MySQL 5.7 vs 8.0, performance PK
mysql tutorial column introduces the performance comparison between MySQL 5.7 and MySQL 8.0.

Background
Test the performance of mysql5.7 and mysql8.0 in different concurrency conditions in read-write, read-only, and write-only modes. (tps, qps)
Prerequisite
- The test version is mysql5.7.22 and mysql8.0.15
- Restart the mysql service before sysbench test, and clear the os cache (to avoid hitting the cache during multiple tests)
- Every time a test is performed, new test data is generated before testing mysql5.7 and mysql8.0
- Guarantee mysql5 during each test .7 The configuration parameters are consistent with mysql8.0
Environment
Machine
cat /etc/redhat-release | xargs echo '版本 ' && dmidecode -s system-product-name | xargs echo '是否虚拟化 ' && cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep "processor"|wc -l | xargs echo 'cpu核数 ' 版本 CentOS Linux release 7.5.1804 (Core) 是否虚拟化 KVM cpu核数 4复制代码
myql5.7.22
5.7.22-log innodb_buffer_pool_size 128M innodb_log_buffer_size 64M innodb_log_file_size 48M binlog_format ROW log_bin ON transaction_isolation REPEATABLE-READ复制代码
mysql8.0.15
8.0.15 innodb_buffer_pool_size 128M innodb_log_buffer_size 64M innodb_log_file_size 48M binlog_format ROW log_bin ON transaction_isolation REPEATABLE-READ复制代码
sysbench
sysbench -V sysbench 1.1.0 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta3)复制代码
Test
Under different persistence strategies (binlog, redo log persistence) mysql5.7 and mysql8.0 are reading and writing Performance in mode, read-only mode, write-only mode (oltp_read_write, oltp_read_only, oltp_write_only)
sysbench test time is 60s, and the number of tables tested is 20
The tests were conducted in double 1 mode (security) and 0 2 mode (high performance) respectively

-

SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES WHERE Variable_name IN('sync_binlog','innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit'); -------------------------------- ------- | Variable_name | Value | -------------------------------- ------- | innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit | 1 | | sync_binlog | 1 | ------------------------ -------
