Detailed introduction to SQLServer dynamic masking (code example)
This article brings you a detailed introduction (code example) about SQLServer dynamic masking. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you. helped.
Dynamic Data Masking (DDM) is a new feature introduced in SQL Server 2016. The purpose is to restrict people without permission from seeing some private information. Admin users can decide which fields need to be masked, so how can they be masked without changing the application code? It is also necessary to ensure that no matter how the data is accessed, it is consistent.
This is a feature introduced for the first time in Azure SQL Database. It is being tested by users on the cloud and has been migrated to the on-premises product. I think many other new features will follow this approach (cloud-local).
It should be noted that like my previous row-level data security, these are data security-related contents (recommended course: MySQL Tutorial)
Column Data Masking
First create a table with a masked version of some data. I'm going to add a mask to one of the fields starting in the table definition. Note that the way to do this is to use the "mask with()" format after the data type, but before the NULL and default options, within parentheses include FUNCTION = ", which specifies our function. Inside the quotes, we Specify the mask. The CREATE TABLE statement is as follows
CREATE TABLE MyTable ( MySSN VARCHAR (10) MASKED WITH (FUNCTION = 'default()') DEFAULT ('0000000000' ) , MyName VARCHAR (200) DEFAULT ( ' ') , MyEmail VARCHAR (250) DEFAULT ( '') , MyInt int ) GO INSERT dbo. MyTable ( MySSN , MyName, MyEmail , MyInt) VALUES ( '1234567890', 'Steve Jones', 'SomeSteve@SomeDomain.com', 10 )
If the creator queries this table, it will see a normal table. I get all the data when it is inserted. This is because I am a user who has Users with dbo privileges. Likewise those with dbo privileges (db_owner or sysadmin role) will not see the masked data. Now create a normal user without high privileges. Of course, I need to grant normal SQL Server privileges to view The data in the table.
CREATE USER mytest WITHOUT LOGIN GRANT SELECT ON mytable TO mytest
Now we can query the table with this user and see what the difference is.

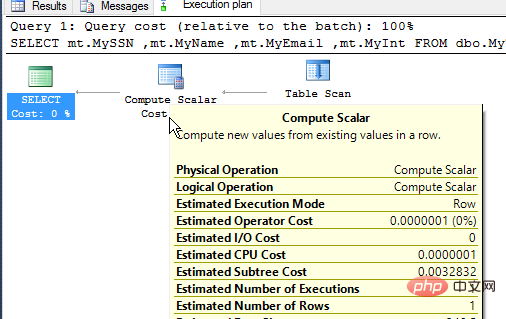
We can see the first column Contains masked data. Only is blocked.
I can see this happening in the last part of the execution plan. I need to give the user permission to view the plan, but when I do that I see the user's plan, using the same query.
# I can define other types of masks on the table. There is a custom mask format that allows control of what is displayed for an email address mask, and a random number mask. We will discuss these issues in detail in another article.
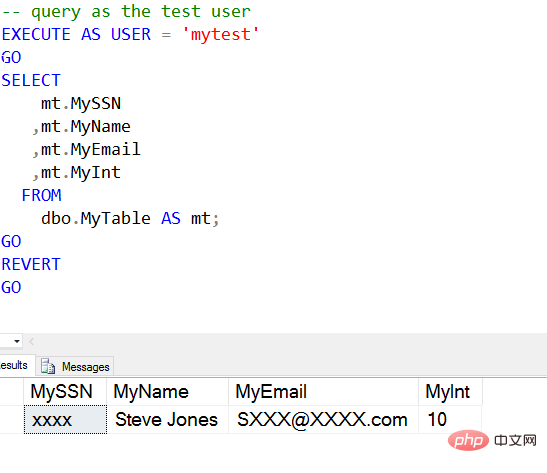
Now you can add a mask to another column, such as the MyEmail column, you can use the mail mask The format, the specific code is as follows:
ALTER TABLE dbo.MyTable ALTER COLUMN MyEmail VARCHAR(250) MASKED WITH (FUNCTION='email()') GO
Then the query result is as follows:
You can also mask multiple sum columns
CREATE TABLE MySecondTable ( MyEmail VARCHAR( 250) MASKED WITH (FUNCTION= 'email()') , MySSN VARCHAR (10) MASKED WITH (FUNCTION ='default()') , MyID INT MASKED WITH (FUNCTION ='random(1,4)') )GOINSERT MySecondTable VALUES ( 'myname@mydomain.com', '1234567890', 100 ) , ( 'abrother@mycorp.com' , '0123456789' , 555) , ( 'somesister@somecompany.org' , '9876543210' , 999)
The query results are as follows:
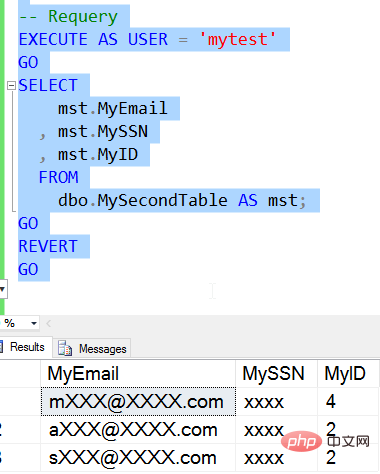
As we can see, I get different masks from different rows, and each mask is applied to a specific row Data.
