Tutorial for beginners on redis cluster building

redis cluster construction
(Learning video sharing: redis video tutorial)
Before introducing the formal content , first let’s introduce the steps to build the stand-alone version of redis.
- Download the redis compressed package, and then decompress the compressed file;
- Enter the decompressed redis file directory (you can see the Makefile file at this time), and compile the redis source file;
- Install the compiled redis source files into the /usr/local/redis directory. If there is no redis directory in the /local directory, a new redis directory will be automatically created;
- Enter /usr/local/ redis/bin directory, start redis directly in ./redis-server (redis is started at the front end at this time);
- Change the redis startup mode to backend startup. The specific method is: put the redis under the decompressed redis file. Copy the .conf file to the /usr/local/redis/bin directory, and then modify the redis.conf file -> daemonize: no to daemonize: yse;
- Pass ./redis in the /bin directory -server redis.conf starts redis (background startup at this time).
In summary, the installation and startup of the redis stand-alone version is completed.
For detailed steps with pictures, please refer to -> Getting started with redis
Please forgive me for being verbose, ok, then let’s return to this topic—redis cluster construction!
1. Introduction to Redis Cluster
- redis is an open source key value storage system that has been favored by the Internet favor of the company. Before the redis3.0 version, it only supported singleton mode, and only supported clusters in version 3.0 and later. I am using the redis3.0.0 version here;
- redis cluster adopts P2P mode, which is completely decentralized and does not There is a central node or agent node;
- The redis cluster does not have a unified entrance. When the client connects to the cluster, it can connect to any node in the cluster. The nodes within the cluster communicate with each other. (PING-PONG mechanism), each node is a redis instance;
- In order to achieve high availability of the cluster, that is, to determine whether the node is healthy (can it be used normally), redis-cluster has such a voting fault tolerance Mechanism: If more than half of the nodes in the cluster vote that a node is down, then this node will fail. This is how to determine whether a node is down;
