How to set up friendly links in wordpress

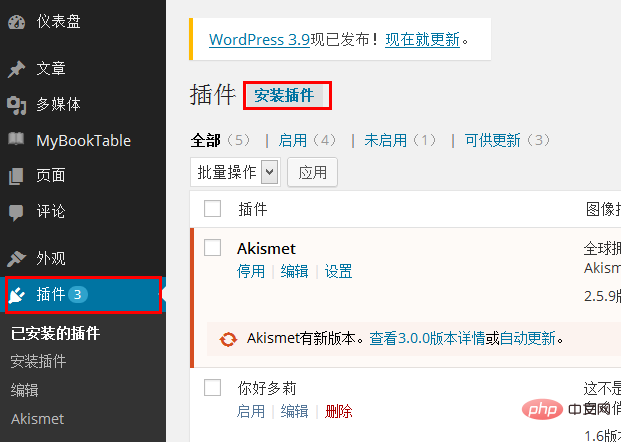
Enter the management background and click "Plug-in" on the left menu bar--"Install Plug-in".
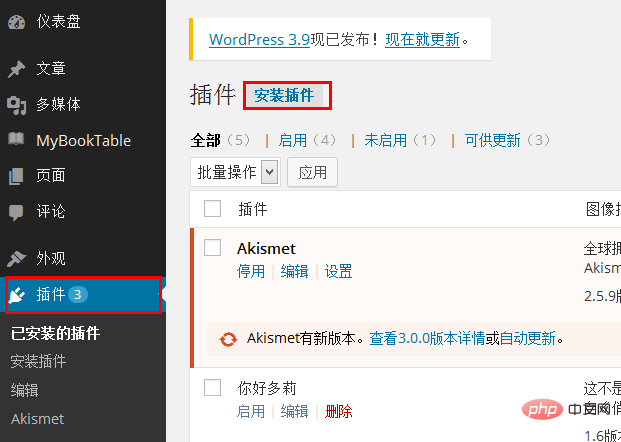
Enter "Link Manager" in the search box and click "Search".
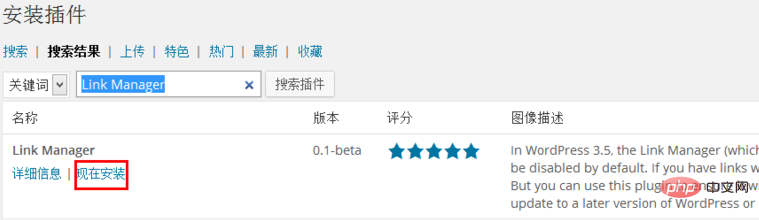
Find Link Manager in the search results, usually the first one, and click "Install Now" below.

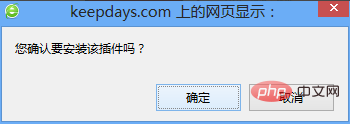
prompts whether to install the plug-in, click "OK".
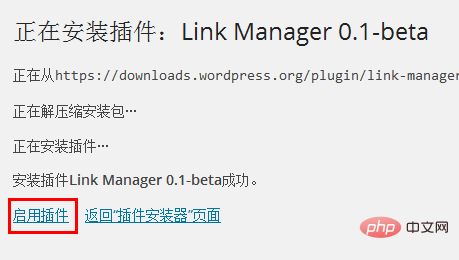
The system will automatically install the plug-in. After the installation is complete, we click "Enable Plug-in" below.
Related recommendations: "WordPress Tutorial"
At this time, the "Link" option will be displayed on the left side of the menu. We click "Add".
On the page to add a link, we enter the title and address of the link and other information, and then click the "Add Link" button on the right.
The link has been added. How to display it? We can use widgets to display them on the page. Click "Appearance"--"Widgets" on the left menu .

