What is java queue

The queue is a special linear table that follows the principle of "first in, first out". In our daily use, we often use it to operate data concurrently. In concurrent programming, it is sometimes necessary to use thread-safe queues. If you want to implement a thread-safe queue, there are usually two ways: one is to use a blocking queue, and the other is to use a thread synchronization lock.
What is a blocking queue?
Suppose there is a bakery with a customer eating bread and a chef baking bread. There are no more than 2 pieces of bread in the basket. After the chef finishes the test, he puts the bread into the basket, and when the guests eat the bread, they take it out of the basket. In order to ensure that there is bread in the basket when the guests eat the bread or the basket does not overflow when the chef bakes the bread, At this time, we need to introduce the concept of blocking queue, which is what we often call the producer-consumer model.
A blocking queue is a queue that supports two additional operations. These two additional operations support blocking insertion and removal methods.
(1) Support blocking insertion method: This means that when the queue is full, the queue will block the thread inserting elements until the queue is not full.
(2) Support blocking removal method: This means that when the queue is empty, the thread that obtains the element will wait for the queue to become non-empty. Blocking queues are often used in producer and consumer scenarios. The producer is the thread that adds elements to the queue, and the consumer is the thread that takes elements from the queue. A blocking queue is a container used by producers to store elements and consumers to obtain elements.
Non-blocking queues in the system: PriorityQueue and ConcurrentLinkedQueue
Let’s take a look at the relationship between non-blocking queues (taking PriorityQueue as an example):
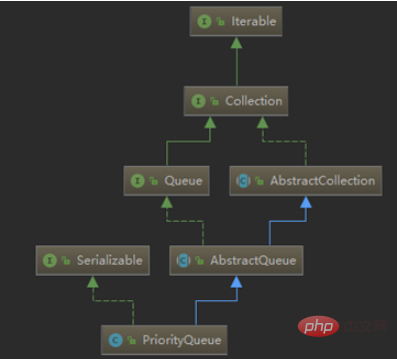
The PriorityQueue class inherits from AbstractQueue and implements the Serializable interface. Essentially maintaining an ordered list, PriorityQueue is located in the Java util package. The word Priority in the first half of its name means priority. In fact, this queue has "priority". Elements added to the Queue are positioned according to their natural ordering (through its java.util.Comparable implementation) or according to the java.util.Comparator implementation passed to the constructor.
ConcurrentLinkedQueue is a thread-safe queue based on linked nodes. Concurrent access does not require synchronization. Because it adds elements to the tail of the queue and removes them from the head, ConcurrentLinkedQueue's shared access to a common collection works just fine without knowing the size of the queue. Collecting information about the queue size will be slow and requires traversing the queue; ConcurrentLinkedQueue is an unbounded thread-safe queue based on linked nodes. It sorts nodes using a first-in, first-out rule. When we add an element, it is added to The tail of the queue; when we get an element, it returns the element at the head of the queue.
Queue that implements blocking interface:
The BlockingQueue interface and five blocking queue classes are added to java.util.concurrent. It's essentially a FIFO data structure with a twist. Rather than immediately adding or removing elements from the queue, the thread executing the operation blocks until space or an element becomes available.
The five queues provide different ones:
·ArrayBlockingQueue: A bounded queue backed by an array.
·LinkedBlockingQueue: An optional bounded queue backed by linked nodes.
·PriorityBlockingQueue: An unbounded priority queue backed by a priority heap.
·DelayQueue: A time-based scheduling queue backed by a priority heap.
·SynchronousQueue: A simple rendezvous mechanism using the BlockingQueue interface.
Let’s take a look at the inheritance relationship between ArrayBlockingQueue and LinkedBlockingQueue:
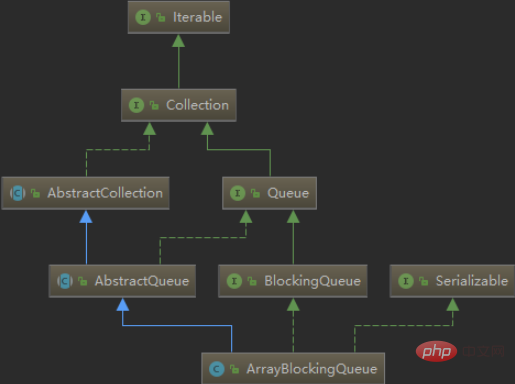
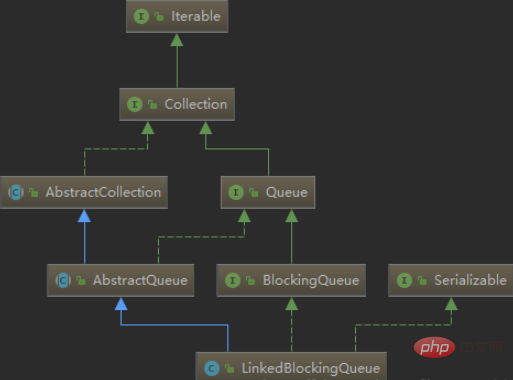
By looking at the inheritance relationship between the two classes, we You can know that they also inherit from AbstractQueue and implement the Serializable interface; the difference is that they also implement the BlockingQueue interface.