- So how to determine whether the cluster is down? -> If any node in the cluster is down, and the node has no slave node (backup node), then this The cluster is down. This is a way to determine whether the cluster is down;
- So why does the cluster hang up when any node hangs up (there is no slave node)? -> Because the cluster has 16384 built-in slots (hash slots), and all physical nodes are mapped to these 16384[0-16383] slots, or these slots are equally distributed to each node. When it is necessary to store a piece of data (key-value) in the Redis cluster, redis will first perform the crc16 algorithm on the key and then obtain a result. Then calculate the remainder of this result to 16384. This remainder will correspond to one of the slots [0-16383], and then determine which node the key-value is stored in. Therefore, once a node hangs up, the slot corresponding to the node cannot be used, which will cause the cluster to not work properly.
- To sum up, each Redis cluster can theoretically have up to 16384 nodes.
2. Environment required for cluster construction
2.1 Redis cluster requires at least 3 nodes, because the voting fault tolerance mechanism requires more than half of the nodes to think that a certain node has failed. It is down, so 2 nodes cannot form a cluster.
2.2 To ensure the high availability of the cluster, each node needs to have a slave node, that is, a backup node, so the Redis cluster requires at least 6 servers. Because I don’t have that many servers, and I can’t start that many virtual machines, so what I build here is a pseudo-distributed cluster, that is, one server runs 6 redis instances virtually, and the port number is modified to (7001-7006). Of course, the actual production environment The Redis cluster setup is the same as here.
2.3 Install ruby
3. The specific steps to build the cluster are as follows (note to turn off the firewall)
3.1 Create a new redis-cluster directory in the usr/local directory to store cluster nodes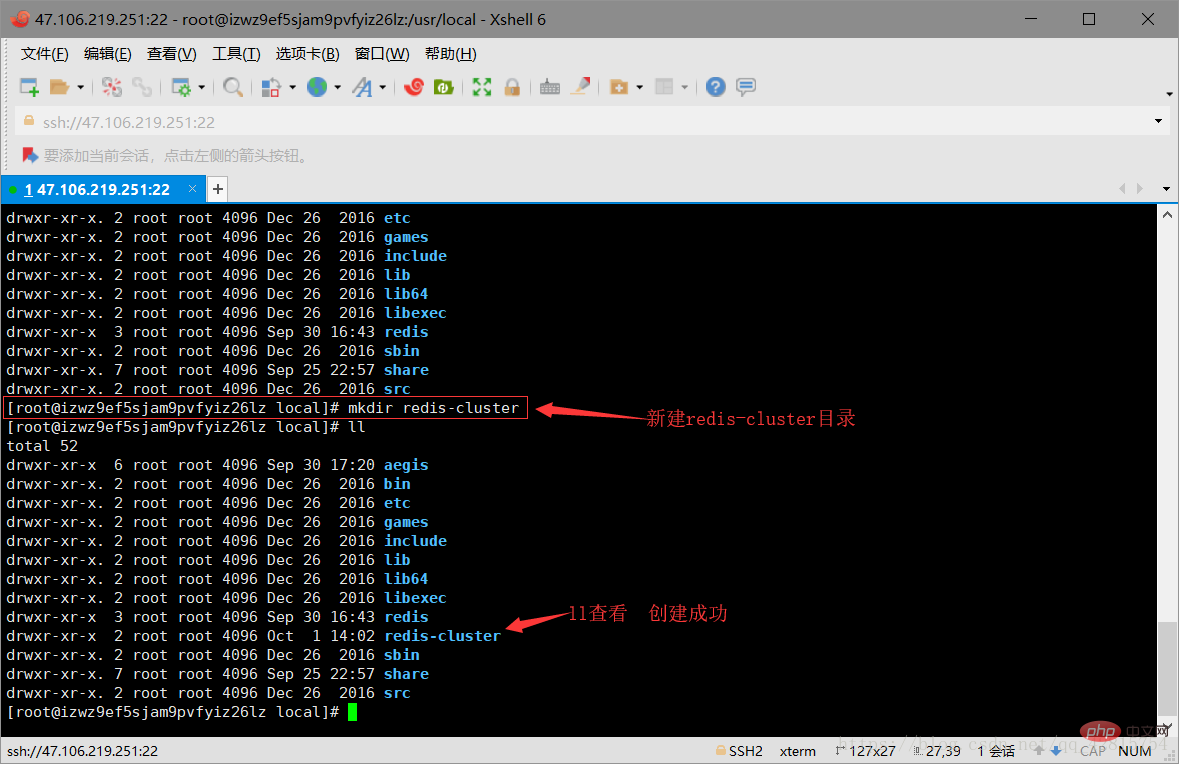
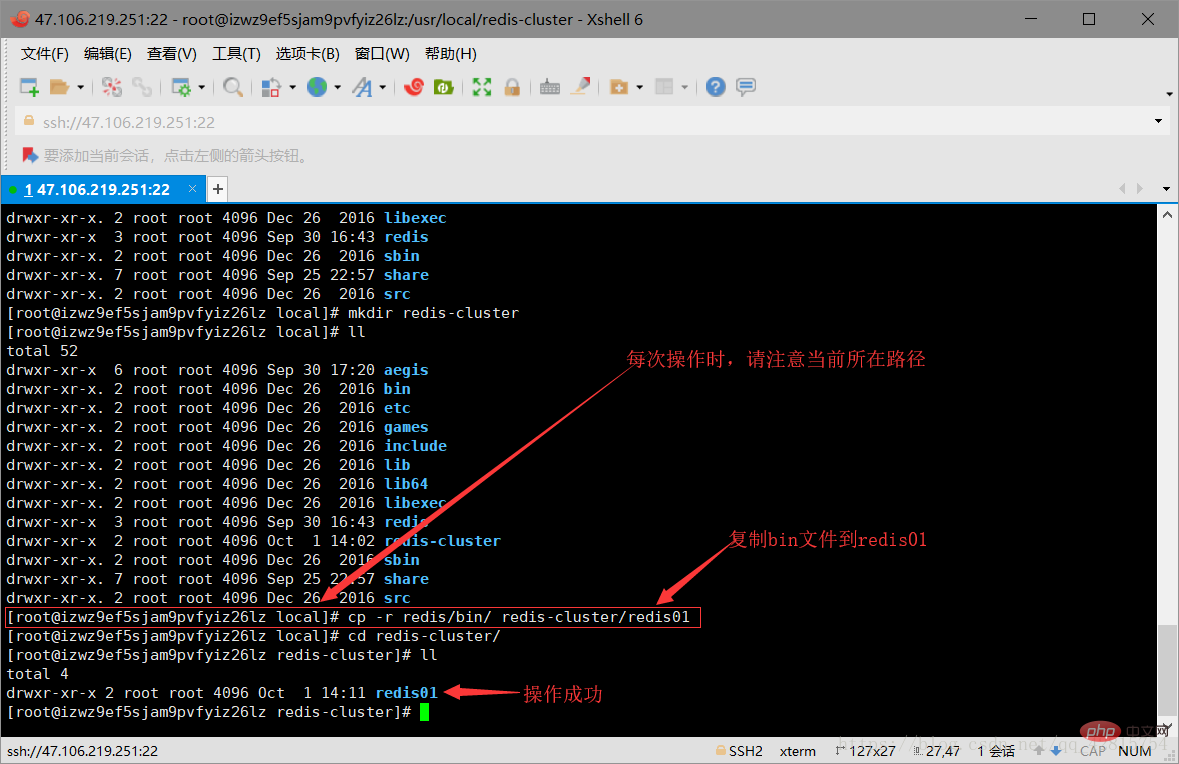
3.2 Copy all the files in the bin directory under the redis directory to the /usr/local/redis-cluster/redis01 directory. Don’t worry there is no redis01 directory here, it will be created automatically. The operation command is as follows (note the current path):