Allow users to see masked real data
There is a new DDM permission in SQL Server 2016. This is the UNMASK permission and it is like any other permission Granted. Let's see how this works. I will create a new user with the same permissions as the existing user. Then I will query the table.
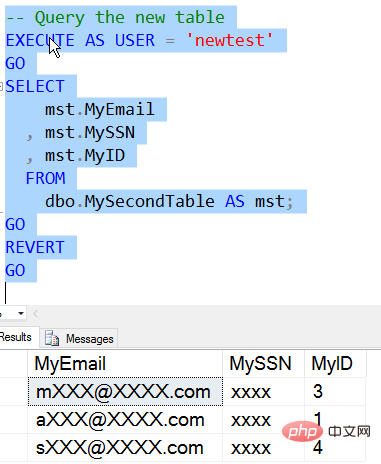
Similar results to before, then we open the mask for authorization.
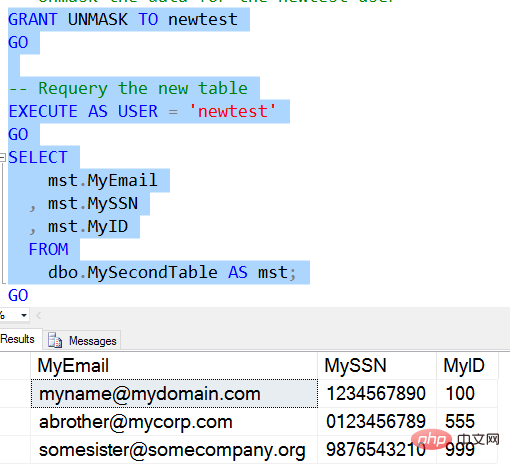
Now we can see that the data is displayed in the same way as a privileged user. For For NewTester users, all data is "unmasked".
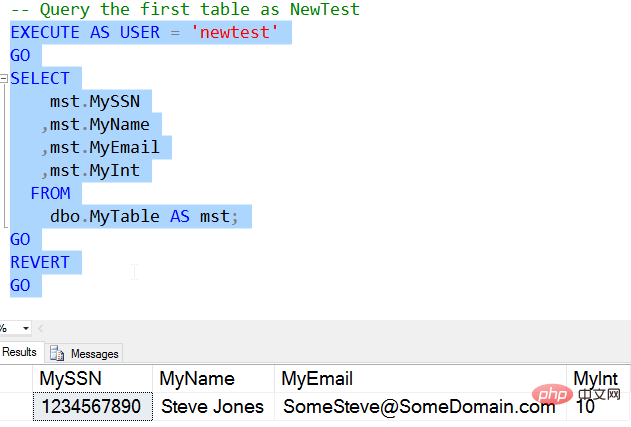
However, there is a downside to this. UNMASK permissions are granted to the user database-wide. There is no granularity by table or column. If a user has UNMASK, they can view all data in tables stored in the database with SELECT permission. We can see this by querying the first table using Newtest.
Remove the mask
The code is as follows:
ALTER TABLE dbo.MySecondTable ALTER COLUMN MySSN DROP MASKED;
Once I do this, the user will see the real data directly.