Performance of mysql5.7 and mysql8.0 in read-write mode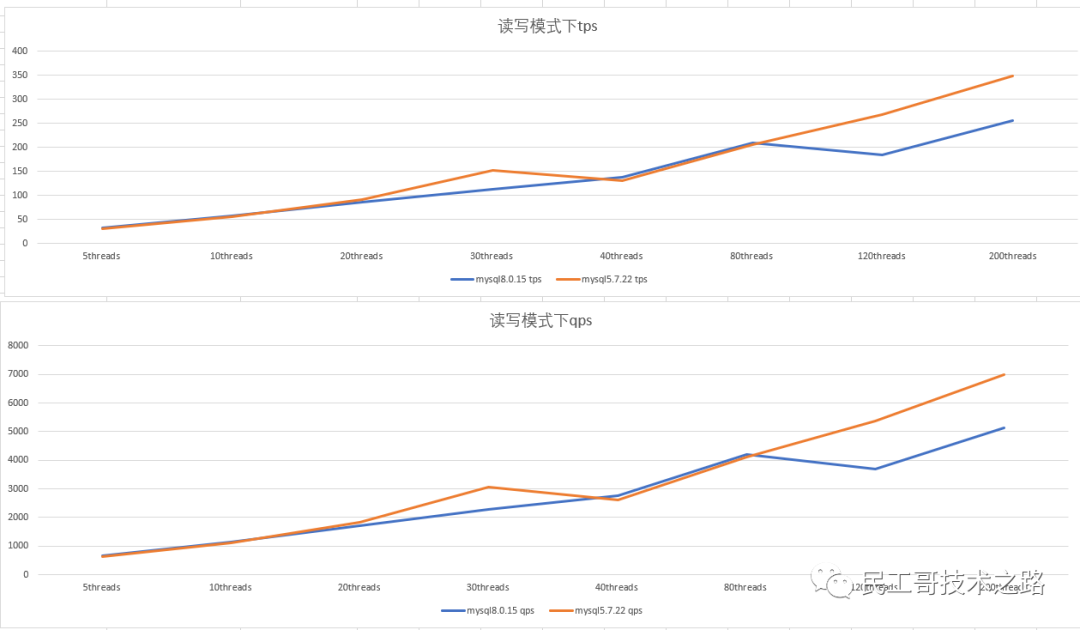
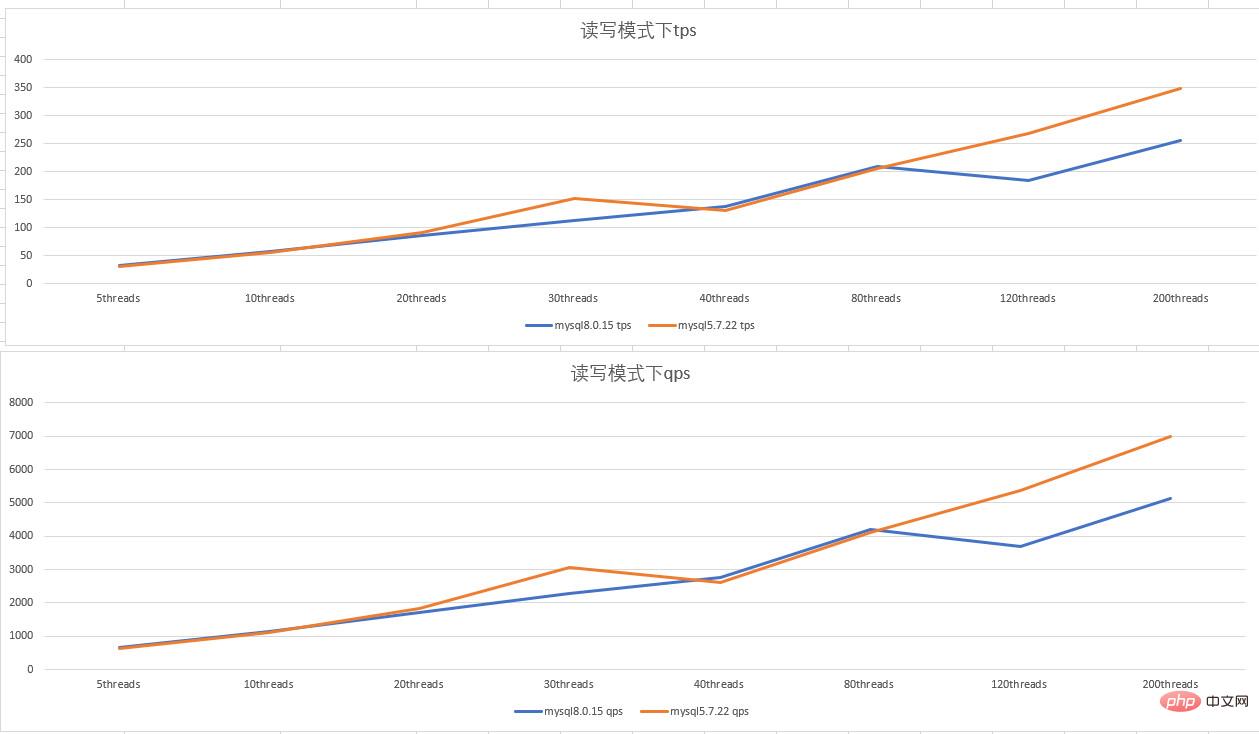
- Double 1 configuration, in read-write mode, mysql5.7.22 and mysql8 .0.15 tps and qps have similar performance. When mysql8.0.15 has 120 threads concurrently, the performance drops and jitters:
Performance of mysql5.7 and mysql8.0 in read-only mode
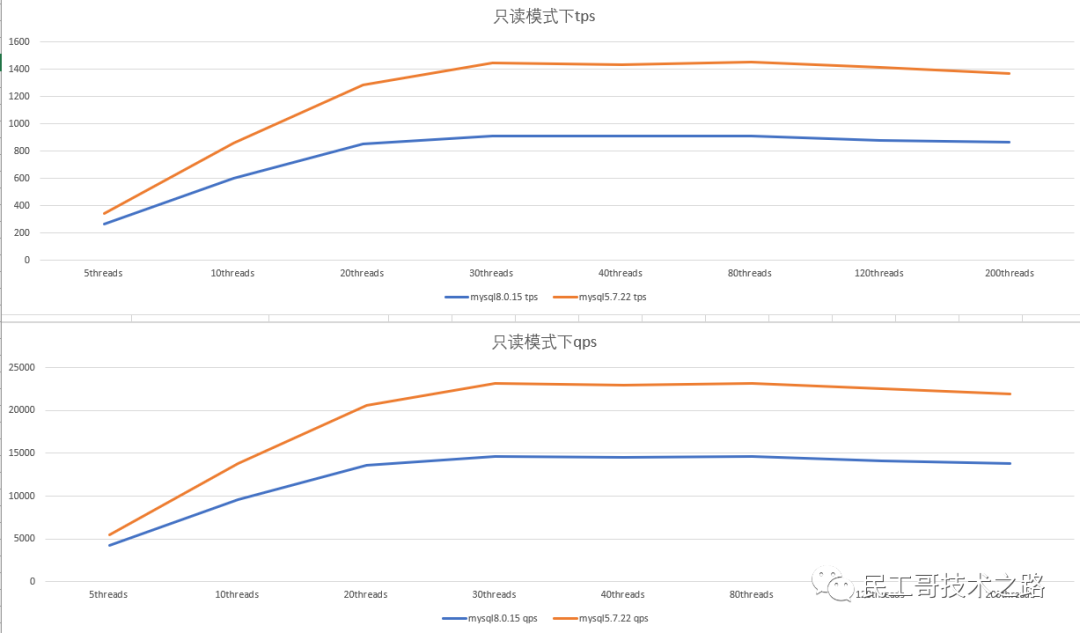
- Double 1 configuration, in read-only mode, the tps and qps of mysql5.7.22 are about 1/3 better than mysql8.0.15; after the number of concurrent threads increases, the tps , qps did not increase, but showed a downward trend.
Performance of mysql5.7 and mysql8.0 in write-only mode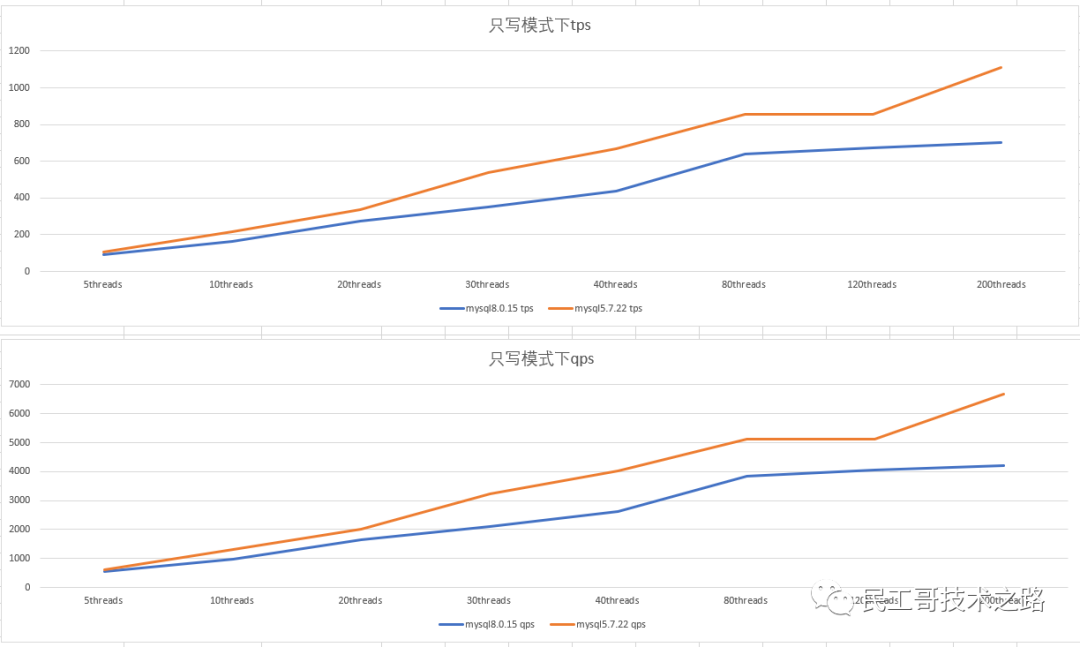
- ##Double 1 configuration, write-only In mode, as the number of concurrency increases, the performance of mysql5.7.22 is about 1/4 better than that of mysql8.0.15.
SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES WHERE Variable_name IN('sync_binlog','innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit');
+--------------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------------------+-------+
| innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit | 2 |
| sync_binlog | 0 |
+--------------------------------+-------+复制代码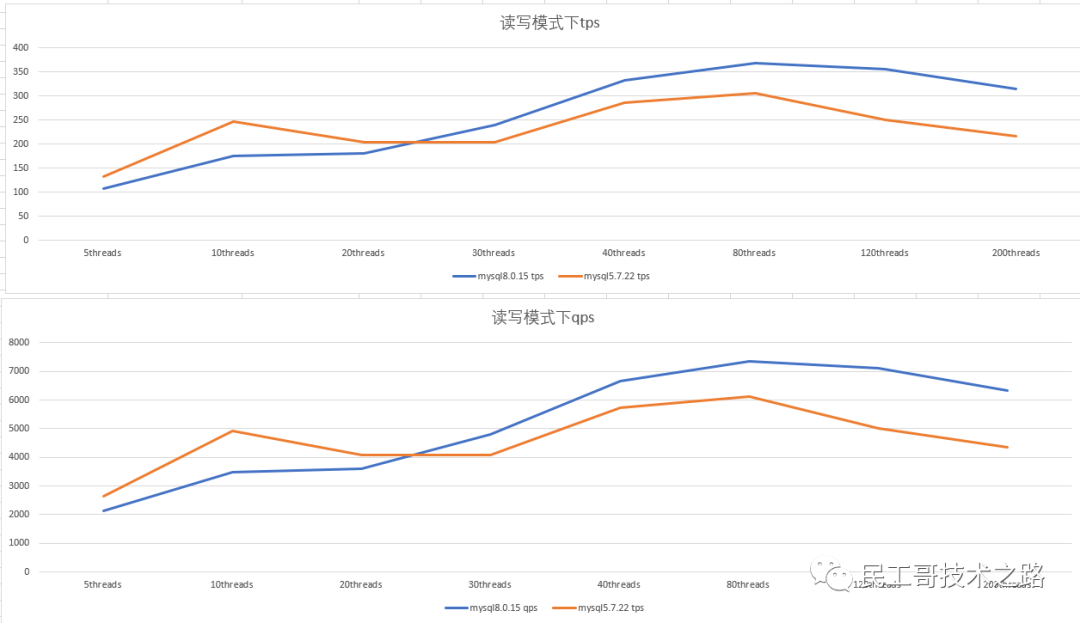
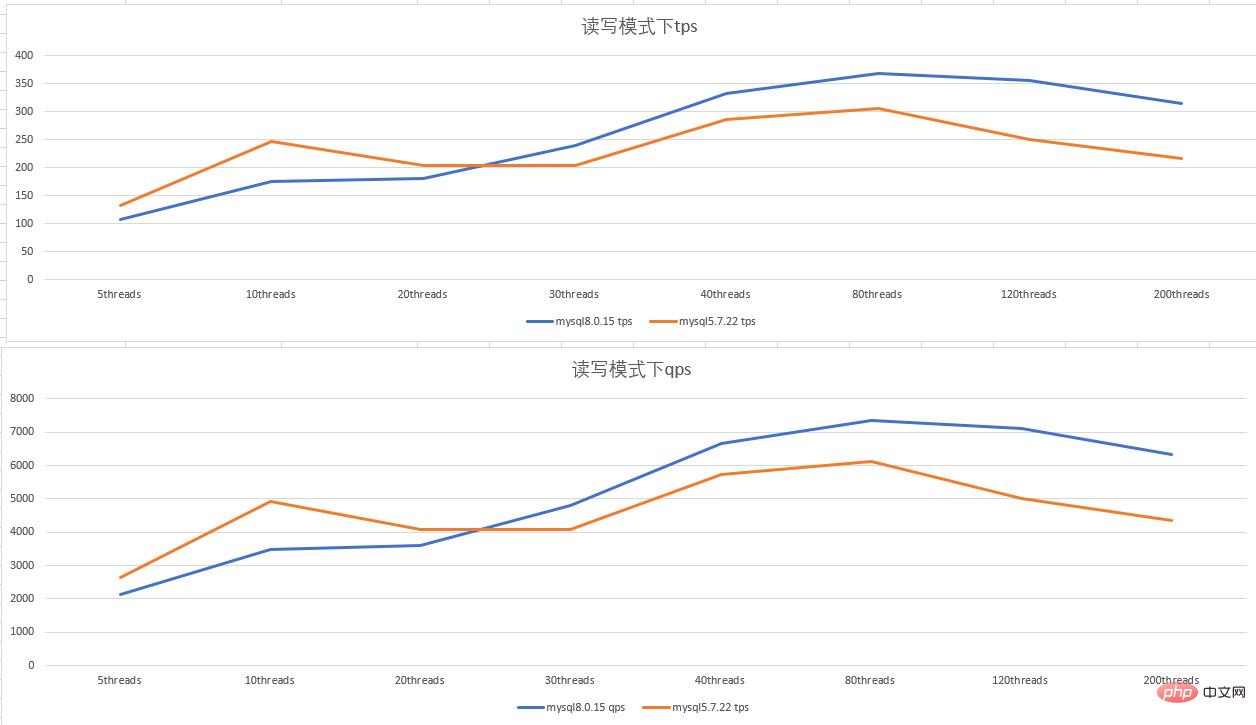
- 0 2 configuration, in read-write mode, when the number of concurrency is low, the performance of mysql5.7.22 is better than that of mysql8.0.15; when the number of concurrency is relatively high, the performance of mysql8.0.15 is better than that of mysql5.7.22; in the concurrency of 80 threads Above that, performance begins to degrade.
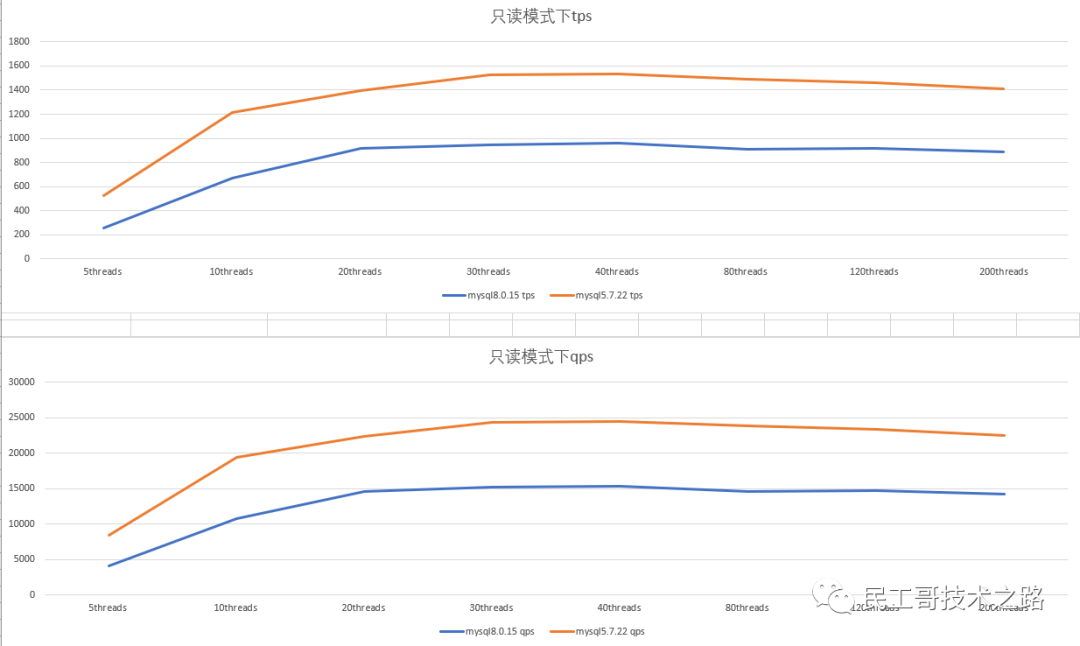
- 0 2配置,只读模式下,mysql5.7.22性能比mysql8.0.15 好1/3左右;随着并发数的上升,性能也没有上升,反而有下降的趋势.
mysql5.7和mysql8.0 在只写模式下的表现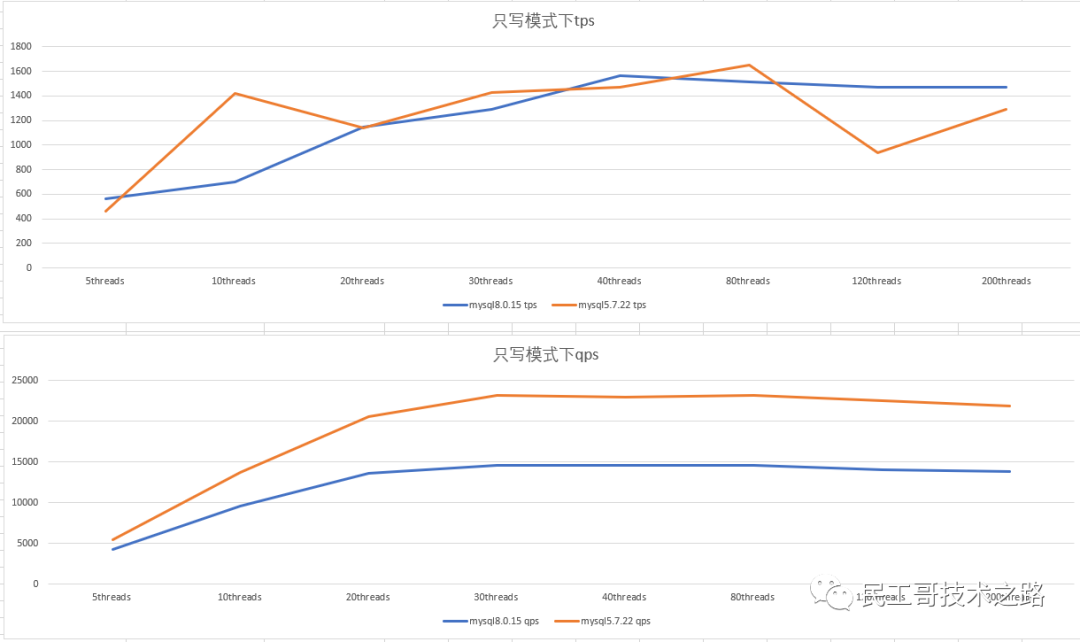
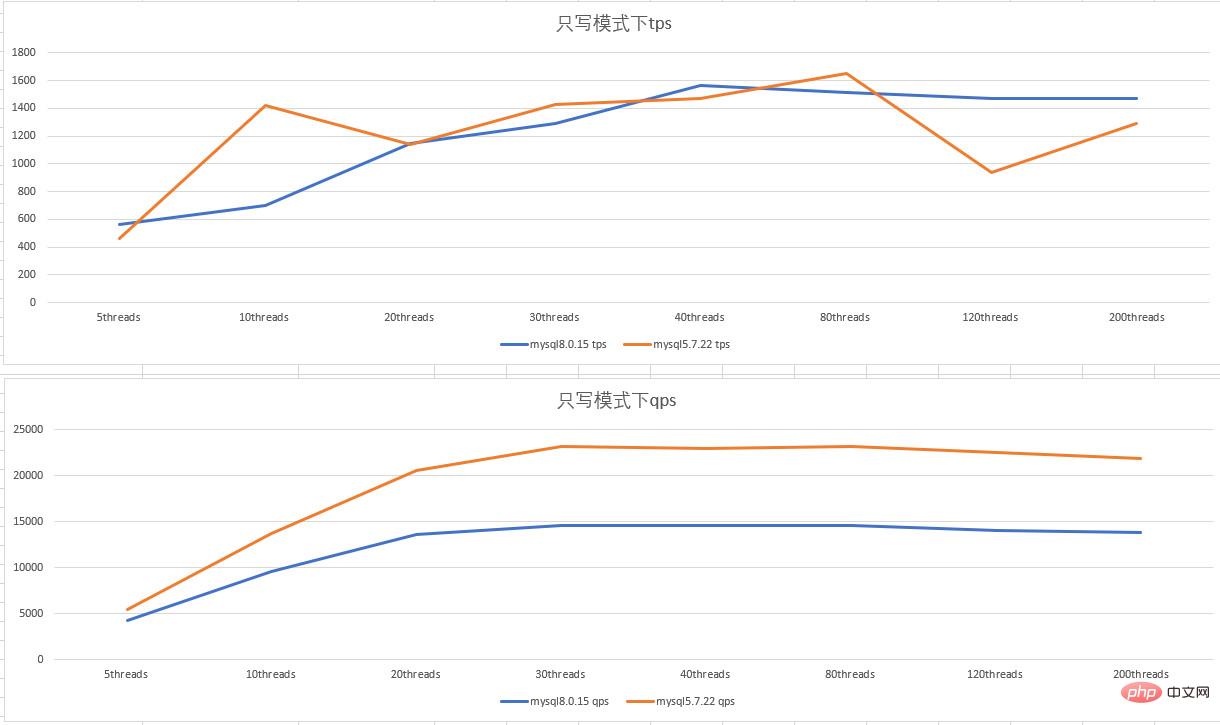
- 0 2 配置,只写模式下,mysql5.7.22的tps 抖动比较大;mysql5.7.22 的qps比mysql8.0.15好1/3左右
结论
- 整体来看,mysql5.7.22在读写模式、只读模式、只写模式下的表现是优于mysql8.0.15的
- 随着并行数的增加,性能表现不会也跟着增加,还会出现下降
- 本次测试结果是在配置很低的情况下进行的,不代表绝对
注意
sysbench 需要设置--db-ps-mode=disable 禁用预编译语句,不然并发测试线程多时会报下面的错误
