 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
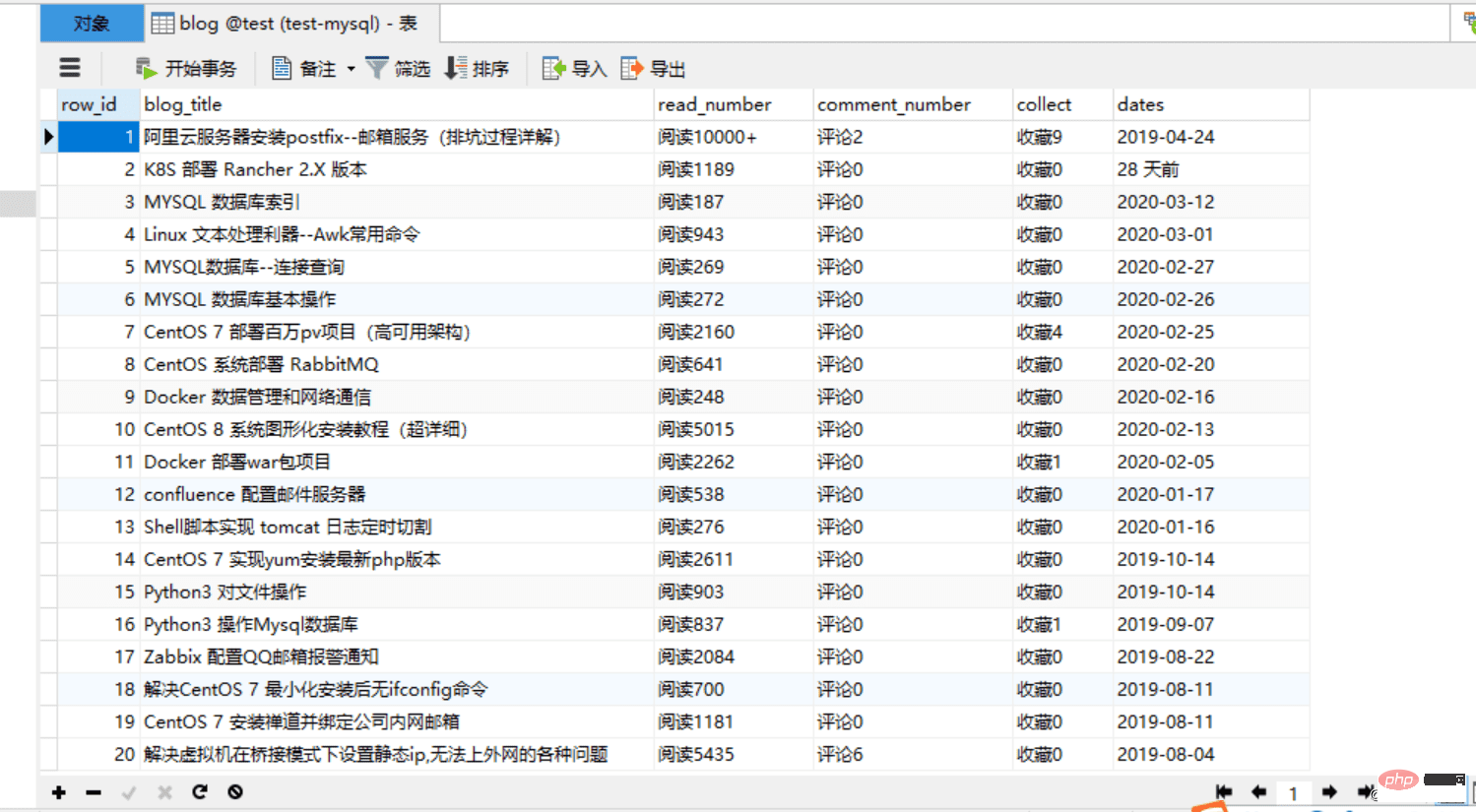
 Detailed explanation of the method of crawling 51cto data in Python and storing it in MySQL
Detailed explanation of the method of crawling 51cto data in Python and storing it in MySQL
Detailed explanation of the method of crawling 51cto data in Python and storing it in MySQL

[Related learning recommendations: python tutorial】
Experimental environment
1. Install Python 3.7
2. Install requests, bs4, pymysql module
Experimental steps 1. Installation environment and module
Please refer to https://www. jb51.net/article/194104.htm
2.Write code
# 51cto 博客页面数据插入mysql数据库
# 导入模块
import re
import bs4
import pymysql
import requests
# 连接数据库账号密码
db = pymysql.connect(host='172.171.13.229',
user='root', passwd='abc123',
db='test', port=3306,
charset='utf8')
# 获取游标
cursor = db.cursor()
def open_url(url):
# 连接模拟网页访问
headers = {
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) '
'Chrome/57.0.2987.98 Safari/537.36'}
res = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
return res
# 爬取网页内容
def find_text(res):
soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(res.text, 'html.parser')
# 博客名
titles = []
targets = soup.find_all("a", class_="tit")
for each in targets:
each = each.text.strip()
if "置顶" in each:
each = each.split(' ')[0]
titles.append(each)
# 阅读量
reads = []
read1 = soup.find_all("p", class_="read fl on")
read2 = soup.find_all("p", class_="read fl")
for each in read1:
reads.append(each.text)
for each in read2:
reads.append(each.text)
# 评论数
comment = []
targets = soup.find_all("p", class_='comment fl')
for each in targets:
comment.append(each.text)
# 收藏
collects = []
targets = soup.find_all("p", class_='collect fl')
for each in targets:
collects.append(each.text)
# 发布时间
dates=[]
targets = soup.find_all("a", class_='time fl')
for each in targets:
each = each.text.split(':')[1]
dates.append(each)
# 插入sql 语句
sql = """insert into blog (blog_title,read_number,comment_number, collect, dates)
values( '%s', '%s', '%s', '%s', '%s');"""
# 替换页面 \xa0
for titles, reads, comment, collects, dates in zip(titles, reads, comment, collects, dates):
