Teach you to install Centos system through the network
下面由centos入门教程栏目给大家介绍通过网络安装Centos系统的方法,希望对需要的朋友有所帮助!
一、基础:
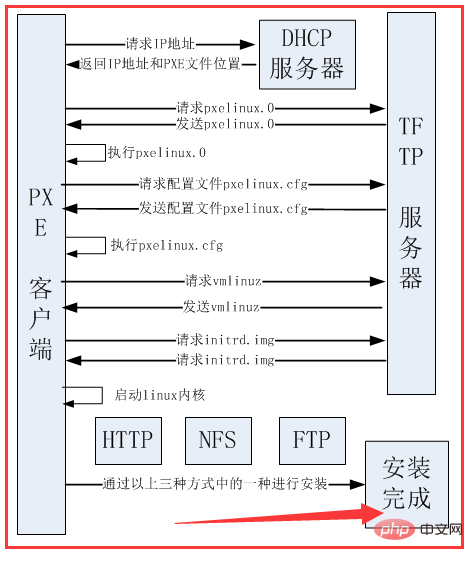
PXE(Pre-bootExecution Environment),预启动执行环境,运行在Client/Server的工作模式;
PXE Client会调用网际协议(IP)、用户数据报协议(UDP)、动态主机设定协议(DHCP)、小型文件传输协议(TFTP)等网络协议。
PXE Client存放在网卡的ROM 中。当计算机引导时,BIOS 把 PXE Client 调入内存中执行,PXE BootROM(自启动芯片)会发送一个UDP广播请求,向本网络中的DHCP服务器索取IP。
PXE的工作过程:
PXE协议运行的详细工作流程,请参考以下图文描述:
1. PXE Client 从自己的PXE网卡启动,向本网络中的DHCP服务器请求IP;
2. DHCP 服务器返回分配给客户机的IP 以及PXE文件的放置位置(该文件一般是放在一台TFTP服务器上) ;
3. PXE Client 向本网络中的TFTP服务器索取pxelinux.0 文件(在 PXE Client 的 ROM 中,已经存在 TFTP Client);
4. PXE Client 取得pxelinux.0 文件后之执行该文件;
5. 根据pxelinux.0 的执行结果,通过TFTP服务器加载内核和文件系统 ;
6. 进入安装画面, 此时可以通过选择HTTP、FTP、NFS 方式之一进行安装;
二、涉及软件安装及配置(syslinux、DHCP服务器、TFTP服务器、File server)
1、syslinux
通过网络引导Linux的引导文件是pxelinux.0,这个文件由syslinux程序提供。SYSLINUX is a suite of bootloaders。
通过yum install syslinux安装程序后,使用rpm -ql syslinux查看文件的时候,竟然没有显示pxelinux.0这个文件,以为自己安装程序的问题,后来才发现只是未显示而已,文件还是在/usr/share/syslinux/目录下,使用ls /usr/share/syslinux/就可以看到了。
将pxelinux.0复制到tftp目录: ~]# cp /usr/share/syslinux/pxelinux.0 /var/lib/tftpboot/
2、将安装光盘images/pxeboot/目录下的initrd.img、vmlinuz复制到tftp目录:cp images/pxeboot/{initrd.img,vmlinuz} /var/lib/tftpboot
复制isolinux目录下的三个文件至tftp目录:mnt]# cp isolinux/{boot.cat,vesamenu.c32,splash.jpg} /var/lib/tftpboot/
注:经验证boot.cat、splash.jpg可以不用复制;boot.cat不复制不影响启动,splash.jpg不复制显示菜单的时候没有背景图片(如下图)。
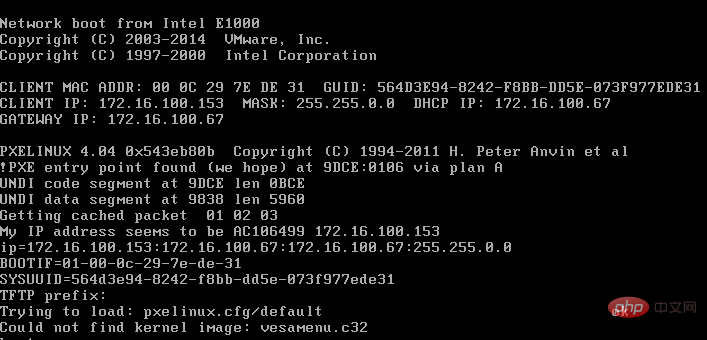
但是vesamenu.c32文件必须要有,不然会报找不到该文件的错误
在/var/lib/tftpboot/下创建pxelinux.cfg:mnt]# mkdir /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg
将isolinux/isolinux.cfg复制到 /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg目录下并命令为default:mnt]# cp isolinux/isolinux.cfg /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg/default
3、dhcp
subnet 172.16.0.0 netmask 255.255.0.0 {
range 172.16.100.151 172.16.100.170;
option routers 172.16.100.67;
filename "pxelinux.0";
next-server 172.16.100.67;
}4、然后启动虚拟机,就可以显示熟悉的安装引导菜单了。(连接不是tftp服务器,检查服务是否有开,iptables和selinux)
三、全自动通过http安装Centos
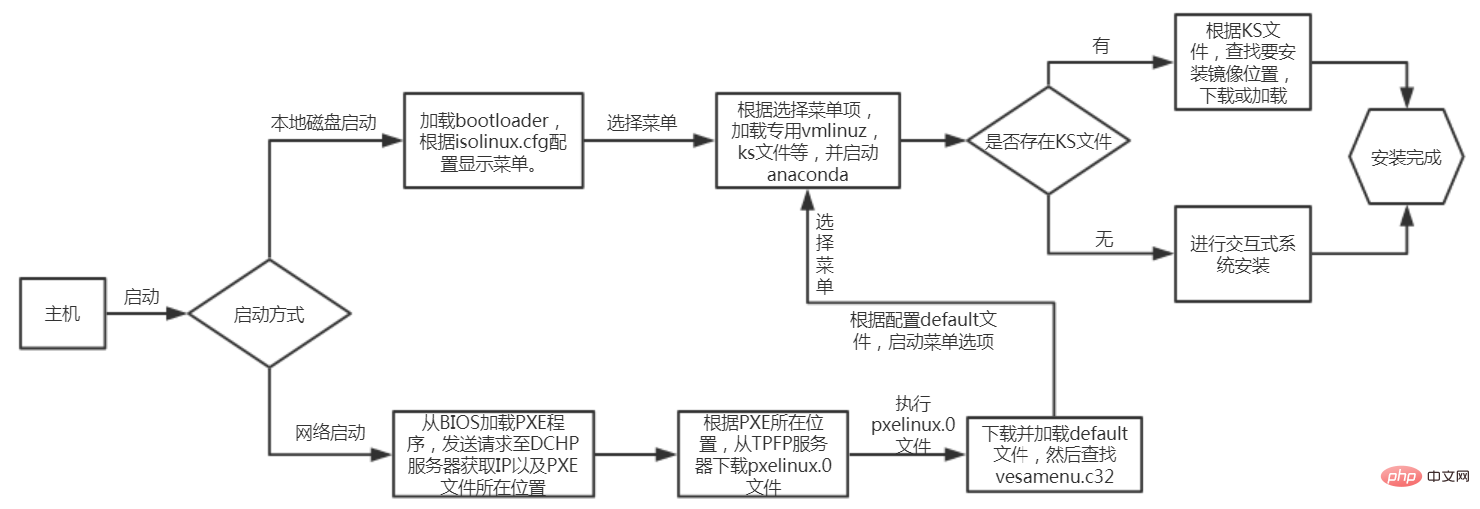
以下内容为我整理的流程图,从图中可以看出pxelinux.0的文件功能相当于bootloader和isolinux.bin的集成版。
1、修改default,增加一项ks;如果想在菜单项时间短一些,可以修改timeout时间。
label ks menu label ^Install system based ks menu default kernel vmlinuz append initrd=initrd.img text ks=http://172.16.100.67/ks.cfg label linux menu label ^Install or upgrade an existing system kernel vmlinuz append initrd=initrd.img
2、修改ks.cfg文件,指定从http服务器加载安装程序