FATAL: mysql_stmt_prepare() failed FATAL: MySQL error: 1461 "Can't create more than max_prepared_stmt_count statements (current value: 16382)" FATAL: mysql_stmt_prepare() failed FATAL: MySQL error: 1461 "Can't create more than max_prepared_stmt_count statements (current value: 16382)" FATAL: thread_init' function failed: /usr/local/share/sysbench/oltp_common.lua:288: SQL API error FATAL: mysql_stmt_prepare() failed FATAL: MySQL error: 1461 "Can't create more than max_prepared_stmt_count statements (current value: 16382)" FATAL:thread_init' function failed: /usr/local/share/sysbench/oltp_common.lua:288: SQL API error FATAL: mysql_stmt_prepare() failed复制代码
使用脚本
cat sysbench_test_mysql5.7_8.0_tps_qps.sh
#!/bin/bash
#用于sysbench 测试在读写模式、只读模式、只写模式下 mysql5.7和mysql8.0 的tps,qps
#nohup bash $0 >/tmp/sysbench_test 2>& 1 &
#
user=admin
passwd=admin
ports="8015 57222"
host=127.0.0.1
sysbench_test_mode="oltp_read_write oltp_read_only oltp_write_only"
sysbench_test_info_path=/tmp/sysbench-test
function red_echo () {
local what="$*"
echo -e "$(date +%F-%T) e[1;31m ${what} e[0m"
}
function check_las_comm(){
if [ $1 -ne 0 ];then
red_echo $2
exit 1
fi
}
function restart_mysqld(){
service mysqld${1} restart
sleep 2
}