On the gadget page, drag and drop the "Link" tab on the left to the right.
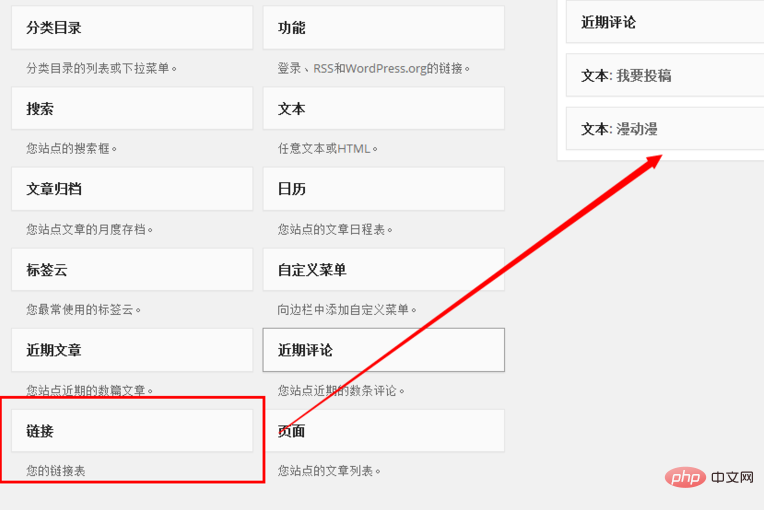
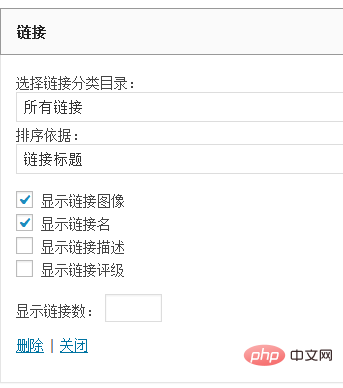
At this point, some displayed setting options will automatically pop up. After the settings are completed, we click "Save".
When we return to the blog homepage, we will see the link we added on the right side.
The above is the detailed content of How to set up friendly links in wordpress. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1657
1657
 14
14
 1415
1415
 52
52
 1309
1309
 25
25
 1257
1257
 29
29
 1231
1231
 24
24
 How to adjust the wordpress article list
Apr 20, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How to adjust the wordpress article list
Apr 20, 2025 am 10:48 AM
There are four ways to adjust the WordPress article list: use theme options, use plugins (such as Post Types Order, WP Post List, Boxy Stuff), use code (add settings in the functions.php file), or modify the WordPress database directly.
 How to build a website for wordpress host
Apr 20, 2025 am 11:12 AM
How to build a website for wordpress host
Apr 20, 2025 am 11:12 AM
To build a website using WordPress hosting, you need to: select a reliable hosting provider. Buy a domain name. Set up a WordPress hosting account. Select a topic. Add pages and articles. Install the plug-in. Customize your website. Publish your website.
 What are the plugins for wordpress blocking ip
Apr 20, 2025 am 08:27 AM
What are the plugins for wordpress blocking ip
Apr 20, 2025 am 08:27 AM
WordPress IP blocking plugin selection is crucial. The following types can be considered: based on .htaccess: efficient, but complex operation; database operation: flexible, but low efficiency; firewall: high security performance, but complex configuration; self-written: highest control, but requires more technical level.
 How to change the head image of the wordpress theme
Apr 20, 2025 am 10:00 AM
How to change the head image of the wordpress theme
Apr 20, 2025 am 10:00 AM
A step-by-step guide to replacing a header image of WordPress: Log in to the WordPress dashboard and navigate to Appearance >Theme. Select the topic you want to edit and click Customize. Open the Theme Options panel and look for the Site Header or Header Image options. Click the Select Image button and upload a new head image. Crop the image and click Save and Crop. Click the Save and Publish button to update the changes.
 How to cancel the editing date of wordpress
Apr 20, 2025 am 10:54 AM
How to cancel the editing date of wordpress
Apr 20, 2025 am 10:54 AM
WordPress editing dates can be canceled in three ways: 1. Install the Enable Post Date Disable plug-in; 2. Add code in the functions.php file; 3. Manually edit the post_modified column in the wp_posts table.
 How to write a header of a wordpress
Apr 20, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to write a header of a wordpress
Apr 20, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The steps to create a custom header in WordPress are as follows: Edit the theme file "header.php". Add your website name and description. Create a navigation menu. Add a search bar. Save changes and view your custom header.
 How to import the source code of wordpress
Apr 20, 2025 am 11:24 AM
How to import the source code of wordpress
Apr 20, 2025 am 11:24 AM
Importing WordPress source code requires the following steps: Create a sub-theme for theme modification. Import the source code and overwrite the files in the sub-topic. Activate the sub-theme to make it effective. Test the changes to make sure everything works.
 How to view the front-end of WordPress
Apr 20, 2025 am 10:30 AM
How to view the front-end of WordPress
Apr 20, 2025 am 10:30 AM
You can view the WordPress front-end by logging into the dashboard and switching to the View Sites tab; automate the viewing process with a headless browser; installing the WordPress plugin to preview the front-end within the dashboard; viewing the front-end via a local URL (if WordPress is set locally).




