 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Introduction to flask_bootstrap decorating web pages in python (with code)
Introduction to flask_bootstrap decorating web pages in python (with code)
Introduction to flask_bootstrap decorating web pages in python (with code)
This article brings you an introduction to flask_bootstrap decorating web pages in python (with code). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
flask_bootstrap
Bootstrap is an open source framework developed by Twitter that provides user interface components for creating clean and attractive web pages that also Compatible with all modern web browsers.
Bootstrap is a client-side framework, so there is no direct involvement of the server. All the server needs to do is provide an HTML response that references Bootstrap Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and JavaScript files, and instantiate the required components in the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code. The ideal place to perform these operations is the template.
Flask-Bootstrap can integrate Bootstrap in the program
Installation:
pip install flask-bootstrap
Use:
from flask_bootstrap import Bootstrap ...... bootstrap = Bootstrap(app)
Inheritance of html files
After initializing Flask-Bootstrap, you can use a base template containing all Bootstrap files in the program. This template uses Jinja2's template inheritance mechanism to allow the program to extend a base template with a basic page structure, which includes elements used to introduce Bootstrap.
bootstrap’s base.html document:
{% block doc -%}
nbsp;html>
{%- block html %}
{%- block head %}
<title>{% block title %}{{title|default}}{% endblock title %}</title>
{%- block metas %}
<meta>
{%- endblock metas %}
{%- block styles %}
<!-- Bootstrap -->
<link>
{%- endblock styles %}
{%- endblock head %}
{% block body -%}
{% block navbar %}
{%- endblock navbar %}
{% block content -%}
{%- endblock content %}
{% block scripts %}
<script></script>
<script></script>
{%- endblock scripts %}
{%- endblock body %}
{%- endblock html %}
{% endblock doc -%}Inherit the base template of the Bootstrap file and write a base template suitable for your own project.
{#自己编写一个基类模板#}
{% extends 'bootstrap/base.html' %}
{% block styles %}
{{ super() }}
<link>
{% endblock %}
{% block navbar %}
<nav>
<p>
<!-- Brand and toggle get grouped for better mobile display -->
</p>
<p>
<button>
<span>Toggle navigation</span>
<span></span>
<span></span>
<span></span>
</button>
<a></a>
</p>
<!-- Collect the nav links, forms, and other content for toggling -->
<p>
</p>
<ul>
<li><a>首页<span>(current)</span></a></li>
<li><a>新闻</a></li>
<li><a>国际</a></li>
<li><a>国内</a></li>
<li><a>系统信息</a></li>
<li><a>登陆用户</a></li>
</ul>
<ul>
{% if 'user' in session %}
<li><a><span></span>
{{ session.user }}</a></li>
<li><a><span></span>
注销 </a></li>
{% else %}
<li><a><span></span>
登陆</a></li>
{% endif %}
<li><a><span></span>
注册</a></li>
</ul>
<!-- /.navbar-collapse -->
<!-- /.container-fluid -->
</nav>
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
{#定义属于自己的block#}
{% block newcontent %}
{% endblock %}
{% block footer %}
<p>
宇宙大魔王--ZAJ
</p>
{% endblock %}
{% endblock %}The extends directive in Jinja2 imports bootstrap/base.html from Flask-Bootstrap to achieve template inheritance. The base template in Flask-Bootstrap provides a web page framework that imports all CSS and JavaScript files in Bootstrap.
The above example redefines three blocks, which are the rewriting of styles, navbar and content of bootstrap/base.html. These blocks are provided by the base template and can be redefined in the derived template.
If the program needs to add new content to a block that already has content, it must use the super() function provided by Jinja2. For example, if you want to add a new CSS file to the derived template, you need to define it like this:
{% block styles %}
{{ super() }}
<link>
{% endblock %}Enable flask_bootstrap and flask_wtf to write a FLASK project
Requirements:
Realize the home page display, login page display, registration page display, and user exit (logout). And only users existing in the database can log in to the web page. Data interaction is mainly achieved through forms. Currently, for user registration, the database is not returned.
