 Database
Database
 Redis
Redis
 Introduction to Redis master-slave replication and detailed explanation of its principles
Introduction to Redis master-slave replication and detailed explanation of its principles
Introduction to Redis master-slave replication and detailed explanation of its principles

#redis is a key-value storage system. Similar to Memcached, it supports relatively more stored value types, including string (string), list (linked list), set (set), zset (sorted set - ordered set) and hash (hash type). These data types all support push/pop, add/remove, intersection, union, difference, and richer operations, and these operations are all atomic. On this basis, redis supports various different ways of sorting. Like memcached, data is cached in memory to ensure efficiency. The difference is that redis will periodically write updated data to disk or write modification operations to additional record files, and on this basis, master-slave (master-slave) synchronization is achieved.
Overview
In existing enterprises, 80% of companies mostly use redis stand-alone service. In actual scenarios, a single node redis is prone to risks.
Facing problems
1. Machine failure. We deploy to a Redis server. When a machine failure occurs, we need to migrate to another server and ensure that the data is synchronized. Data is the most important thing. If you don't care, you basically won't use Redis. 2. Capacity bottleneck. When we need to expand Redis memory, from 16G memory to 64G, a single machine will definitely not be able to satisfy it. Of course, you can buy a new 128G machine.
Solution
To achieve greater storage capacity of the distributed database and withstand high concurrent access, we will convert the original centralized data
The data in the library is stored on multiple other network nodes. In order to solve the problem of this single node, Redis will also deploy multiple copies of data toother nodes for replication to achieve high availability of Redis and redundant backup of data,
To ensure the high availability of data and services.
Master-slave replicationWhat is master-slave replication
Master-slave replication , refers to copying data from one Redis server to other Redis servers. The former is called the master node (master), and the latter is called the slave node (slave). Data replication is one-way and can only be from the master node to the slave node.
By default, each Redis server is a master node; and a master node can have multiple slave nodes (or no slave nodes), but a slave node can only have one master node.
The role of master-slave replication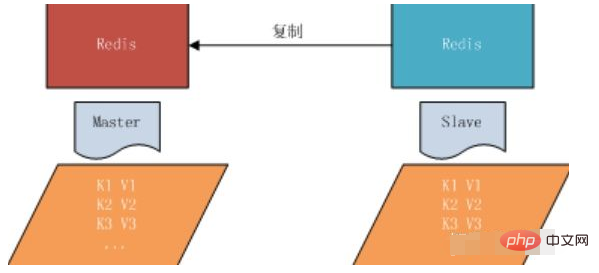
1. Data redundancy: Master-slave replication realizes hot backup of data , is a data redundancy method other than persistence. 2. Fault recovery: When a problem occurs on the master node, the slave node can provide services to achieve rapid fault recovery; it is actually a kind of service redundancy.
3. Load balancing: Based on master-slave replication, combined with read-write separation, the master node can provide write services,the slave nodes can provide read services (that is, when writing Redis data The application connects to the master node, and when reading Redis data, the application connects to the slave node) to share the server load; especially in the scenario of less writing and more reading, the read load is shared through multiple slave nodes
, which can greatly increase the concurrency of the Redis server. 4. Read and write separation: It can be used to achieve read and write separation, main library writing, slave library reading. Reading and writing separation can not only improve the load capacity of the server, but also can be used as needed. Change, change the number of slave libraries;
5. The cornerstone of high availability: In addition to the above functions, master-slave replication is also the basis for the implementation of sentinels and clusters.Therefore, master-slave replication is Redis High availability foundation.
Enable master-slave replication
There are 3 ways to enable master-slave replication from the slave node:1. Configuration file: Add to the configuration file of the slave server:
slaveof <masterip> <masterport>
2. Start command: Add redis-server after starting the command
--slaveof <masterip> <masterport>
3. 客户端命令: Redis 服务器启动后,直接通过客户端执行命令:
slaveof <masterip> <masterport>
则该 Redis 实例成为从节点。
通过 info replication 命令可以看到复制的一些信息主从复制原理主从复制过程大体可以分为 3 个阶段:连接建立阶段(即准备阶段)、数据同步阶段、命令传播阶段。在从节点执行 slaveof 命令后,复制过程便开始运作,下面图示大概可以看到,从图中可以看出复制过程大致分为 6 个过程
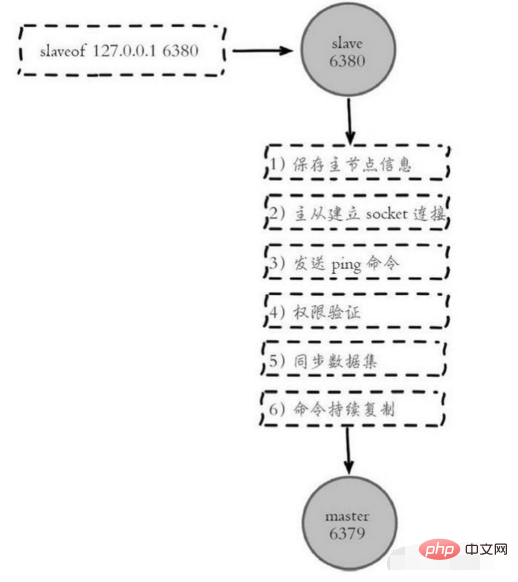
主从配置之后的日志记录也可以看出这个流程
1)保存主节点(master)信息。
执行 slaveof 后 Redis 会打印如下日志:

2)从节点(slave)内部通过每秒运行的定时任务维护复制相关逻辑,当定时任务发现存在新的主节点后,会尝试与该节点建立网络连接
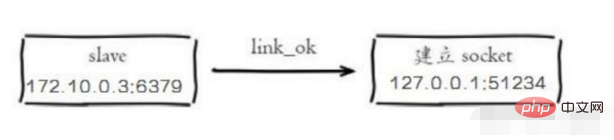
从节点与主节点建立网络连接
从节点会建立一个 socket 套接字,从节点建立了一个端口为 51234 的套接字,专门用于接受主节点发送的复制命令。从节点连接成功后打印如下日志:

如果从节点无法建立连接,定时任务会无限重试直到连接成功或者执行 slaveof noone 取消复制关于连接失败,可以在从节点执行 info replication 查看<span style="font-size: 14px; line-height: 1.76em;">master_link_down_since_seconds</span> 指标,它会记录与主节点连接失败的系统时间。从
节点连接主节点失败时也会每秒打印如下日志,方便发现问题:
# Error condition on socket for SYNC: {socket_error_reason}3)发送 ping 命令。
连接建立成功后从节点发送 ping 请求进行首次通信,ping 请求主要目的如下:
·检测主从之间网络套接字是否可用。
·检测主节点当前是否可接受处理命令。
如果发送 ping 命令后,从节点没有收到主节点的 pong 回复或者超时,比如网络超时或者主节点正在阻塞无法响应命令,从节点会断开复制连接,下次定时任务会发起重连
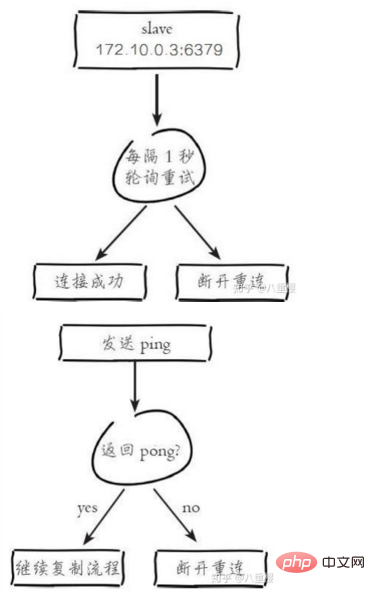
从节点发送的 ping 命令成功返回,Redis 打印如下日志,并继续后续复制流程:

4)权限验证。如果主节点设置了 requirepass 参数,则需要密码验证,从节点必须配
置 masterauth 参数保证与主节点相同的密码才能通过验证;如果验证失败复制将终
止,从节点重新发起复制流程。
5)同步数据集。主从复制连接正常通信后,对于首次建立复制的场景,主节点会把持
有的数据全部发送给从节点,这部分操作是耗时最长的步骤。
6)命令持续复制。当主节点把当前的数据同步给从节点后,便完成了复制的建立流程。
接下来主节点会持续地把写命令发送给从节点,保证主从数据一致性。
更多redis知识请关注redis数据库教程栏目。
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to Redis master-slave replication and detailed explanation of its principles. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1311
1311
 25
25
 1262
1262
 29
29
 1235
1235
 24
24
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Redis counter is a mechanism that uses Redis key-value pair storage to implement counting operations, including the following steps: creating counter keys, increasing counts, decreasing counts, resetting counts, and obtaining counts. The advantages of Redis counters include fast speed, high concurrency, durability and simplicity and ease of use. It can be used in scenarios such as user access counting, real-time metric tracking, game scores and rankings, and order processing counting.
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information