cp -r redis/bin/ redis-cluster/redis01
3.3 Delete the snapshot file dump.rdb in the redis01 directory, and modify the redis.cnf file in the directory. Specifically, modify two places: one is to change the port number to 7001, and the other is to open In cluster creation mode, just open comments. As shown in the figure below:
Delete the dump.rdb file 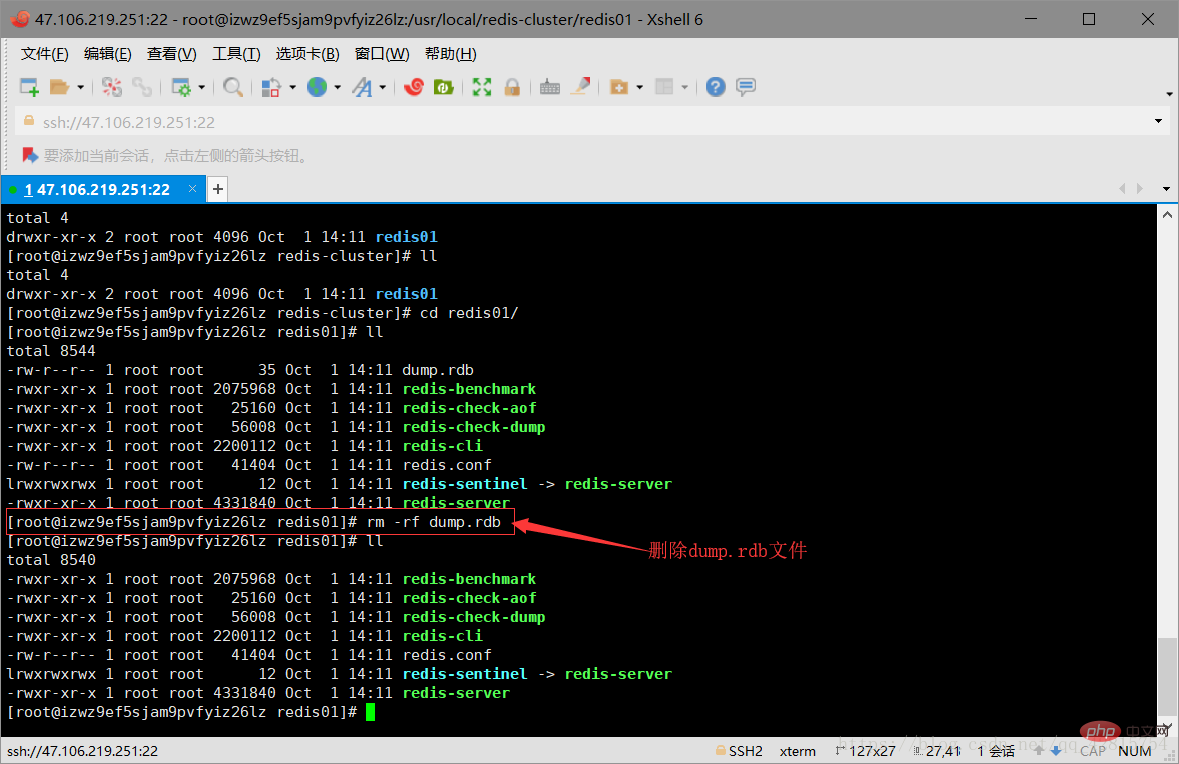
Modify the port number to 7001, the default is 6379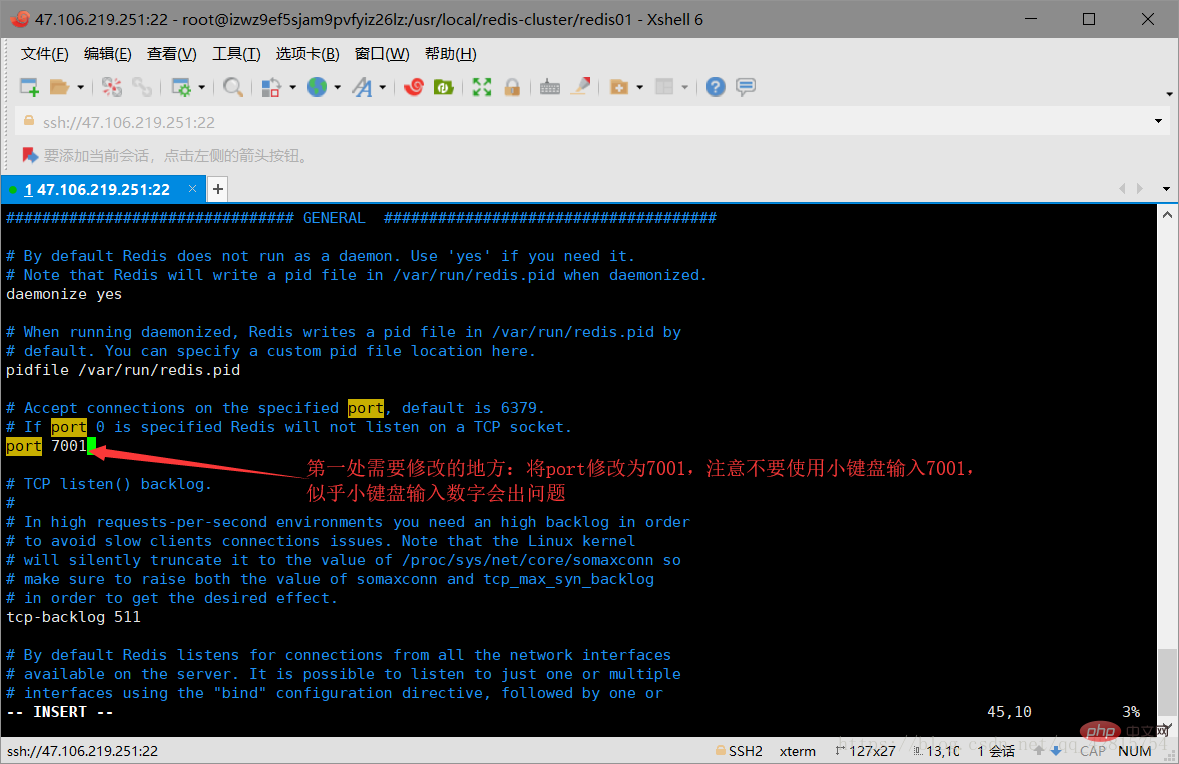
Turn on the comment of cluster-enabled yes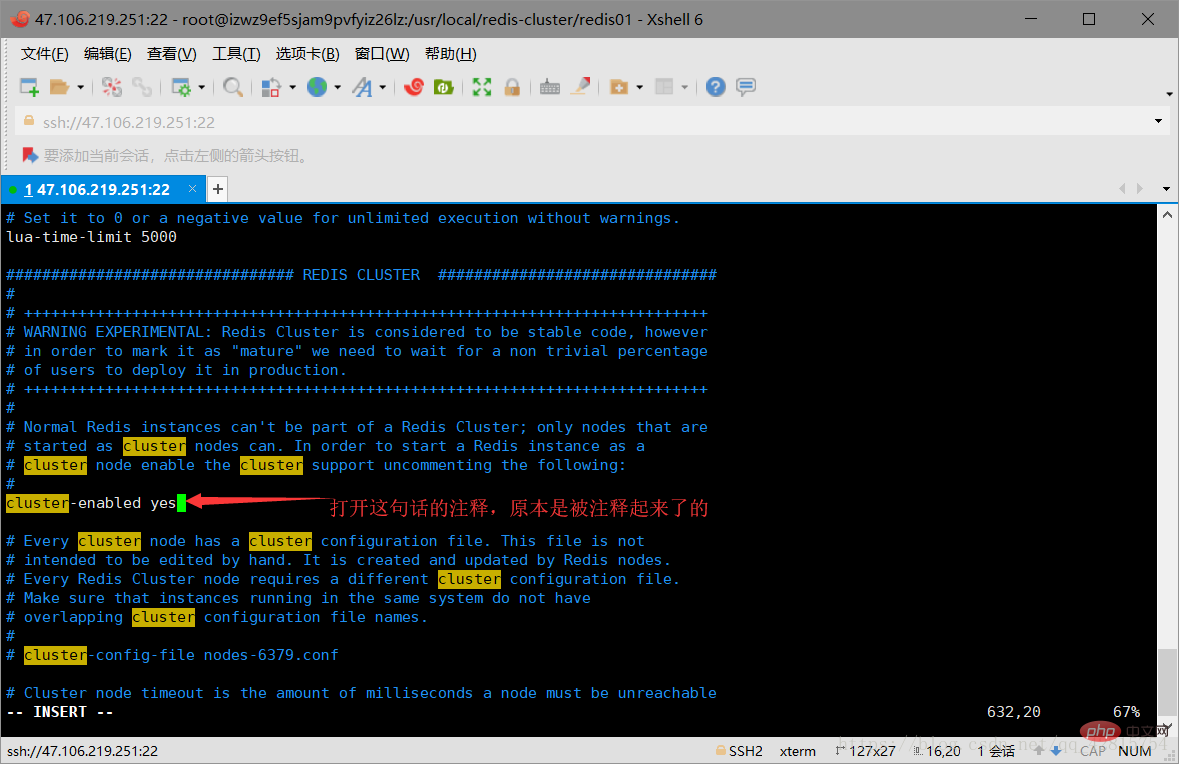
3.4 Copy 5 copies of the redis-cluster/redis01 file to the redis-cluster directory (redis02-redis06), create 6 redis instances, and simulate 6 nodes of the Redis cluster. Then change the port numbers in redis.conf under the remaining five files to 7002-7006 respectively. As shown in the figure below:
Create the redis02-06 directory 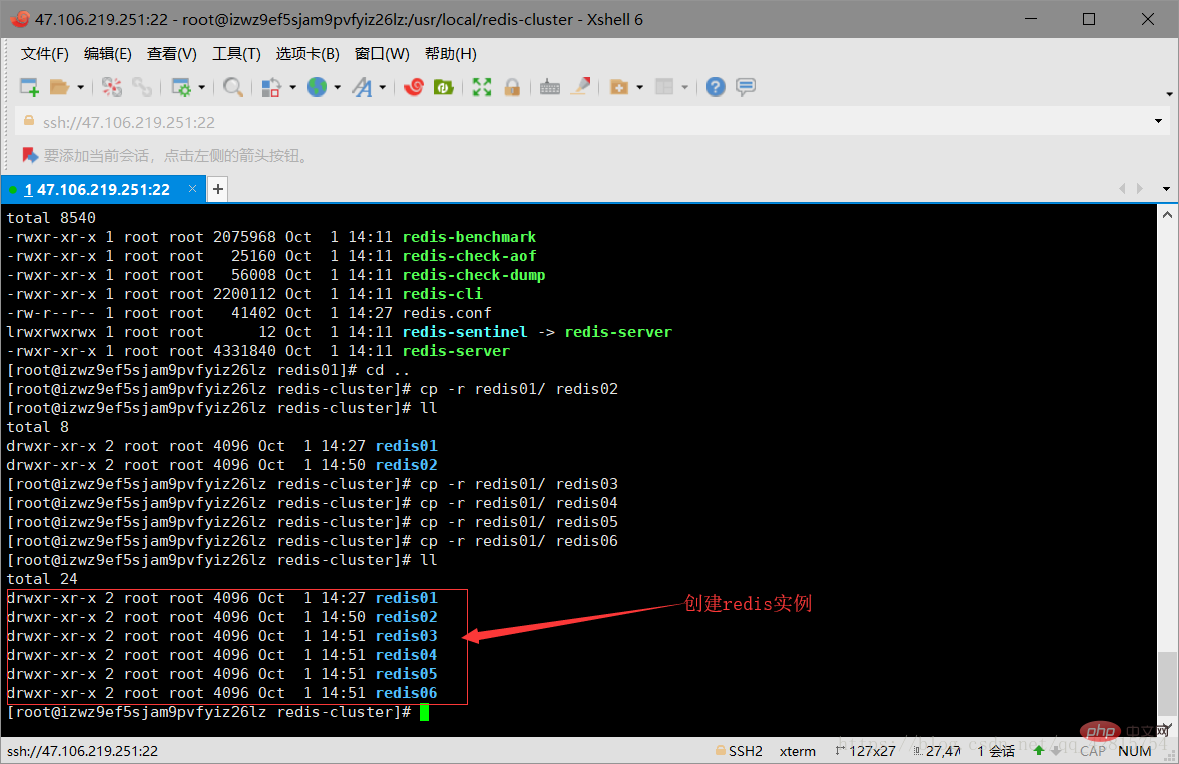
Modify the port number of the redis.conf file to 7002-7006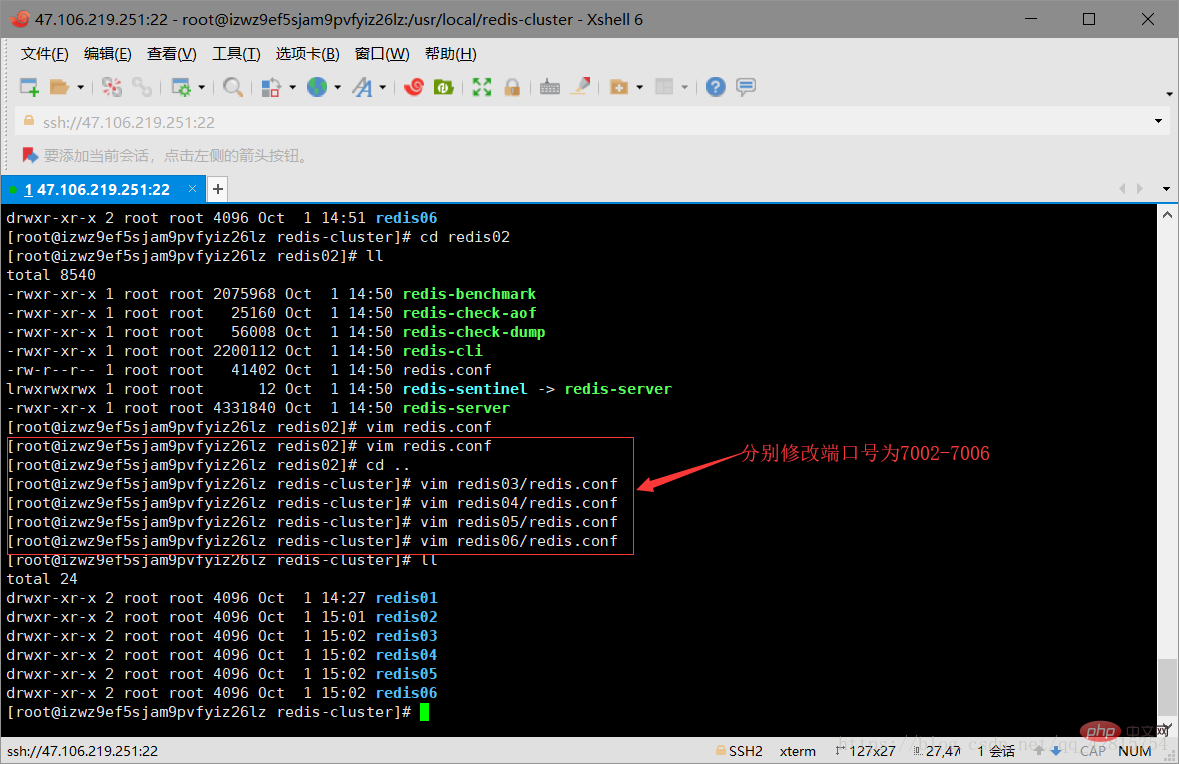