模板文件有templates/base.html , templates/index.html , templates/login.html , templates/register.html Py文件有 zaj_run.py , zaj_ forms.py , zaj_modles.py , zaj_config.py
Template file link
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Uov-i8b2fZMr9fOe32tcgg 提取码:jrbs
# zaj_run.py
from flask import Flask,render_template,session,redirect,url_for
from flask_bootstrap import Bootstrap
from zaj_forms import LoginForm,RegisterFrom
from zaj_models import isPasswdOk
import functools
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SECRET_KEY'] = 'SHEEN'
bootstrap = Bootstrap(app)
def is_login(f):
"""判断用户是否登陆的装饰器"""
@functools.wraps(f)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# 主函数代码里面, 如果登陆, session加入user, passwd两个key值;
# 主函数代码里面, 如果注销, session删除user, passwd两个key值;
# 如果没有登陆成功, 则跳转到登陆界面
if 'user' not in session:
return redirect('/login/')
# 如果用户是登陆状态, 则访问哪个路由, 就执行哪个路由对应的视图函数;
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/login/',methods=['GET','POST'])
def login():
# session.pop('user',None)
# session.pop('passwd',None)
form = LoginForm()
print(form.data) #{'user': 'root123', 'passwd': 'sheen123', 'submit': True,....}
if form.validate_on_submit():
user = form.data['user']
passwd = form.data['passwd']
if isPasswdOk(user,passwd):
session['user'] = user
session['passwd'] = passwd
return redirect(url_for('index'))
else:
return render_template('login.html',form=form,message='密码或用户名错误')
else:
return render_template('login.html',form=form)
@app.route('/register/',methods=['GET','POST'])
def register():
form = RegisterFrom()
# 如果是post方法并且表单验证通过的话, 返回True;
if form.validate_on_submit():
# 用户提交的表单信息
print(form.data)
return 'ok'
return render_template('register.html', form=form)
@app.route('/logout/')
def logout():
session.pop('user', None)
session.pop('passwd', None)
# 注销即删除用户的session信息, 注销成功, 跳转到首页;
return redirect(url_for('index'))
# return redirect('/')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run( port = 8900)
# 报错1:TypeError: __init__() takes from 1 to 2 positional arguments but 3 were given
# 解决:把输入表单LoginForm,RegisterFrom中的Required去掉
# 问题2:每次重新运行程序,都会显示root123用户已登陆,即session里面有数据
# 解决:添加判别session内容的函数is_login()。# zaj_models.py,存放数据库操作
import pymysql
from zaj_config import DB
# 1. 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host=DB.HOST,
user = DB.USER,
passwd = DB.PASSWD,
port = DB.PORT,
db = DB.DBNAME,
)
cur = conn.cursor()
def isUserExist(username):
"""判断用户名是否存在"""
sqli = "select * from user where name='%s'" %(username)
res = cur.execute(sqli)
# res返回的是sql语句查询结果的个数;
# 如果为0, 没有查到。
if res == 0:
return False
else:
return True
def isPasswdOk(username, passwd):
sqli = "select * from user where name='%s' and passwd='%s'" %(
username, passwd)
res = cur.execute(sqli)
if res == 0 :
return False
else:
return True
def addUser(username, passwd):
"""用户注册时, 添加信息到数据库中"""
sqli = "insert into user(name, passwd) values('%s', '%s')" %(
username, passwd)
try:
res = cur.execute(sqli)
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback()
return e
#
# cur.close()
# conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
addUser('root', 'root')
print(isUserExist('root'))
print(isPasswdOk('root', 'root'))# zaj_forms.py,存放表单操作
from flask_wtf import FlaskForm
# 每个Web表单都由一个继承自FlaskForm的类表示
from wtforms import StringField,PasswordField,SubmitField
# StringField类表示的是属性为type="text"的<input>元素。
# SubmitField类表示的是是属性为type="submit"的<input>元素
#WTForms内建的验证函数validators,而且是以数组形式,正对应了前面说的一个字段可以有一个或者多个验证函数
from wtforms.validators import Length, Required, EqualTo, Regexp,Email
class LoginForm(FlaskForm):
user = StringField(
label='用户名',
validators=[
Length(5,13)
]
)
passwd = PasswordField(
label='密码',
validators=[
Length(6,12),
]
)
submit = SubmitField(
label='登陆'
)
class RegisterFrom(FlaskForm):
user = StringField(
label='用户名/邮箱/手机号',
validators=[
Length(5,13)
]
)
passwd = PasswordField(
label='密码',
validators=[
Length(6,12),
]
)
repasswd = PasswordField(
label='确认密码',
validators=[
EqualTo('passwd',message='密码不一致!')
