Detailed introduction to Redis compression list (example explanation)
This article brings you a detailed introduction (example explanation) about Redis compression list. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you. help.
This article mainly introduces one of Redis's methods of data storage, compressed list.
This article will introduce
1 and compressed list (ziplist) usage scenarios
2. How to achieve the effect of saving memory?
3. Storage format of compressed list
4. Chain update problem
5 .conf file configuration.
In practice, the main operation is to configure the conf configuration file. There is no exact value, but more of an empirical value. Some projects will directly use the original default values. This article will be helpful to better understand the underlying storage logic of a database. To study and store energy, you need both broad knowledge and profound knowledge. I hope this article will be useful to friends who are also learning Redis. (Recommended tutorial: Redis tutorial)
1. Usage scenarios of compressed list (ziplist):
Redis is used to optimize data storage and save memory , the optimization scheme of using compressed lists is implemented at the bottom of lists, dictionaries (hash keys) and sorted sets.
For example, if the string stored in a hash key is relatively short, Redis will store it in a compressed list format, that is, convert it to a byte array for storage. If the integer value stored internally in a hash key is relatively small, it will also be stored as a node in the compressed list. In the same way, the storage of small data by list keys is similar to the operation of hash keys.
In this way, the compressed list is not a storage data structure in Redis that developers can call directly, but an underlying effort in Redis to optimize data storage. It is still important to understand this.
2. How to achieve the effect of saving memory?
Compressed list is a serialized data structure. The function of this data structure is to store a series of data and its encoding information in a continuous memory area. This memory is physically continuous. . But it is logically divided into components, i.e. nodes. The purpose is to reduce unnecessary memory overhead as much as possible under certain controllable time complexity conditions, so as to achieve the effect of saving memory. You need to understand how to achieve the effect of saving memory, and you also need to understand the storage format of the compressed list.
3. Storage format of compressed list:
Compressed list (ziplist) is Redis list key, hash key and ordered set key One of the underlying implementations, its essence is a serialized data storage structure. Different from ordinary situations, Redis uses double-ended linked lists to represent lists, hash tables to represent hash keys, and hash tables and jump lists to represent ordered sets. When a list or hash dictionary/ordered set contains only a small amount of content, and each list item or hash item/ordered set item is a small integer, or a relatively short string. Then Redis will use the compressed list for the underlying implementation.
The compressed list consists of a series of continuous memory blocks specially encoded by Redis. Each memory block is called a node (entry), and a compressed list can contain many nodes. The data format stored in each node can be a byte array (Chinese strings, etc. will be converted into byte arrays) or integer values.
The length of the byte array can be one of the following:
1. The length is less than or equal to 63 bytes (2 to the 6th power)
2. The length is less than Equal to 16383 bytes (2 to the 14th power)
3. The length is less than or equal to 4294967295 bytes (2 to the 32nd power)
The integer value may be one of the following six types :
1. 4-bit long unsigned integer between 0-12
2. 1-byte long signed integer
3. 3 words Section length signed integer
4. int16_t type integer
5. int32_type integer
6. int64_t type integer
Normal The difference between the storage format and the compressed list storage format:
The list storage structure is typically a double-ended linked list. Each value is represented by a node, and each node will point to the previous Pointers to one node and the following node, and a pointer to the string value the node contains. The string value is stored in three parts. The first part stores the string length, the second part stores the remaining available bytes in the string value, and the third part stores the string data itself. Therefore, a node often needs to store 3 pointers, 2 integers recording string information, the string itself and an extra byte. The overall additional overhead is significant (21 bytes).
Format of compressed list nodes:
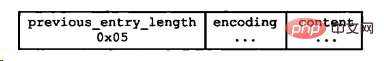
Each node consists of three parts: previous_entry_length, encoding, and content. When traversing the compression list, it is traversed from back to front.
1. previous_entry_length records the length of the previous node. Just subtract this value from the current pointer to reach the starting address of the previous node.
2. encoding records the type and length of data stored in the node content attribute

3. content records the value of a node
Obviously compressing the list saves a lot of storage space. But it will also cause the following problems.
4. Issues with chain updates:
Generally speaking, if the overall length of the previous node is less than 254 bytes, the previous_entry_length attribute only needs 1 byte of space to store this length value. When the previous node is larger than 254 bytes, the previous_entry_length attribute uses 5 bytes of space to record the length value.
