How to avoid deadlock?

Methods to avoid deadlock:
A deadlock occurs when two threads wait for each other to release resources. The Python interpreter does not monitor and will not actively take measures to deal with deadlock situations, so measures should be taken to avoid deadlocks when performing multi-threaded programming.
Once a deadlock occurs, the entire program will neither produce any exceptions nor give any prompts, but all threads will be blocked and unable to continue.
Deadlock is very easy to occur, especially when there are multiple synchronization monitors in the system, the following program will cause a deadlock:
import threading
import time
class A:
def __init__(self):
self.lock = threading.RLock()
def foo(self, b):
try:
self.lock.acquire()
print("当前线程名: " + threading.current_thread().name\
+ " 进入了A实例的foo()方法" ) # ①
time.sleep(0.2)
print("当前线程名: " + threading.current_thread().name\
+ " 企图调用B实例的last()方法") # ③
b.last()
finally:
self.lock.release()
def last(self):
try:
self.lock.acquire()
print("进入了A类的last()方法内部")
finally:
self.lock.release()
class B:
def __init__(self):
self.lock = threading.RLock()
def bar(self, a):
try:
self.lock.acquire()
print("当前线程名: " + threading.current_thread().name\
+ " 进入了B实例的bar()方法" ) # ②
time.sleep(0.2)
print("当前线程名: " + threading.current_thread().name\
+ " 企图调用A实例的last()方法") # ④
a.last()
finally:
self.lock.release()
def last(self):
try:
self.lock.acquire()
print("进入了B类的last()方法内部")
finally:
self.lock.release()
a = A()
b = B()
def init():
threading.current_thread().name = "主线程"
# 调用a对象的foo()方法
a.foo(b)
print("进入了主线程之后")
def action():
threading.current_thread().name = "副线程"
# 调用b对象的bar()方法
b.bar(a)
print("进入了副线程之后")
# 以action为target启动新线程
threading.Thread(target=action).start()
# 调用init()函数
init()Run the above program, it will See the effect shown in Figure 1.
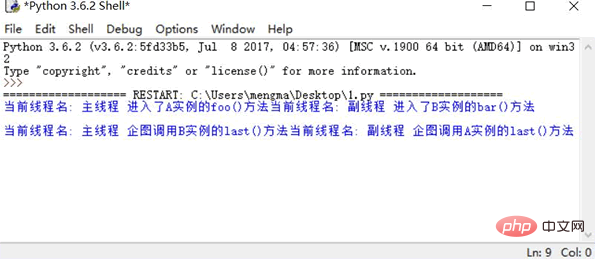
Figure 1 Deadlock effect
As can be seen from Figure 1, the program can neither execute downward nor throw any Abnormal, it has been "stalemate". The reason is that the methods of object A and object B in the above program are both thread-safe methods.
There are two threads executing in the program. The thread execution body of the secondary thread is the action() function, and the thread execution body of the main thread is the init() function (the main program calls the init() function). In the action() function, let the B object call the bar() method, and in the init() function, let the A object call the foo() method.
Figure 1 shows that the action() function is executed first and calls the bar() method of the B object. Before entering the bar() method, the thread locks the Lock of the B object (when the program executes to No. 2 code, the secondary thread pauses for 0.2s); the CPU switches to executing another thread and lets the A object execute the foo() method, so you see that the main thread begins to execute the foo() method of the A instance. Before entering the foo() method, This thread locks the Lock of object A (when the program executes code ①, the main thread also pauses for 0.2s).
Next, the secondary thread will wake up first and continue to execute downwards until it reaches code ④ and hopes to call the last() method of the A object (before executing this method, the Lock of the A object must be first Lock), but at this time the main thread is maintaining the Lock of the A object, so the secondary thread is blocked.
The main thread should wake up next and continue to execute downwards until it reaches code ③ where it hopes to call the last() method of the B object (before executing this method, the B object must first be Lock), but at this time the secondary thread does not release the Lock of the B object.
At this point, it appears that the main thread holds the lock on object A and waits for object B to be locked, while the secondary thread holds the lock on object B and waits for object A to be locked. The two threads wait for each other. The lock is released first, so a deadlock occurs.
Deadlocks should not occur in programs. You should try to avoid deadlocks when writing programs. There are several common ways to solve the deadlock problem below:
Avoid multiple locks. Try to avoid locking multiple Locks on the same thread. For example, in the above deadlock program, the main thread needs to lock the Lock of two objects A and B, and the secondary thread also needs to lock the Lock of two objects A and B, which lays the hidden danger of deadlock.
has the same locking sequence. If multiple threads need to lock multiple Locks, they should ensure that they request locks in the same order. For example, in the above deadlock program, the main thread first locks the Lock of object A, and then locks the Lock of object B; while the secondary thread first locks the Lock of object B, and then locks the Lock of object A. This locking sequence can easily form nested locks, which can lead to deadlocks. This problem can be avoided if the main thread and the secondary thread lock in the same order.
Use timing lock. The program can specify the timeout parameter when calling the acquire() method to lock. This parameter specifies that the Lock will be automatically released after timeout seconds, so that the deadlock can be unlocked.