3.5 Then start Since starting all redis nodes one by one is too troublesome, here is a script file to start redis nodes in batches. The command is start-all.sh. The content of the file is as follows:
cd redis01 ./redis-server redis.conf cd .. cd redis02 ./redis-server redis.conf cd .. cd redis03 ./redis-server redis.conf cd .. cd redis04 ./redis-server redis.conf cd .. cd redis05 ./redis-server redis.conf cd .. cd redis06 ./redis-server redis.conf cd ..
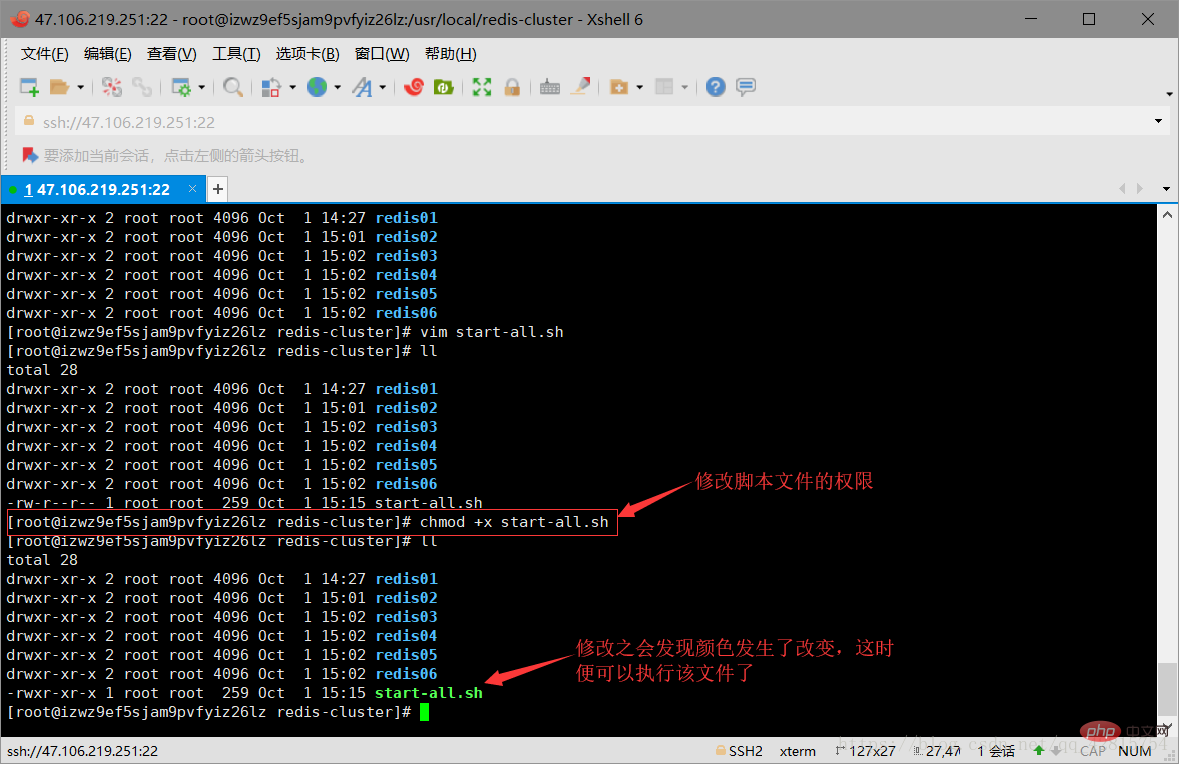
3.6 Create the startup script file After that, you need to modify the permissions of the script so that it can be executed. The instructions are as follows:
chmod +x start-all.sh
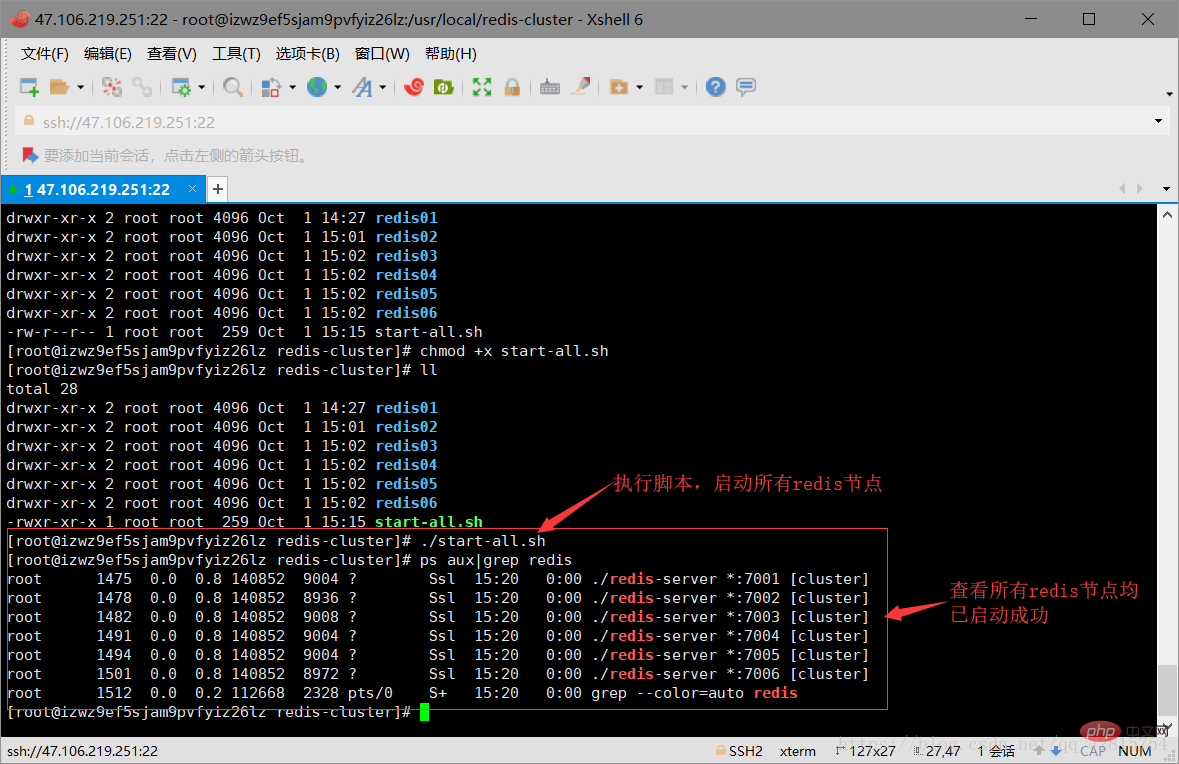
3.8 ok. So far, the six redis nodes have been started successfully. Next, the cluster will be officially started. The above are all preparatory conditions. Don’t think it’s troublesome because the pictures look lengthy. In fact, the above steps are just one sentence: create 6 redis instances (6 nodes) and start them. To build a cluster, you need to use a tool (script file), which is in the source code of the redis decompression file. Because this tool is a ruby script file, the