Let’s briefly introduce some of them:
LinkedBlockingQueueThe default size of LinkedBlockingQueue is Integer.MAX_VALUE, which can be understood as a cached bounded waiting queue. You can choose to specify its maximum capacity. It is a queue based on a linked list. This queue sorts elements according to FIFO (first in, first out). When the producer puts a piece of data into the queue, it is cached inside the queue. When the queue buffer reaches the maximum cache capacity (LinkedBlockingQueue can specify this value through the constructor), the producer queue is blocked until the consumer consumes from the queue. When a piece of data is dropped, the producer thread will be awakened, and vice versa for consumers.
ArrayBlockingQueue needs to specify capacity when constructing, and you can choose whether fairness is required. If the fairness parameter is set to true, the thread with the longest waiting time will be processed first (actually achieved by setting ReentrantLock to true This kind of fairness: that is, the thread with the longest waiting time will operate first). Generally, fairness will cost you in performance, so use it only when you really need it. It is an array-based blocking circular queue that sorts elements according to the FIFO (first in first out) principle.
PriorityBlockingQueue is a priority queue, not a first-in-first-out queue. Elements are removed in order of priority, and the queue has no upper limit (after looking at the source code, PriorityBlockingQueue is a repackage of PriorityQueue, based on the heap data structure, and PriorityQueue has no capacity limit, the same as ArrayList, so in priority It will not be blocked when putting on the blocking queue. Although this queue is logically unbounded, because the resources are exhausted, trying to perform an add operation may cause an OutOfMemoryError), but if the queue is empty, then the operation of taking the element take will block, so its retrieval operation take is blocked. In addition, the elements entering the queue must have comparison capabilities.
About ConcurrentLinkedQueue and LinkedBlockingQueue:
can also be understood as the difference between blocking queue and non-blocking queue:
1.LinkedBlockingQueue uses a lock mechanism, ConcurrentLinkedQueue uses the CAS algorithm, although the underlying lock acquisition of LinkedBlockingQueue also uses the CAS algorithm.
2. Regarding fetching elements, ConcurrentLinkedQueue does not support blocking to fetch elements, and LinkedBlockingQueue supports the blocking take() method.
3. Regarding the performance of inserting elements, in actual use, especially on multi-CPU servers, the gap between locking and lock-free is reflected. ConcurrentLinkedQueue will be much faster than LinkedBlockingQueue.
Producer-consumer code:
I saw a small example of a producer-consumer on the Internet, which is very helpful for understanding blocking queues. The code is as follows:
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class BlockingQueueTest {
public static class Basket {
BlockingQueue<String> basket = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
private void produce() throws InterruptedException {
basket.put("苹果");
}
private void consume() throws InterruptedException {
basket.take();
}
private int getAppleNumber() {
return basket.size();
}
}
private static void testBasket() {
final Basket basket = new Basket();
class Producer implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
System.out.println("生产者开始生产苹果###");
basket.produce();
System.out.println("生产者生产苹果完毕###");
System.out.println("篮子中的苹果数量:" + basket.getAppleNumber() + "个");
Thread.sleep(300);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
}
}
class Consumer implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
System.out.println("消费者开始消费苹果***");
basket.consume();
System.out.println("消费者消费苹果完毕***");
System.out.println("篮子中的苹果数量:" + basket.getAppleNumber() + "个");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
}
}
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Producer producer = new Producer();
Consumer consumer = new Consumer();
service.submit(producer);
service.submit(consumer);
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
service.shutdownNow();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueueTest.testBasket();
}
}Many java training videos, all on the PHP Chinese website, welcome to learn online!
The above is the detailed content of What is java queue. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1655
1655
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1306
1306
 25
25
 1252
1252
 29
29
 1226
1226
 24
24
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.




