How to use constructors in JavaScript
This article will share knowledge about constructors in JavaScript and has certain reference value. I hope it will be helpful to everyone's learning.
The constructor is actually a regular function, but the first letter should be capitalized when naming, and when calling the constructor, be careful to instantiate it with the new keyword. Such use means that this is created empty at the beginning, and Return the filled space at the end, which will be introduced in detail in the article.
Constructor generation
this creates null at the beginning and returns the filled null at the end
function Student(name age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
var student=new Student("张三","18");
var student1=new Student("李四","19");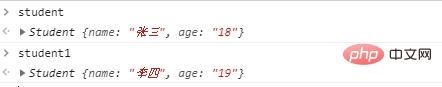
When Student() is executing the function, the following steps will be performed:
(1) Create and allocate a new empty object this.
(2) Function body execution. Usually it will modify this, adding new properties to it.
(3)this return value.
Similarly, if we want to create more students, we can call new Student(), each time the method is simple and easy to read.
This is the main purpose of the constructor: to implement reusable object creation code.
Constructor return
Generally, constructors do not have a return statement, and their task is to write the required things into this. and generate results automatically.
But if there is a return, it will become very simple. For example, if return is called using object, it will return not this, that is, the return object returns the object, and this returns all other situations
For example, return overrides this by returning an object
function Student() {
this.name = "张三";
return { name: "李四" }; //return 一个对象
}
console.log( new Student().name );Because an object is returned, the value in return is returned instead of the value in this

But if we return a null value, then what is returned is this value
<script>
function Student() {
this.name = "张三";
return; //return 一个空对象
}
console.log(new Student().name );
</script>
Methods in the constructor
The constructor can not only add properties but also methods, making the constructor more flexible in creating objects
<script>
function Student(name) {
this.name = name;
this.friend=function(){
console.log("this my friend:"+this.name);
};
}
var student=new Student("张三");
student.friend();
</script>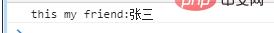
Summary: That’s it for this article That’s the entire content of the article. I hope it will be helpful for everyone to learn constructors.
The above is the detailed content of How to use constructors in JavaScript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1653
1653
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1304
1304
 25
25
 1251
1251
 29
29
 1224
1224
 24
24
 Constructor in Python
Sep 02, 2023 pm 04:29 PM
Constructor in Python
Sep 02, 2023 pm 04:29 PM
In Python, every class has a constructor, which is a special method specified inside the class. The constructor/initializer will be called automatically when a new object is created for the class. When an object is initialized, the constructor assigns values to data members in the class. There is no need to define the constructor explicitly. But in order to create a constructor, we need to follow the following rules - For a class, it is allowed to have only one constructor. The constructor name must be __init__. Constructors must be defined using instance properties (just specify the self keyword as the first argument). It cannot return any value except None. Syntax classA():def__init__(self):pass Example Consider the following example and
 C++ syntax error: The same constructor signature appears multiple times, how to solve it?
Aug 22, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
C++ syntax error: The same constructor signature appears multiple times, how to solve it?
Aug 22, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
C++ is a powerful programming language, but it is inevitable to encounter various problems during use. Among them, the same constructor signature appearing multiple times is a common syntax error. This article explains the causes and solutions to this error. 1. Cause of the error In C++, the constructor is used to initialize the data members of the object when creating the object. However, if the same constructor signature is defined in the same class (that is, the parameter types and order are the same), the compiler cannot determine which constructor to call, causing a compilation error. For example,
 Does go language have constructors?
Jan 10, 2023 pm 02:15 PM
Does go language have constructors?
Jan 10, 2023 pm 02:15 PM
Go language does not have constructors. Go language, as a structured language, does not have constructors in object-oriented languages. However, similar effects of constructors in object-oriented languages can be achieved in some ways, that is, using the process of structure initialization to simulate the implementation of constructors.
 C++ syntax error: The constructor defined outside the class must be added with the class name as a qualifier. How should it be corrected?
Aug 22, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
C++ syntax error: The constructor defined outside the class must be added with the class name as a qualifier. How should it be corrected?
Aug 22, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
C++ is a widely used object-oriented programming language. When defining the constructor of a class in C++, if you want to place the definition of the constructor outside the class, you need to add the class name as a qualifier to the definition of the constructor. To specify which class this constructor belongs to. This is a basic rule of C++ syntax. If this rule is not followed when defining the constructor of a class, a compilation error will appear, prompting "Constructors defined outside the class must be qualified with the class name." So, if you encounter this kind of compilation error, you should
 C++ error: The constructor must be declared in the public area, how to deal with it?
Aug 21, 2023 pm 08:26 PM
C++ error: The constructor must be declared in the public area, how to deal with it?
Aug 21, 2023 pm 08:26 PM
In C++ programming, the constructor is an important function used to initialize the member variables of a class. It is automatically called when an object is created to ensure proper initialization of the object. The constructor must be declared in the class, but sometimes you will encounter the error message "The constructor must be declared in the public area." This error is usually caused by incorrect access modifiers on the constructor. In C++, class member variables and member functions have an access modifier, including public, private, and protected.
 What is a constructor? Detailed explanation of constructors in JavaScript
Aug 04, 2022 pm 03:22 PM
What is a constructor? Detailed explanation of constructors in JavaScript
Aug 04, 2022 pm 03:22 PM
As the basis of prototypes and prototype chains, first understanding the constructor and its execution process can better help us learn the knowledge of prototypes and prototype chains. This article will take you to learn more about the constructor in JavaScript and introduce how to use the constructor to create a js object. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 C++ syntax error: A constructor with only a single parameter must be declared explicit. How to solve it?
Aug 22, 2023 am 09:01 AM
C++ syntax error: A constructor with only a single parameter must be declared explicit. How to solve it?
Aug 22, 2023 am 09:01 AM
In C++ programming, you may encounter the following error message: Constructors with only a single parameter must be declared explicit. This error message may confuse beginners. Next, let's take a look at what explicit is in C++, the reasons why this error message appears, and how to solve this problem. The role of explicit in C++, if we define a constructor that only receives one parameter, then we need to use the keyword explici
 Let's talk about how to use the Object() function to create objects in JavaScript
Aug 04, 2022 pm 04:32 PM
Let's talk about how to use the Object() function to create objects in JavaScript
Aug 04, 2022 pm 04:32 PM
How to create objects using the Object() function? The following article will introduce you to the method of creating objects using the Object() constructor (with three other methods of creating objects). I hope it will be helpful to you!




