending on skills and industry needs. 1. Python may be paid more in data science and machine learning. 2. JavaScript has great demand in front-end and full-stack development, and its salary is also considerable. 3. Influencing factors include experience, geographical location, company size and specific skills.
 How to achieve parallax scrolling and element animation effects, like Shiseido's official website?
or:
How can we achieve the animation effect accompanied by page scrolling like Shiseido's official website?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
How to achieve parallax scrolling and element animation effects, like Shiseido's official website?
or:
How can we achieve the animation effect accompanied by page scrolling like Shiseido's official website?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Discussion on the realization of parallax scrolling and element animation effects in this article will explore how to achieve similar to Shiseido official website (https://www.shiseido.co.jp/sb/wonderland/)...
 Is JavaScript hard to learn?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Is JavaScript hard to learn?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Learning JavaScript is not difficult, but it is challenging. 1) Understand basic concepts such as variables, data types, functions, etc. 2) Master asynchronous programming and implement it through event loops. 3) Use DOM operations and Promise to handle asynchronous requests. 4) Avoid common mistakes and use debugging techniques. 5) Optimize performance and follow best practices.
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.
 How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object using JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object using JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object in JavaScript? When processing data, we often encounter the need to have the same ID...
 How to implement panel drag and drop adjustment function similar to VSCode in front-end development?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
How to implement panel drag and drop adjustment function similar to VSCode in front-end development?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
Explore the implementation of panel drag and drop adjustment function similar to VSCode in the front-end. In front-end development, how to implement VSCode similar to VSCode...