Deadlock detection. Deadlock detection is a deadlock prevention mechanism that relies on algorithmic mechanisms. It is mainly targeted at scenarios where sequential locking is impossible and timed locks cannot be used.
The above is the detailed content of How to avoid deadlock?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to deal with deadlock problems in C++ development
Aug 22, 2023 pm 02:24 PM
How to deal with deadlock problems in C++ development
Aug 22, 2023 pm 02:24 PM
How to deal with deadlock problems in C++ development Deadlock is one of the common problems in multi-threaded programming, especially when developing in C++. Deadlock problems may occur when multiple threads wait for each other's resources. If not handled in time, deadlock will not only cause the program to freeze, but also affect the performance and stability of the system. Therefore, it is very important to learn how to deal with deadlock problems in C++ development. 1. Understand the causes of deadlocks. To solve the deadlock problem, you first need to understand the causes of deadlocks. Deadlock usually occurs when
 Deadlock prevention and detection mechanism in C++ multi-threaded programming
Jun 01, 2024 pm 08:32 PM
Deadlock prevention and detection mechanism in C++ multi-threaded programming
Jun 01, 2024 pm 08:32 PM
Multi-thread deadlock prevention mechanism includes: 1. Lock sequence; 2. Test and set up. The detection mechanism includes: 1. Timeout; 2. Deadlock detector. The article takes an example of a shared bank account and avoids deadlock through lock sequence. The transfer function first requests the lock of the transfer out account and then the transfer in account.
 Prevention and solution of deadlock and starvation in golang function concurrency control
Apr 24, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
Prevention and solution of deadlock and starvation in golang function concurrency control
Apr 24, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
Deadlock and starvation in Go: Preventing and solving deadlock: Coroutines are waiting for each other and cannot perform operations. Use the runtime.SetBlockProfileRate function to detect. Prevent deadlocks: Use fine-grained locking, timeouts, and lock-free data structures to prevent deadlocks. Starvation: The coroutine continues to be unable to obtain resources, and fair locks are used to prevent starvation. Fair lock practice: Create a fair lock and wait for the coroutine to try to acquire the lock for the longest time to acquire the lock first.
 How to debug deadlocks in C++ programs?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 05:24 PM
How to debug deadlocks in C++ programs?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 05:24 PM
Deadlock is a common error in concurrent programming that occurs when multiple threads wait for locks held by each other. Deadlocks can be resolved by detecting them using a debugger, analyzing thread activity, and identifying the threads and locks involved. Ways to resolve deadlocks include avoiding circular dependencies, using deadlock detectors, and using timeouts. In practice, deadlocks can be avoided by ensuring that threads acquire locks in the same order or by using recursive locks or condition variables.
 How to solve deadlock in Go development
Jun 30, 2023 pm 04:58 PM
How to solve deadlock in Go development
Jun 30, 2023 pm 04:58 PM
Methods to solve the deadlock problem in Go language development Go language is an open source statically typed compiled language that is widely used in concurrent programming. However, due to the characteristics of the concurrency model of the Go language, developers often encounter deadlock problems when writing concurrent programs. This article will introduce some methods to solve the deadlock problem in Go language development. First, we need to understand what deadlock is. Deadlock refers to a situation where multiple concurrent tasks are unable to continue execution because they are waiting for each other to release resources. In Go language, deadlock problems are usually due to competition for resources or
 How do C++ functions solve the deadlock problem in concurrent programming?
Apr 26, 2024 pm 01:18 PM
How do C++ functions solve the deadlock problem in concurrent programming?
Apr 26, 2024 pm 01:18 PM
In C++, the use of mutex functions can solve the deadlock problem in multi-threaded concurrent programming. The specific steps are as follows: create a mutex; when the thread needs to access the shared variable, obtain the mutex; modify the shared variable; release the mutex. This ensures that only one thread accesses the shared variable at any time, effectively preventing deadlock.
 How to solve the deadlock problem in Go language?
Oct 08, 2023 pm 05:07 PM
How to solve the deadlock problem in Go language?
Oct 08, 2023 pm 05:07 PM
How to solve the deadlock problem in Go language? Go language has the characteristics of concurrent programming, and concurrent operations can be achieved by using goroutine and channel. However, deadlock is a common problem in concurrent programming. When goroutines depend on each other's resources and create circular dependencies when accessing these resources, deadlocks may occur. This article will introduce how to solve the deadlock problem in the Go language and provide specific code examples. First, let’s understand what
 Concurrent programming challenges in Python: battling deadlocks and race conditions
Feb 19, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
Concurrent programming challenges in Python: battling deadlocks and race conditions
Feb 19, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
Deadlock Deadlock is when multiple threads wait for each other for resources, forming a loop that eventually causes all threads to block. In python, deadlock usually occurs when multiple locks or mutexes are locked in the wrong order. Example: importthreading#Two threads share two locks lock1=threading.Lock()lock2=threading.Lock()defthread1_func():lock1.acquire()lock2.acquire()#Do some operations lock2.release()lock1. release()defthread2_func():loc