running of this tool requires a ruby running environment, which is equivalent to the running of the java language on the jvm. So you need to install ruby. The instructions are as follows:
yum install ruby
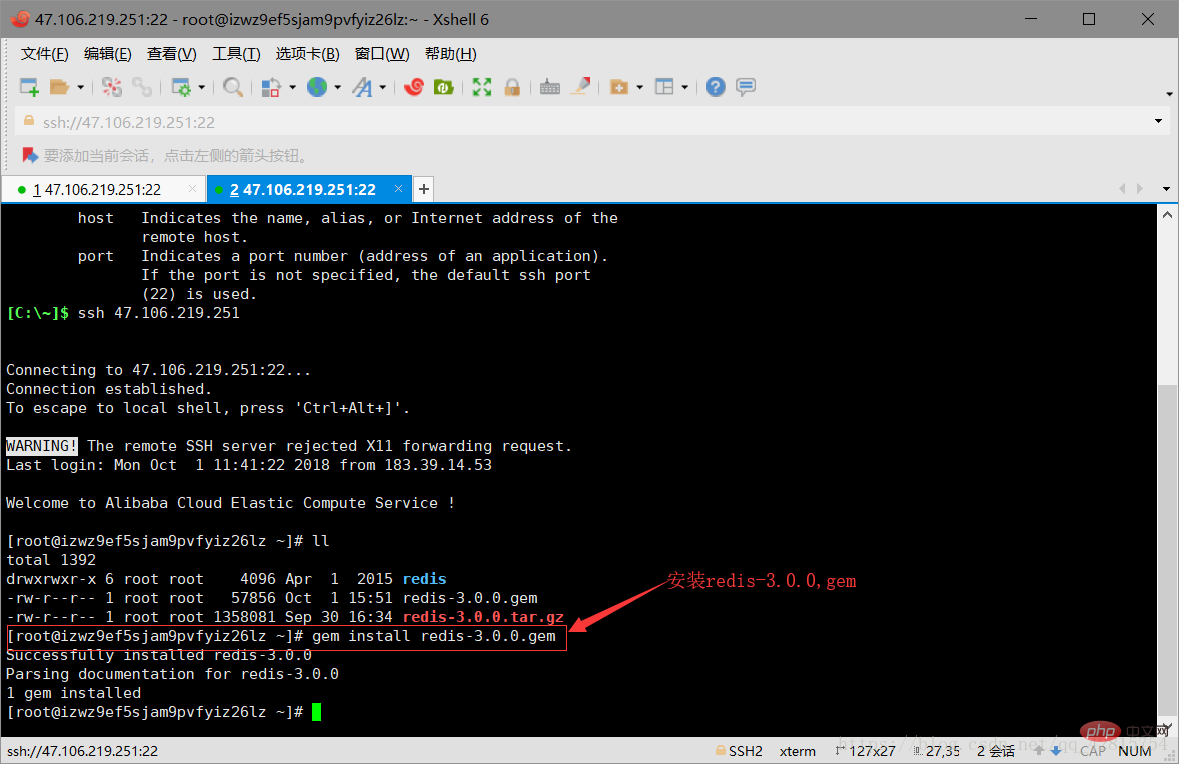
 The installation command is as follows:
The installation command is as follows:
gem install redis-3.0.0.gem

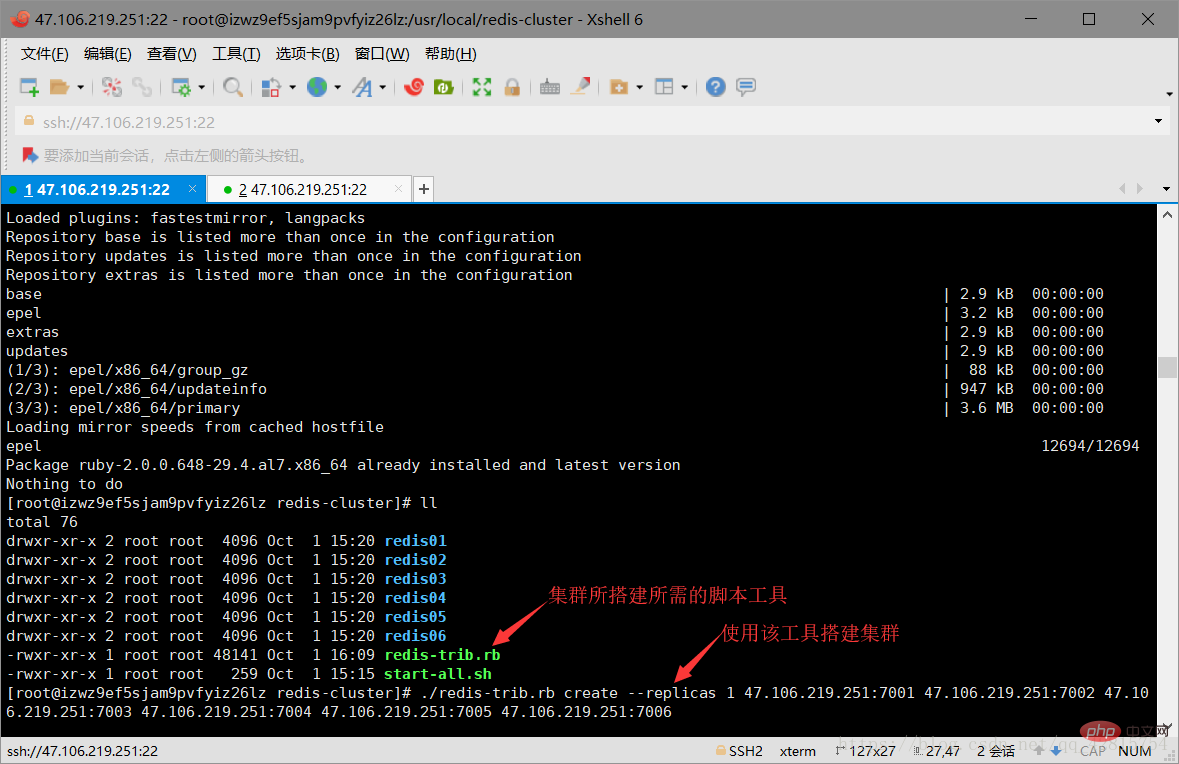
 3.10 Copy the ruby tool (redis-trib.rb) to the redis-cluster directory. The instructions are as follows:
3.10 Copy the ruby tool (redis-trib.rb) to the redis-cluster directory. The instructions are as follows:
cp redis-trib.rb /usr/local/redis-cluster
./redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 47.106.219.251:7001 47.106.219.251:7002 47.106.219.251:7003 47.106.219.251:7004 47.106.219.251:7005 47.106.219.251:7006
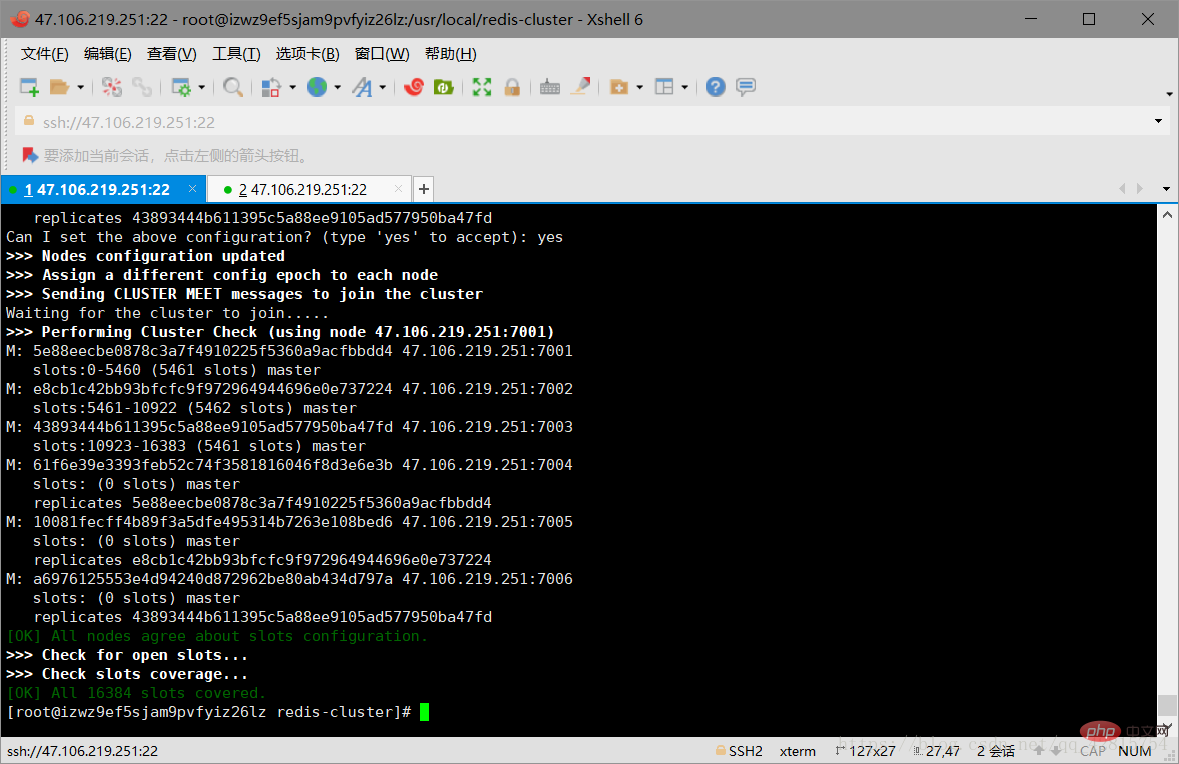 At this point, the Redi cluster is successfully established! Please pay attention to the last paragraph of text, which shows the slots (hash slots) assigned to each node. There are a total of 6 nodes here, 3 of which are slave nodes, so the 3 master nodes map 0-5460, 5461-10922, 10933-16383solts.
