 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Use the TUS protocol in PHP to implement breakpoint and resume downloading of large files
Use the TUS protocol in PHP to implement breakpoint and resume downloading of large files
Use the TUS protocol in PHP to implement breakpoint and resume downloading of large files
Have you ever struggled with uploading large files? If the file upload process is interrupted for some reason, can I continue uploading from the interrupted point without re-uploading the entire file? If you have such confusion, then please continue reading below.
In modern website applications, uploading files is very common. In any language, by using some tools, the file upload function can be realized. However, it is still a bit troublesome to deal with the need to upload large files.
Suppose you are uploading a large file at this time. About an hour has passed and the progress is 90%. If the Internet is suddenly disconnected or the browser crashes, the uploaded program will exit and you will have to start all over again. Really uncomfortable, right? What’s even more depressing is that if your Internet speed is very slow, then no matter how many times you try again, you will never be able to upload successfully.
In PHP, we can try to use the breakpoint resume function of the tus protocol to solve this problem.
What is tus?
Tus is an HTTP-based open protocol for file breakpoint resume transfer. Resume uploading means that whether it is interrupted by the user or unexpectedly due to network or other reasons, the upload can be resumed from where it was interrupted without starting over.
The Tus protocol was adopted by Vimeo in May 2017.
Why use tus?
Quoting Vimeo’s blog:
The reason why we decided to use tus is because it can be used in a concise and open form. Standardize the file upload process. This standardization helps API developers focus more on the logic of the application itself rather than the file upload process.
Another benefit of uploading in this way is that you can start uploading files on your laptop, and then move to your mobile phone or other device to continue uploading the same file, which can greatly improve the user experience.
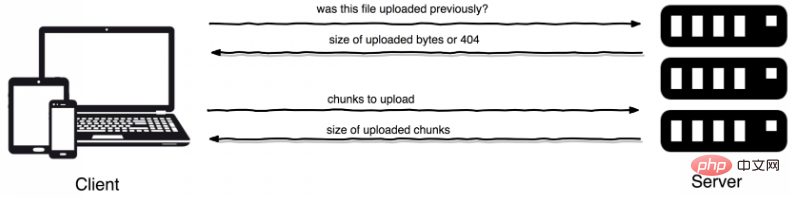
Picture: Tus rough workflow
Start
The first step is to load dependencies.
$ composer require ankitpokhrel/tus-php
tus-php is a pure PHP framework used for tus breakpoint resume protocol v1.0.0, which perfectly realizes the interaction between the server and the client.
Update: Now v3 of Vimeo official PHP library uses TusPHP.
Create a server that handles requests
You can create a server as follows.
// server.php $server = new \TusPhp\Tus\Server('redis'); $response = $server->serve(); $response->send(); exit(0); // 退出当前 PHP 进程
You need to configure your server so that it can Respond to a specific terminal. If you use Nginx, you can configure it as follows:
# nginx.conf
location /files {
try_files $uri $uri/ /path/to/server.php?$query_string;
}Assume that the URL of our server is http://server.tus.local. Therefore, based on our Nginx configuration above, we can pass http:// server.tus.local/files. To access our tus terminal.
RESTful-style endpoint configuration:
# 获取有关服务器目前配置的信息\
OPTIONS /files
# 检查上传的文件是否合法\
HEAD /files/{upload-key}
# 创建\
POST /files
# 修改\
PATCH /files/{upload-key}
# 删除\
DELETE /files/{upload-key}ViewProtocol details Get more information about routing Information.
If you are using a framework similar to Laravel, then you do not need to define these in the configuration file. You can directly define routes to access the basic endpoints of tus. We will introduce the relevant details in another tutorial.
Use tus-php client to handle uploads
With the server in place, clients can upload files in chunks. Let's start by creating a simple HTML form to get input from the user.
<form action="upload.php" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="tus_file" id="tus-file" />
<input type="submit" value="Upload" />
</form>After submitting the form, we need to follow a few steps to process the upload.
Create a tus-php client object
// Tus client $client = new \TusPhp\Tus\Client('http://server.tus.local');
The first parameter in the above code is your tus server address.
2. Initialize the client using file metadata
In order to ensure the uniqueness of uploaded files, we need to uniquely identify each uploaded file. In this way, when the file is interrupted and subsequently transmitted, the server can clearly identify which fragments belong to the same file. This identification code can be specified by yourself or generated by the system.
// 设置标识码和文件元数据
$client->setKey($uploadKey)
->file($_FILES['tus_file']['tmp_name'], 'your file name');If you don’t want to specify the identification code, you can write it like this, and the system will automatically generate it:
$client->file($_FILES['tus_file']['tmp_name'], 'your file name'); $uploadKey = $client->getKey(); // Unique upload key
3. Upload the file in parts
// $chunkSize 是以字节为单位的,例如 5000000 等于 5 MB $bytesUploaded = $client->upload($chunkSize);
When When you want to resume the transmission of the next block, you can bring the same identification code parameter to resume the transmission.