reads = re.sub('\s', '', reads)
comment = re.sub('\s', '', comment)
collects = re.sub('\s', '', collects)
cursor.execute(sql % (titles, reads, comment, collects,dates))
db.commit()
pass
# 统计总页数
def find_depth(res):
soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(res.text, 'html.parser')
depth = soup.find('li', class_='next').previous_sibling.previous_sibling.text
return int(depth)
# 主函数
def main():
host = "https://blog.51cto.com/13760351"
res = open_url(host) # 打开首页链接
depth = find_depth(res) # 获取总页数
# 爬取其他页面信息
for i in range(1, depth + 1):
url = host + '/p' + str(i) # 完整链接
res = open_url(url) # 打开其他链接
find_text(res) # 爬取数据
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()3..MySQL creates the corresponding table
CREATE TABLE `blog` ( `row_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键', `blog_title` varchar(52) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '博客标题', `read_number` varchar(26) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '阅读数量', `comment_number` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '评论数量', `collect` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '收藏数量', `dates` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '发布日期', PRIMARY KEY (`row_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
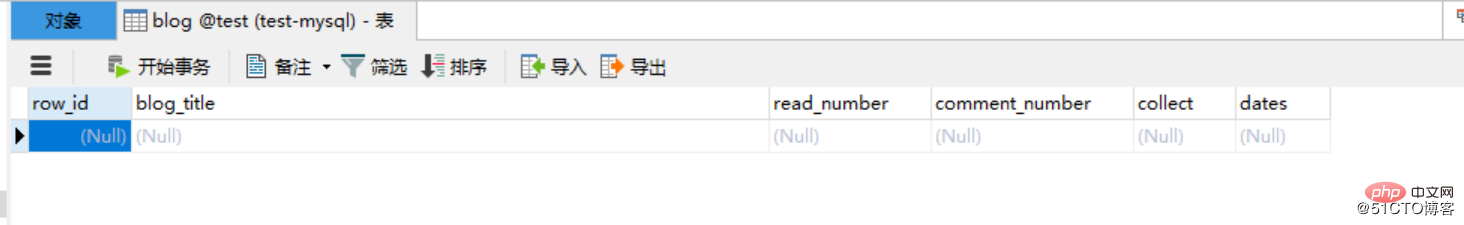
import re
import bs4
import pymysql
import requests
# 连接数据库
db = pymysql.connect(host='172.171.13.229',
user='root', passwd='abc123',
db='test', port=3306,
charset='utf8')
# 获取游标
cursor = db.cursor()
def open_url(url):
# 连接模拟网页访问
headers = {
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) '
'Chrome/57.0.2987.98 Safari/537.36'}
res = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
return res
# 爬取网页内容
def find_text(res):
soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(res.text, 'html.parser')
# 博客标题
titles = []
targets = soup.find_all("a", class_="tit")
for each in targets:
each = each.text.strip()
if "置顶" in each:
each = each.split(' ')[0]
titles.append(each)
# 阅读量
reads = []
read1 = soup.find_all("p", class_="read fl on")