At this point, the Redi cluster is successfully established! Please pay attention to the last paragraph of text, which shows the slots (hash slots) assigned to each node. There are a total of 6 nodes here, 3 of which are slave nodes, so the 3 master nodes map 0-5460, 5461-10922, 10933-16383solts.
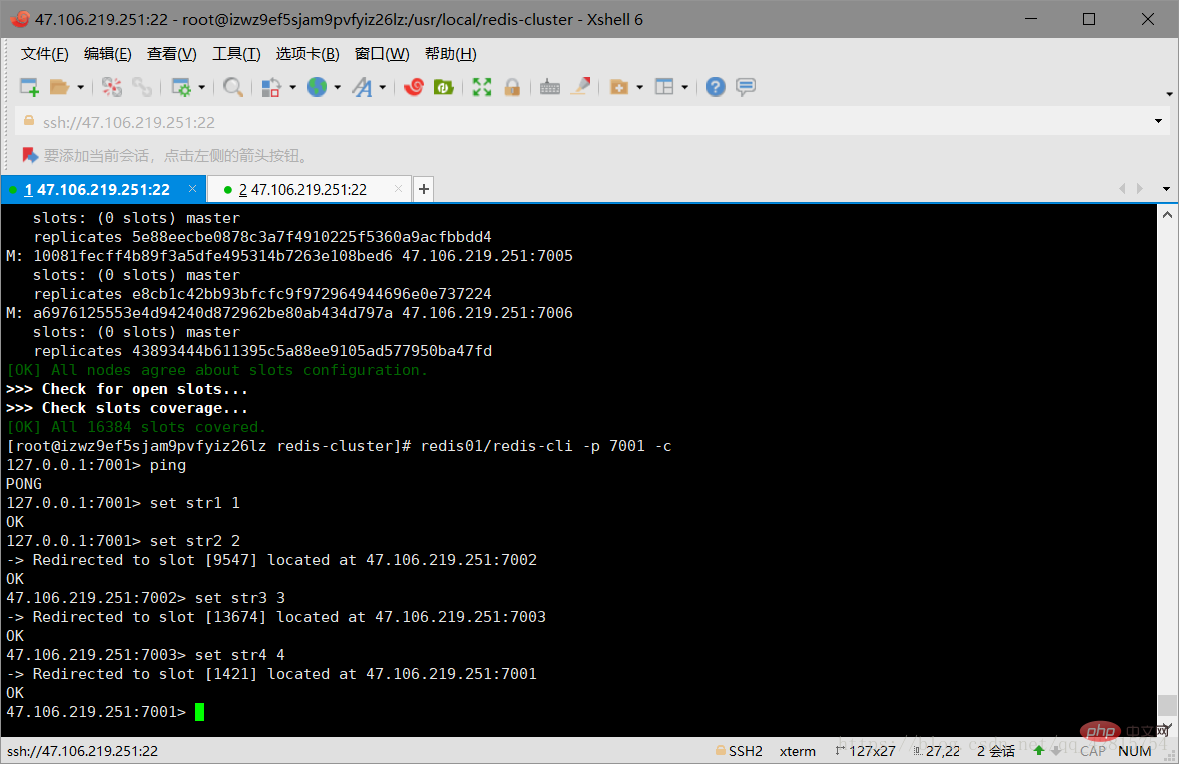
redis01/redis-cli -p 7001 -c
注意:一定要加上-c,不然节点之间是无法自动跳转的!如下图可以看到,存储的数据(key-value)是均匀分配到不同的节点的:
四、结语
呼~~~长舒一口气…终于搭建好了Redis集群。
整个过程其实挺简单,本篇主要正对入门级别的小伙伴,插入了很多图片,所以显得冗长,希望大家多多理解,如果不当之处,还望及时指正~
最后,加上两条redis集群基本命令:
1.查看当前集群信息
cluster info
2.查看集群里有多少个节点
cluster nodes
相关推荐:redis数据库教程
The above is the detailed content of Tutorial for beginners on redis cluster building. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1663
1663
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1313
1313
 25
25
 1264
1264
 29
29
 1237
1237
 24
24
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Redis counter is a mechanism that uses Redis key-value pair storage to implement counting operations, including the following steps: creating counter keys, increasing counts, decreasing counts, resetting counts, and obtaining counts. The advantages of Redis counters include fast speed, high concurrency, durability and simplicity and ease of use. It can be used in scenarios such as user access counting, real-time metric tracking, game scores and rankings, and order processing counting.
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information