// 在下一个请求中续传文件 $bytesUploaded = $client->setKey($uploadKey)->upload($chunkSize);
After all files are uploaded, by default, the server will use sha256 to verify the sum of the files to ensure that no files are lost.
Use tus-js-client client to handle file upload
The team of tus protocol also developed a modular file upload plug-in Uppy. This plugin can establish a connection between the official tus-js-client and tus-php servers. In other words, we can use php and js to upload files.
uppy.use(Tus, {
endpoint: 'https://server.tus.local/files/', // 你的 tus 服务器
resume: true,
autoRetry: true,
retryDelays: [0, 1000, 3000, 5000]
})更多细节可以查看 uppy 的文档, 这里 还有些例子可以供你参考。
分块上传
tus-php 服务器支持 concatenation 扩展,可以把多次上传的文件合为一个文件。因此,我们可以在客户端支持并行上传以及非连续的分块文件上传。
使用 tus-php 实现分块上传
tus-partial-upload.php
<?php // 文件唯一标识码 $uploadKey = uniqid(); $client->setKey($uploadKey)->file('/path/to/file', 'chunk_a.ext'); // 从第 1000 个字节开始上传 10000 字节 $bytesUploaded = $client->seek(1000)->upload(10000); $chunkAkey = $client->getKey(); // 从 第 0 个字节开始上传 10000 字节 $bytesUploaded = $client->setFileName('chunk_b.ext')->seek(0)->upload(1000); $chunkBkey = $client->getKey(); // 从第 11000 个字节 (10000 + 1000) 开始上传剩余的字节 $bytesUploaded = $client->setFileName('chunk_c.ext')->seek(11000)->upload(); $chunkCkey = $client->getKey(); // 把分块上传的文件组合起来 $client->setFileName('actual_file.ext')->concat($uploadKey, $chunkAkey, $chunkBkey, $chunkCkey);
分块上传的完整例子 在这里.
总结
由于 tus-php 项目 本身还出于初级阶段,后面可能还会有一些改动。在 example 文件夹里,有三个不同的例子供你参考。如果任何问题或者建议,欢迎留言交流。
The above is the detailed content of Use the TUS protocol in PHP to implement breakpoint and resume downloading of large files. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals. This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivati
 Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JWT is an open standard based on JSON, used to securely transmit information between parties, mainly for identity authentication and information exchange. 1. JWT consists of three parts: Header, Payload and Signature. 2. The working principle of JWT includes three steps: generating JWT, verifying JWT and parsing Payload. 3. When using JWT for authentication in PHP, JWT can be generated and verified, and user role and permission information can be included in advanced usage. 4. Common errors include signature verification failure, token expiration, and payload oversized. Debugging skills include using debugging tools and logging. 5. Performance optimization and best practices include using appropriate signature algorithms, setting validity periods reasonably,
 How do you parse and process HTML/XML in PHP?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
How do you parse and process HTML/XML in PHP?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to efficiently process XML documents using PHP. XML (eXtensible Markup Language) is a versatile text-based markup language designed for both human readability and machine parsing. It's commonly used for data storage an
 Explain late static binding in PHP (static::).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain late static binding in PHP (static::).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Static binding (static::) implements late static binding (LSB) in PHP, allowing calling classes to be referenced in static contexts rather than defining classes. 1) The parsing process is performed at runtime, 2) Look up the call class in the inheritance relationship, 3) It may bring performance overhead.
 PHP Program to Count Vowels in a String
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
PHP Program to Count Vowels in a String
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
A string is a sequence of characters, including letters, numbers, and symbols. This tutorial will learn how to calculate the number of vowels in a given string in PHP using different methods. The vowels in English are a, e, i, o, u, and they can be uppercase or lowercase. What is a vowel? Vowels are alphabetic characters that represent a specific pronunciation. There are five vowels in English, including uppercase and lowercase: a, e, i, o, u Example 1 Input: String = "Tutorialspoint" Output: 6 explain The vowels in the string "Tutorialspoint" are u, o, i, a, o, i. There are 6 yuan in total
 What are PHP magic methods (__construct, __destruct, __call, __get, __set, etc.) and provide use cases?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:03 AM
What are PHP magic methods (__construct, __destruct, __call, __get, __set, etc.) and provide use cases?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:03 AM
What are the magic methods of PHP? PHP's magic methods include: 1.\_\_construct, used to initialize objects; 2.\_\_destruct, used to clean up resources; 3.\_\_call, handle non-existent method calls; 4.\_\_get, implement dynamic attribute access; 5.\_\_set, implement dynamic attribute settings. These methods are automatically called in certain situations, improving code flexibility and efficiency.
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7