read2 = soup.find_all("p", class_="read fl")
for each in read1:
reads.append(each.text)
for each in read2:
reads.append(each.text)
# 评论数
comment = []
targets = soup.find_all("p", class_='comment fl')
for each in targets:
comment.append(each.text)
# 收藏
collects = []
targets = soup.find_all("p", class_='collect fl')
for each in targets:
collects.append(each.text)
# 发布时间
dates=[]
targets = soup.find_all("a", class_='time fl')
for each in targets:
each = each.text.split(':')[1]
dates.append(each)
# 插入sql 语句
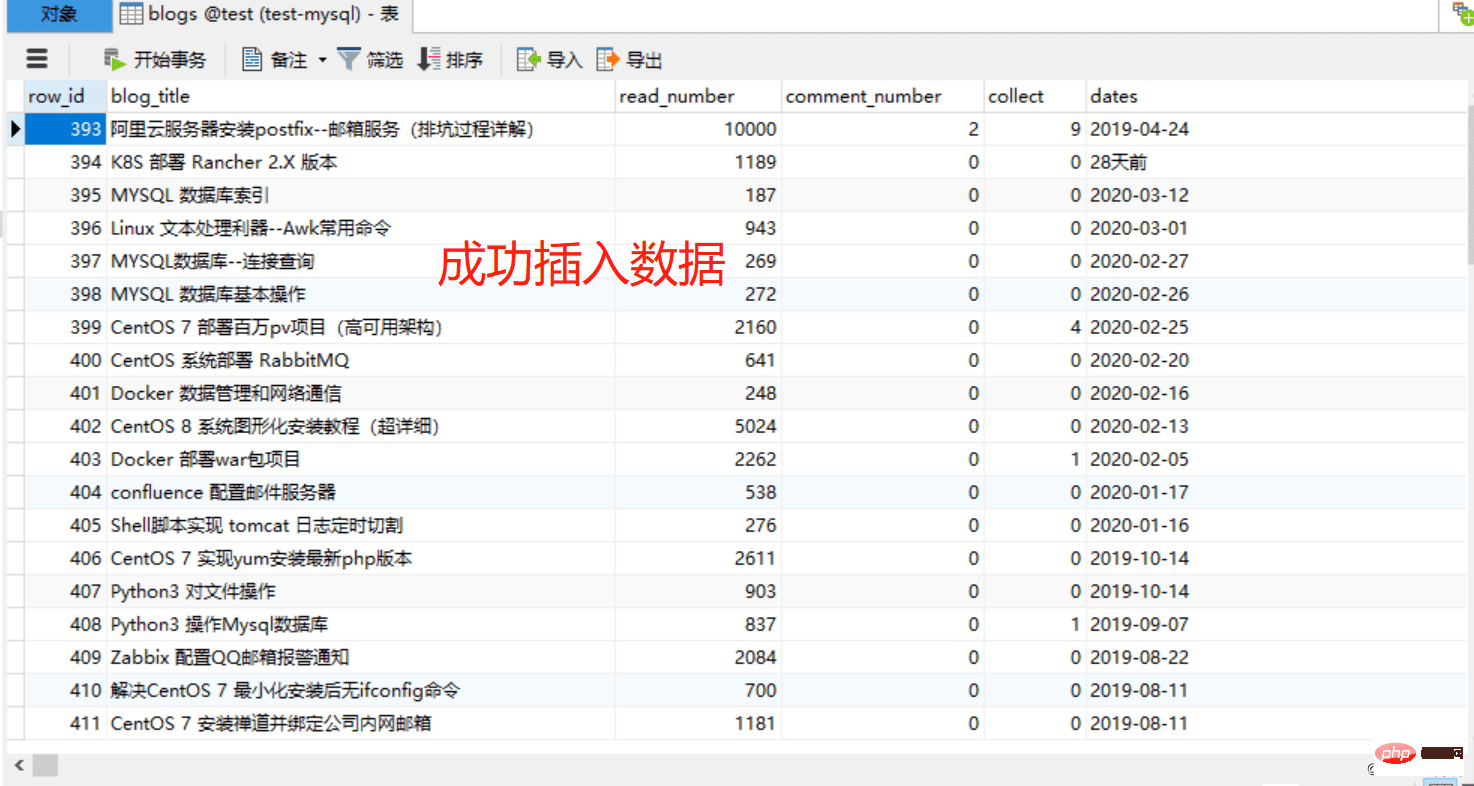
sql = """insert into blogs (blog_title,read_number,comment_number, collect, dates)
values( '%s', '%s', '%s', '%s', '%s');"""
# 替换页面 \xa0
for titles, reads, comment, collects, dates in zip(titles, reads, comment, collects, dates):
reads = re.sub('\s', '', reads)
reads=int(re.sub('\D', "", reads)) #匹配数字,转换为整型
comment = re.sub('\s', '', comment)
comment = int(re.sub('\D', "", comment)) #匹配数字,转换为整型
collects = re.sub('\s', '', collects)
collects = int(re.sub('\D', "", collects)) #匹配数字,转换为整型
dates = re.sub('\s', '', dates)
cursor.execute(sql % (titles, reads, comment, collects,dates))
db.commit()
pass
# 统计总页数
def find_depth(res):
soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(res.text, 'html.parser')
depth = soup.find('li', class_='next').previous_sibling.previous_sibling.text
return int(depth)
# 主函数
def main():
host = "https://blog.51cto.com/13760351"
res = open_url(host) # 打开首页链接
depth = find_depth(res) # 获取总页数
# 爬取其他页面信息
for i in range(1, depth + 1):
url = host + '/p' + str(i) # 完整链接
res = open_url(url) # 打开其他链接
find_text(res) # 爬取数据
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
#主程序入口
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()CREATE TABLE `blogs` ( `row_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键', `blog_title` varchar(52) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '博客标题', `read_number` int(26) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '阅读数量', `comment_number` int(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '评论数量', `collect` int(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '收藏数量', `dates` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '发布日期', PRIMARY KEY (`row_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