When a new node is inserted before a node with a length of about 254 bytes, previous_entry_length needs to be added to record the offset of this node to the new node. At this time, the length of this node must be greater than 254 bytes. Therefore, the node after this node cannot only use one byte of previous_entry_length to record the information of this node, but requires 5 bytes to record. If the length of multiple consecutive nodes is about 254 bytes, the insertion and deletion of nodes occurs before/after one of the nodes (the reasoning of deletion is opposite to that of insertion, and the original record of the previous node with 5 bytes may become 1 byte), may trigger chain updates. Obviously, this is very detrimental to the operating efficiency of the system. However, this situation still rarely occurs in practical applications.
The double-ended linked list will be much "easier" in updating, adding and deleting nodes. Because the information stored in each node is relatively independent.
Practical significance:
To estimate how many bytes of storage space a node occupies, appropriately adjust the storage format of the field without making the stored field value occupy less than 254 words of storage space. section (minus the encoding attribute and previous_entry_length attribute) or so. Related commands to view the length of string and hash key values in
Redis:
1. Query the length of the value corresponding to the string key
Command:
Strlen
For example:
127.0.0.1:6379> strlen m_name
(integer) 8
2. Query the length of a certain field in the hash key
Command:
Hstrlen
For example:
127.0.0.1:6379> hstrlen good_list good_list1
(integer) 226
5. Conf file configuration:
By modifying the configuration file , you can control whether to use a compressed list to store the maximum number of elements and the size of the maximum element of the relevant key
Configuration in the Conf file:
1.
[] -max-ziplist-entries: Indicates that the maximum number of elements of the key, that is, the number of nodes under the specified value in a key will be stored in a compressed list
[] -max-ziplist-value: Indicates the maximum size of each node in the compressed list in bytes
In actual use, a certain element of a list key/hash key often stores a relatively large The amount of information will be greater than 64 bytes, so it is likely to be greater than 64 during configuration. At the same time, taking into account the actual storage capacity of data and the size of previous_entry_length mentioned above, [] -max-ziplist-value should be reasonably adjusted Configuration.
Configuration file content:
############## ADVANCED CONFIG ########################## 哈希键 # Hashes are encoded using a memory efficient data structure when they have a # small number of entries, and the biggest entry does not exceed a given # threshold. These thresholds can be configured using the following directives. hash-max-ziplist-entries 512 hash-max-ziplist-value 64 有序集合键 # Similarly to hashes and lists, sorted sets are also specially encoded in # order to save a lot of space. This encoding is only used when the length and # elements of a sorted set are below the following limits: zset-max-ziplist-entries 128 zset-max-ziplist-value 64 列表键,比较特殊,直接使用制定大小kb字节数表示(有些conf文件的列表键与hash键的表达式没太大区别) # Lists are also encoded in a special way to save a lot of space. # The number of entries allowed per internal list node can be specified # as a fixed maximum size or a maximum number of elements. # For a fixed maximum size, use -5 through -1, meaning: # -5: max size: 64 Kb <-- not recommended for normal workloads # -4: max size: 32 Kb <-- not recommended # -3: max size: 16 Kb <-- probably not recommended # -2: max size: 8 Kb <-- good # -1: max size: 4 Kb <-- good # Positive numbers mean store up to _exactly_ that number of elements # per list node. # The highest performing option is usually -2 (8 Kb size) or -1 (4 Kb size), # but if your use case is unique, adjust the settings as necessary. list-max-ziplist-size -2
Case:
Use the default configuration before modifying the configuration:
hash-max-ziplist-entries 512
hash-max-ziplist-value 64
127.0.0.1:6379> hstrlen good_list good_list1
(integer) 226
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding good_list
"hashtable"
Modify configuration:
hash-max-ziplist-entries 512
hash-max-ziplist-value 254
Note: You need to restart the server after modifying the configuration
127.0.0.1:6379> hstrlen good_list good_list1
(integer) 226
127.0.0.1 :6379> object encoding good_list
"ziplist"
You can see that the storage method has been changed to ziplist
More official pressure Testing and guidance suggestions:
When the number of elements in a compressed list rises to several thousand (actual use may be far less than this value), the performance of the compressed list may decrease because Redis operates this When using this structure, there will be a certain amount of pressure on encoding and decoding.
The length of the compressed list is limited to 500-2000, and the size of each element is limited to 128 bytes or less. The performance of the compressed list will be within a reasonable range.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to Redis compression list (example explanation). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.