# Kickstart file automatically generated by anaconda. #version=DEVELinstall#cdromurl --url=http://172.16.100.67/centos6.6/lang en_US.UTF-8keyboard usnetwork --onboot no --device eth0 --bootproto dhcp --noipv6rootpw --iscrypted $6$3.bn6KZ9zigMQq.Z$V/Q8xF2asfM8KCWm6GsjhYBvTTmMM6B50i6A/AFFx38xkg1sP2kL.ECBAda4SLwG6itOZhLXG/41sgRCJBLf11firewall --service=sshauthconfig --enableshadow --passalgo=sha512selinux --enforcingtimezone --utc Asia/Shanghaibootloader --location=mbr --driveorder=sda --append="crashkernel=auto rhgb quiet"# The following is the partition information you requested# Note that any partitions you deleted are not expressed# here so unless you clear all partitions first, this is# not guaranteed to workclearpart --all part /boot --fstype=ext4 --size=200part / --fstype=ext4 --size=7000part swap --size=2000 #repo --name="CentOS" --baseurl=cdrom:repodata/ --cost=100reboot%packages --nobase@core%end
3、开启dchpd、tftpd、httpd,关闭iptable、selinux,就可以完成自动安装了。
后续:
在安装的时候出现一个问题,提示this device may need to be reinitialized。
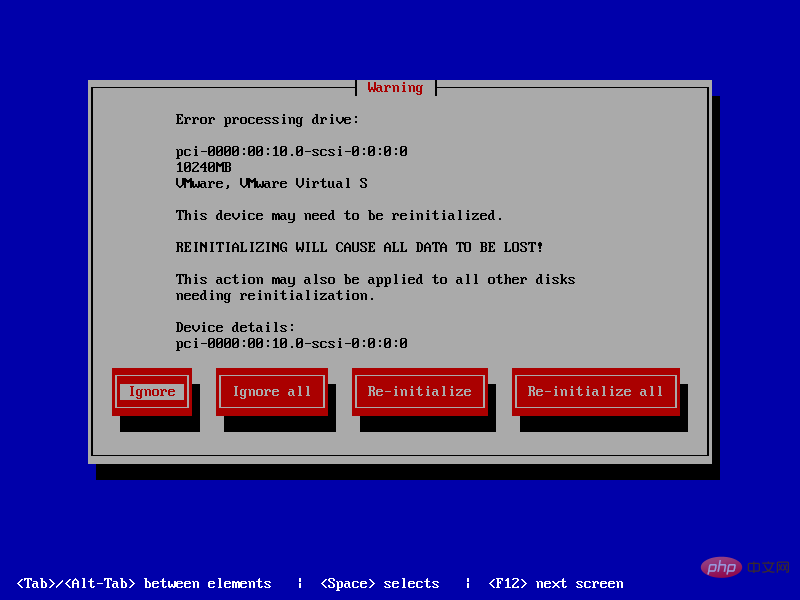
解决方法:
在ks文件中增加zeromb就可以了,#号这一行,可有可无,不影响。
# Clear the Master Boot Record zeromb
配置修改为:
url --url=http://172.16.100.67/centos6.6/ lang en_US.UTF-8 keyboard us network --onboot no --device eth0 --bootproto dhcp --noipv6 rootpw --iscrypted $6$3.bn6KZ9zigMQq.Z$V/Q8xF2asfM8KCWm6GsjhYBvTTmMM6B50i6A/AFFx38xkg1sP2kL.ECBAda4SLwG6itOZhLXG/41sgRCJBLf11 firewall --service=ssh authconfig --enableshadow --passalgo=sha512 selinux --enforcing timezone --utc Asia/Shanghai bootloader --location=mbr --driveorder=sda --append="crashkernel=auto rhgb quiet" zerombr PEX部分内容来自于:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunhongleibibi/archive/2017/11/17/7851382.html
The above is the detailed content of Teach you to install Centos system through the network. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the methods of tuning performance of Zookeeper on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
What are the methods of tuning performance of Zookeeper on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
Zookeeper performance tuning on CentOS can start from multiple aspects, including hardware configuration, operating system optimization, configuration parameter adjustment, monitoring and maintenance, etc. Here are some specific tuning methods: SSD is recommended for hardware configuration: Since Zookeeper's data is written to disk, it is highly recommended to use SSD to improve I/O performance. Enough memory: Allocate enough memory resources to Zookeeper to avoid frequent disk read and write. Multi-core CPU: Use multi-core CPU to ensure that Zookeeper can process it in parallel.
 What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
Backup and Recovery Policy of GitLab under CentOS System In order to ensure data security and recoverability, GitLab on CentOS provides a variety of backup methods. This article will introduce several common backup methods, configuration parameters and recovery processes in detail to help you establish a complete GitLab backup and recovery strategy. 1. Manual backup Use the gitlab-rakegitlab:backup:create command to execute manual backup. This command backs up key information such as GitLab repository, database, users, user groups, keys, and permissions. The default backup file is stored in the /var/opt/gitlab/backups directory. You can modify /etc/gitlab