#末尾修改为:
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
print("\n\t\t所有数据已成功存放数据库!!! \n")
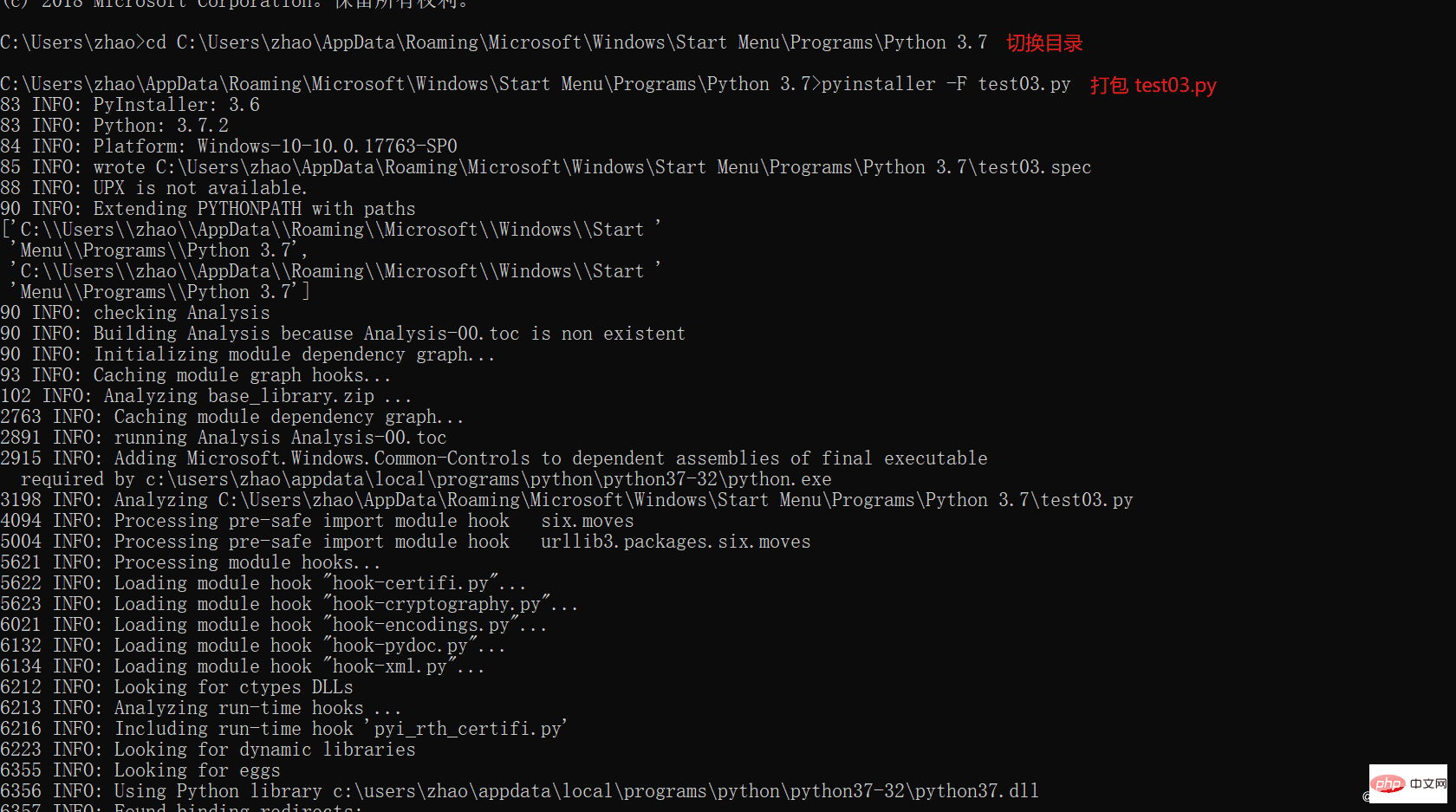
time.sleep(5)pip install pyinstaller -i https://pypi.tuna. tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
Related learning recommendations:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the method of crawling 51cto data in Python and storing it in MySQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1672
1672
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1332
1332
 25
25
 1277
1277
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and Tools
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and Tools
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Both Python and JavaScript's choices in development environments are important. 1) Python's development environment includes PyCharm, JupyterNotebook and Anaconda, which are suitable for data science and rapid prototyping. 2) The development environment of JavaScript includes Node.js, VSCode and Webpack, which are suitable for front-end and back-end development. Choosing the right tools according to project needs can improve development efficiency and project success rate.
 Python vs. C : Understanding the Key Differences
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python vs. C : Understanding the Key Differences
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python and C each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1) Python is suitable for rapid development and data processing due to its concise syntax and dynamic typing. 2)C is suitable for high performance and system programming due to its static typing and manual memory management.
 Golang vs. Python: The Pros and Cons
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Golang vs. Python: The Pros and Cons