function purge_binlog(){
port=$1
mysql -u$user -p$passwd -P$port -h$host /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
}
function sysbench_with_diff_thread(){
thread_num=$1
port=$2
order=$3
test_mode=$4
sysbench /usr/local/share/sysbench/${test_mode}.lua --mysql_storage_engine=innodb --table-size=100000 --tables=20 --mysql-db=test_1 --mysql-user=$user --mysql-password=$passwd --mysql-port=$port --mysql-host=$host --threads=$thread_num --time=60 --report-interval=2 --db-ps-mode=disable --events=0 --db-driver=mysql $order
}
function main(){
for test_mode in $sysbench_test_mode;do
for port in $ports;do
for thread_num in {5,10,20,30,40,80,120,200};do
restart_mysqld "$port"
check_las_comm "$?" "restart mysqld${port} failed "
clean_os_cache
purge_binlog "$port"
red_echo "sysbench $thread_num threads cleanup mysqld${port}"
sysbench_with_diff_thread "$thread_num" "$port" "cleanup" "$test_mode">/dev/null
red_echo "sysbench $thread_num threads prepare mysqld${port}"
sysbench_with_diff_thread "$thread_num" "$port" "prepare" "$test_mode">/dev/null
mkdir -p $sysbench_test_info_path
red_echo "sysbench $thread_num threads run mysqld${port} $test_mode"
sysbench_with_diff_thread "$thread_num" "$port" "run" "$test_mode" > $sysbench_test_info_path/${test_mode}_${thread_num}_$port