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Improve HDFS performance on CentOS: A comprehensive optimization guide to optimize HDFS (Hadoop distributed file system) on CentOS requires comprehensive consideration of hardware, system configuration and network settings. This article provides a series of optimization strategies to help you improve HDFS performance. 1. Hardware upgrade and selection resource expansion: Increase the CPU, memory and storage capacity of the server as much as possible. High-performance hardware: adopts high-performance network cards and switches to improve network throughput. 2. System configuration fine-tuning kernel parameter adjustment: Modify /etc/sysctl.conf file to optimize kernel parameters such as TCP connection number, file handle number and memory management. For example, adjust TCP connection status and buffer size
 CentOS Containerization with Docker: Deploying and Managing Applications
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:08 AM
CentOS Containerization with Docker: Deploying and Managing Applications
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Using Docker to containerize, deploy and manage applications on CentOS can be achieved through the following steps: 1. Install Docker, use the yum command to install and start the Docker service. 2. Manage Docker images and containers, obtain images through DockerHub and customize images using Dockerfile. 3. Use DockerCompose to manage multi-container applications and define services through YAML files. 4. Deploy the application, use the dockerpull and dockerrun commands to pull and run the container from DockerHub. 5. Carry out advanced management and deploy complex applications using Docker networks and volumes. Through these steps, you can make full use of D
 CentOS Backup and Recovery: Ensuring Data Integrity and Availability
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:02 AM
CentOS Backup and Recovery: Ensuring Data Integrity and Availability
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:02 AM
The steps for backup and recovery in CentOS include: 1. Use the tar command to perform basic backup and recovery, such as tar-czvf/backup/home_backup.tar.gz/home backup/home directory; 2. Use rsync for incremental backup and recovery, such as rsync-avz/home//backup/home_backup/ for the first backup. These methods ensure data integrity and availability and are suitable for the needs of different scenarios.
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)