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Golangisidealforbuildingscalablesystemsduetoitsefficiencyandconcurrency,whilePythonexcelsinquickscriptinganddataanalysisduetoitssimplicityandvastecosystem.Golang'sdesignencouragesclean,readablecodeanditsgoroutinesenableefficientconcurrentoperations,t
 Laravel vs. Python (with Frameworks): A Comparative Analysis
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Laravel vs. Python (with Frameworks): A Comparative Analysis
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Laravel is suitable for projects that teams are familiar with PHP and require rich features, while Python frameworks depend on project requirements. 1.Laravel provides elegant syntax and rich features, suitable for projects that require rapid development and flexibility. 2. Django is suitable for complex applications because of its "battery inclusion" concept. 3.Flask is suitable for fast prototypes and small projects, providing great flexibility.
 Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
In MySQL, the function of foreign keys is to establish the relationship between tables and ensure the consistency and integrity of the data. Foreign keys maintain the effectiveness of data through reference integrity checks and cascading operations. Pay attention to performance optimization and avoid common errors when using them.
 Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
The main difference between MySQL and MariaDB is performance, functionality and license: 1. MySQL is developed by Oracle, and MariaDB is its fork. 2. MariaDB may perform better in high load environments. 3.MariaDB provides more storage engines and functions. 4.MySQL adopts a dual license, and MariaDB is completely open source. The existing infrastructure, performance requirements, functional requirements and license costs should be taken into account when choosing.
 SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL is a standard language for managing relational databases, while MySQL is a database management system that uses SQL. SQL defines ways to interact with a database, including CRUD operations, while MySQL implements the SQL standard and provides additional features such as stored procedures and triggers.



