How to view users in linux

When using a Linux system, you often need to check user information. In addition to the cat /etc/passwd file, there are actually many commands that can directly check system user information.
The following summarizes some common methods for viewing users under Linux systems:
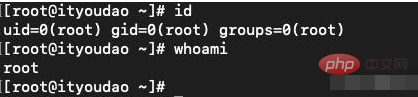
id command
Function: Print the user and group information of the specified user.
Syntax: id [option]...[username]
Description: If the username is omitted, print the user and group information of the current user.
whois command
Function: Find and display user information.
Syntax: whois [options] ... Object...
Description: The whois command will find and display user-related information for the specified account. Because it searches the WHOIS database, this The account name must be registered above to be found, and there is no case difference in the name. To use the whois command, you need to install the whois software package first.
whoami command
Function: Display the user name associated with the current effective user ID.
Syntax: whoami [options]...
Description: Same as id -un.
Parameters:
--help Display this help information and exit
--version Display version information and exit
Linux id and whoami commands
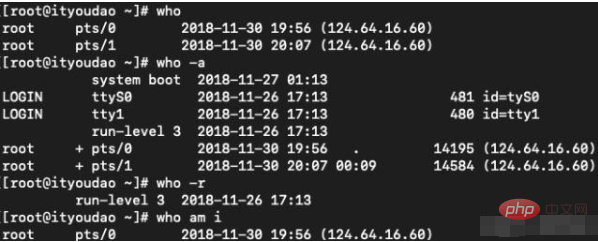
who command
Function: Display the currently logged in user information.
Syntax: who [option]... [File | Parameter 1 Parameter 2]
Description: Executing this command can know which users are currently logged in to the system. Executing the who command alone will Lists the login account, the terminal used, the time of login, and where you logged in from or which X monitor you are using.
Parameters:
-a, --all is equal to -b -d --login -p -r -t -T -u option combination
-b, --boot Last system startup time
-d, --dead Display dead processes
-H, --heading Output the title bar of the header
- l, --login displays the system login process
--lookup attempts to check the host name through DNS
-m only faces hosts and users that interact directly with standard input
-p, --process Display the active processes derived from the init process
-q, --count List the login names and user numbers of all logged-in users
-r, -- runlevel Display the current running level
-s, --short Display only the name, line and time (default)
-T, -w, --mesg Use, - or ? to mark the user Message status
-u, --users List logged in users
--message equals-T
--writable equals-T
--help Display this help information and exit
--version Display version information and exit
Linux who command
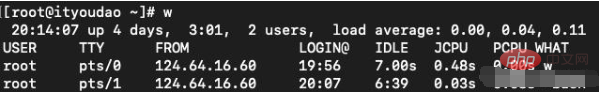
wCommand
Function: Display the information of the users currently logged in to the system.
Syntax: w [-fhlsuV][user name]
Description: Execute this command to know who are the users currently logged into the system and the programs they are executing. Executing the w command alone will display all users. You can also specify a user name to display only the relevant information of a certain user.
Parameters:
-f Turn on or off the display of where the user logs in to the system.
-h Does not display the title information column of each field.
-l Use detailed format list, this is the default value.
-s Use a concise format list and do not display the user login time, terminal stage operations and CPU time consumed by the program.
-u Ignore the name of the executing program and information about the CPU time consumed by the program.
-V Display version information.
Linux w command
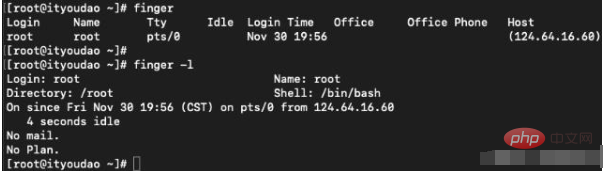
finger command
The function of the finger command is to query user information, usually Information such as the user name, home directory, dead time, login time, login shell, etc. of a user in the system will be displayed. If you want to query the user information on the remote machine, you need to follow the user name with "@hostname" in the format of [username@hostname]. However, the network host to be queried needs to run the finger daemon.
The general format of this command is:
finger [option] [user] [user@host]
The meaning of each option in the command is as follows:
-s Displays the user's registered name, actual name, terminal name, writing status, dead time, login time and other information.
-l In addition to the information displayed with the -s option, it also displays information such as the user's home directory, login shell, email status, and the contents of the .plan, .project, and .forward files in the user's home directory.
-p is the same as the -l option except that .plan files and .project files are not displayed.
Linux finger command
vlock command
Function: Lock the virtual terminal.
Syntax: vlock [-achv]
Description: Executing the vlock command can lock the virtual terminal to prevent others from using it.
Parameters:
-a or --all Lock all terminal stage jobs. If you use this parameter in a full-screen terminal, you will use the keyboard to switch the terminal function. Close together.
-c or --current Lock the current terminal phase job, this is the default value.
-h or --help Online help.
-v or --version Display version information.
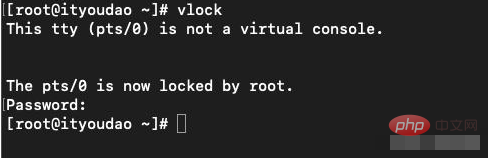
vlock command under Linux
These are common methods for viewing users under Linux systems. You no longer need to directly search for the /etc/passwd file in the future.
Related recommendations: "Linux Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to view users in linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
Causes and solutions for the VS Code terminal commands not available: The necessary tools are not installed (Windows: WSL; macOS: Xcode command line tools) Path configuration is wrong (add executable files to PATH environment variables) Permission issues (run VS Code as administrator) Firewall or proxy restrictions (check settings, unrestrictions) Terminal settings are incorrect (enable use of external terminals) VS Code installation is corrupt (reinstall or update) Terminal configuration is incompatible (try different terminal types or commands) Specific environment variables are missing (set necessary environment variables)






