How to catch and handle java exceptions
Java exception capture and processing methods: 1. throws keyword, the system automatically throws the captured exception information to the superior calling method; 2. The function of throw is to manually throw the instantiation object of the exception class ;3. RunException is a subclass of Exception, and it is up to the user to choose whether to process it.

[Related learning recommendations: java basic tutorial]
Java exception catching and handling methods:
1. The use of exception handling
Since the finally block can be omitted, the exception handling format can be divided into three categories: try{}——catch { }, try{ }——catch{ }——finally{ }, try{ }——finally{ }.
1 public class DealException
2 {
3 public static void main(String args[])
4 {
5 try
6 //要检查的程序语句
7 {
8 int a[] = new int[5];
9 a[10] = 7;//出现异常
10 }
11 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex)
12 //异常发生时的处理语句
13 {
14 System.out.println("超出数组范围!");
15 }
16 finally
17 //这个代码块一定会被执行
18 {
19 System.out.println("*****");
20 }
21 System.out.println("异常处理结束!");
22 }
23 }It can be seen that two judgments must be made during the exception catching process. The first is whether an exception is generated in the try program block, and the second is whether the generated exception is consistent with the one you want to catch in the catch() brackets. The exception is the same.
So, what should you do if the exception that occurs is different from the exception you want to catch in catch()? In fact, we can follow a try statement with multiple exception handling catch statements to handle many different types of exceptions.
1 public class DealException
2 {
3 public static void main(String args[])
4 {
5 try
6 //要检查的程序语句
7 {
8 int a[] = new int[5];
9 a[0] = 3;
10 a[1] = 1;
11 //a[1] = 0;//除数为0异常
12 //a[10] = 7;//数组下标越界异常
13 int result = a[0]/a[1];
14 System.out.println(result);
15 }
16 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex)
17 //异常发生时的处理语句
18 {
19 System.out.println("数组越界异常");
20 ex.printStackTrace();//显示异常的堆栈跟踪信息
21 }
22 catch(ArithmeticException ex)
23 {
24 System.out.println("算术运算异常");
25 ex.printStackTrace();
26 }
27 finally
28 //这个代码块一定会被执行
29 {
30 System.out.println("finally语句不论是否有异常都会被执行。");
31 }
32 System.out.println("异常处理结束!");
33 }
34 }In the above example, ex.printStackTrace(); is the use of the exception class object ex, which outputs detailed exception stack trace information, including the type of exception, which package, which class, and which method the exception occurred in. and the line number where the exception occurred.
2. The throws keyword
The method declared by throws means that the method does not handle exceptions, but the system automatically throws the captured exception information to the superior calling method.
1 public class throwsDemo
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 int[] a = new int[5];
6 try
7 {
8 setZero(a,10);
9 }
10 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex)
11 {
12 System.out.println("数组越界错误!");
13 System.out.println("异常:"+ex);
14 }
15 System.out.println("main()方法结束。");
16 }
17 private static void setZero(int[] a,int index) throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
18 {
19 a[index] = 0;
20 }
21 }The throws keyword throws an exception. "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" indicates the type of exception that may exist in the setZero() method. Once an exception occurs in the method, the setZero() method does not handle it itself, but submits the exception to it. The superior caller main() method.
3. Throw keyword
The function of throw is to manually throw the instantiated object of the exception class.
1 public class throwDemo
2 {
3 public static void main(String[] args)
4 {
5 try
6 {
7 //抛出异常的实例化对象
8 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("\n个性化异常信息:\n数组下标越界");
9 }
10 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex)
11 {
12 System.out.println(ex);
13 }
14 }
15 }We can find that throw seems to be looking for trouble, causing runtime exceptions and customizing prompt information. In fact, throw is usually used in conjunction with throws, and what is thrown is an instance of the exception class that has been generated in the program.
ExceptionDemo
Output result:
setZero method starts:
setZero method ends.
Exception: java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 10
main() method ends!
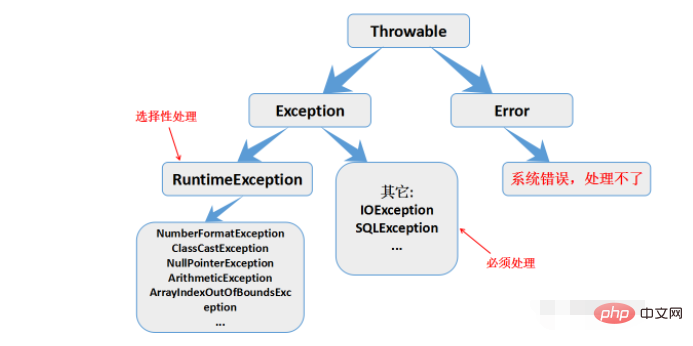
4. RuntimeException class
The difference between Exception and RuntimeException:
Exception: It is mandatory for users to handle it;
RunException : is a subclass of Exception, and it is up to the user to choose whether to handle it.
The custom exception class inherits from the Exception class and can be used There are a lot of methods in the parent class, and you can also write your own methods to handle specific events. Java provides an inheritance method to run exception classes written by users. Programming video The above is the detailed content of How to catch and handle java exceptions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website! 1 class MyException extends Exception
2 {
3 public MyException(String message)
4 {
5 super(message);
6 }
7 }
8 public class DefinedException
9 {
10 public static void main(String[] args)
11 {
12 try
13 {
14 throw new MyException("\n自定义异常类!");
15 }
16 catch(MyException e)
17 {
18 System.out.println(e);
19 }
20 }
21 }

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1669
1669
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.
 PHP vs. Python: Use Cases and Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP vs. Python: Use Cases and Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and content management systems, and Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and automation scripts. 1.PHP performs well in building fast and scalable websites and applications and is commonly used in CMS such as WordPress. 2. Python has performed outstandingly in the fields of data science and machine learning, with rich libraries such as NumPy and TensorFlow.