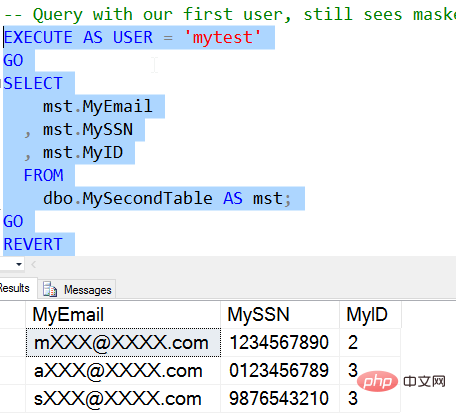
The data in the MySSN column is not masked, but the data in MyEmail and MyID are still masked
Summary
Dynamic Data Masking is a great new feature designed to make it easier to protect data from non-privileged users. This can be implemented in the database without changing any application code, allowing you to mask sensitive data from application users with minimal cost and effort. I would also like to remind you that this is not a true security feature. The data stored in disks and tables is not changed in any way. This is still plain text data, and if users are able to query the system, they can still potentially query your data and discover its value.
In any case, this feature is undoubtedly helpful, especially for systems that require data decryption. Of course, the functions have also made great progress since 17. I will continue to introduce them when I have the opportunity.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to SQLServer dynamic masking (code example). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to import mdf file into sqlserver
Apr 08, 2024 am 11:41 AM
How to import mdf file into sqlserver
Apr 08, 2024 am 11:41 AM
The import steps are as follows: Copy the MDF file to SQL Server's data directory (usually C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL\DATA). In SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), open the database and select Attach. Click the Add button and select the MDF file. Confirm the database name and click the OK button.
 How to solve the problem that the object named already exists in the sqlserver database
Apr 05, 2024 pm 09:42 PM
How to solve the problem that the object named already exists in the sqlserver database
Apr 05, 2024 pm 09:42 PM
For objects with the same name that already exist in the SQL Server database, the following steps need to be taken: Confirm the object type (table, view, stored procedure). IF NOT EXISTS can be used to skip creation if the object is empty. If the object has data, use a different name or modify the structure. Use DROP to delete existing objects (use caution, backup recommended). Check for schema changes to make sure there are no references to deleted or renamed objects.
 How to check sqlserver port number
Apr 05, 2024 pm 09:57 PM
How to check sqlserver port number
Apr 05, 2024 pm 09:57 PM
To view the SQL Server port number: Open SSMS and connect to the server. Find the server name in Object Explorer, right-click it and select Properties. In the Connection tab, view the TCP Port field.
 What to do if the sqlserver service cannot be started
Apr 05, 2024 pm 10:00 PM
What to do if the sqlserver service cannot be started
Apr 05, 2024 pm 10:00 PM
When the SQL Server service fails to start, here are some steps to resolve: Check the error log to determine the root cause. Make sure the service account has permission to start the service. Check whether dependency services are running. Disable antivirus software. Repair SQL Server installation. If the repair does not work, reinstall SQL Server.
 How to recover accidentally deleted database in sqlserver
Apr 05, 2024 pm 10:39 PM
How to recover accidentally deleted database in sqlserver
Apr 05, 2024 pm 10:39 PM
If you accidentally delete a SQL Server database, you can take the following steps to recover: stop database activity; back up log files; check database logs; recovery options: restore from backup; restore from transaction log; use DBCC CHECKDB; use third-party tools. Please back up your database regularly and enable transaction logging to prevent data loss.
 Where is the sqlserver database?
Apr 05, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Where is the sqlserver database?
Apr 05, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
SQL Server database files are usually stored in the following default location: Windows: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL\DATALinux: /var/opt/mssql/data The database file location can be customized by modifying the database file path setting.
 How to solve Java connection SqlServer error
May 01, 2023 am 09:22 AM
How to solve Java connection SqlServer error
May 01, 2023 am 09:22 AM
The problem was found that this time I was using the SqlServer database, which I had not used before, but the problem was not serious. After I connected the SqlServer according to the steps in the requirements document, I started the SpringBoot project and found an error, as follows: At first I thought it was a SqlServer connection. There was a problem, so I went to check the database and found that everything was normal. I first asked my colleagues if they had such a problem, and found that they did not, so I started my best part, facing Baidu. programming. The specific error message I started to solve was this, so I started Baidu error reporting: ERRORc.a.d.p.DruidDataSource$CreateCo
 How to delete sqlserver if the installation fails?
Apr 05, 2024 pm 11:27 PM
How to delete sqlserver if the installation fails?
Apr 05, 2024 pm 11:27 PM
If the SQL Server installation fails, you can clean it up by following these steps: Uninstall SQL Server Delete registry keys Delete files and folders Restart the computer