# service mysqld{port} stop
done
done
done
}
main复制代码更多相关免费学习推荐:mysql教程(视频)
The above is the detailed content of MySQL 5.7 vs 8.0, performance PK. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main role of MySQL in web applications is to store and manage data. 1.MySQL efficiently processes user information, product catalogs, transaction records and other data. 2. Through SQL query, developers can extract information from the database to generate dynamic content. 3.MySQL works based on the client-server model to ensure acceptable query speed.
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
I encountered a tricky problem when developing a small application: the need to quickly integrate a lightweight database operation library. After trying multiple libraries, I found that they either have too much functionality or are not very compatible. Eventually, I found minii/db, a simplified version based on Yii2 that solved my problem perfectly.
 How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
The key to installing MySQL elegantly is to add the official MySQL repository. The specific steps are as follows: Download the MySQL official GPG key to prevent phishing attacks. Add MySQL repository file: rpm -Uvh https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm Update yum repository cache: yum update installation MySQL: yum install mysql-server startup MySQL service: systemctl start mysqld set up booting
 Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Installing MySQL on CentOS involves the following steps: Adding the appropriate MySQL yum source. Execute the yum install mysql-server command to install the MySQL server. Use the mysql_secure_installation command to make security settings, such as setting the root user password. Customize the MySQL configuration file as needed. Tune MySQL parameters and optimize databases for performance.
 Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Article summary: This article provides detailed step-by-step instructions to guide readers on how to easily install the Laravel framework. Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that speeds up the development process of web applications. This tutorial covers the installation process from system requirements to configuring databases and setting up routing. By following these steps, readers can quickly and efficiently lay a solid foundation for their Laravel project.
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.