]
)
phone = StringField(
label='电话号码',
validators=[
Regexp(r'1\d{10}', message='手机号码格式错误')
]
)
email = StringField(
label='邮箱',
validators=[
Email(message='邮箱格式错误!')
]
)
submit = SubmitField(
label='注册'
)# zaj_config.py , 存放数据库类 class DB: HOST = 'localhost' USER= 'root' PASSWD = 'sheen' PORT = 3306 DBNAME = 'zaj_form'
Ensure that there is already a table user in the database zaj_form, user has elements name, passwd, add user name= 'python', passwd='1234567'
Home page:
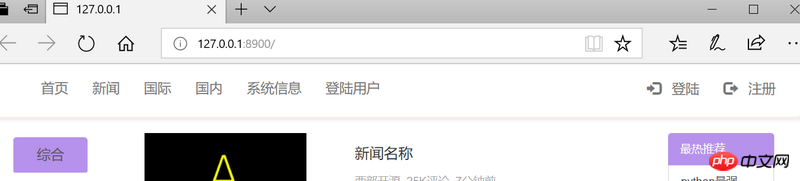
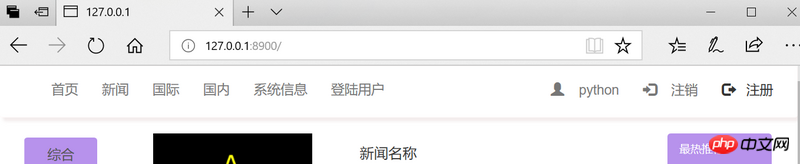
# After logging in, the home page will automatically jump to display the session cache.
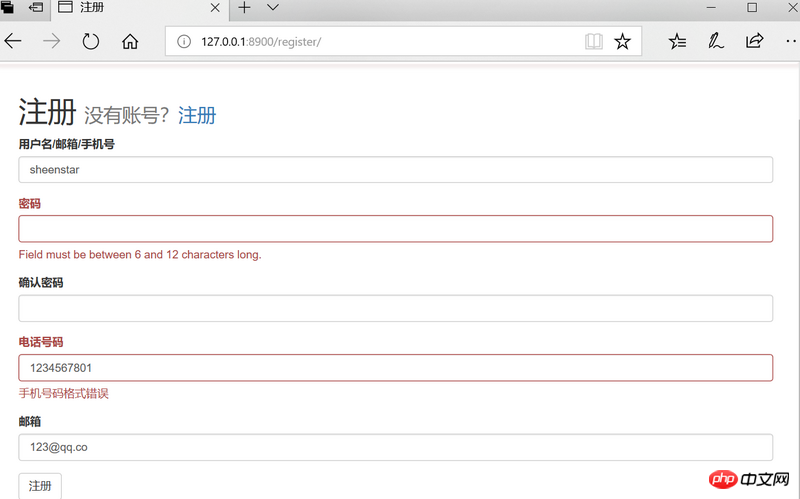
When an item in the registration form does not meet the rules defined by the program
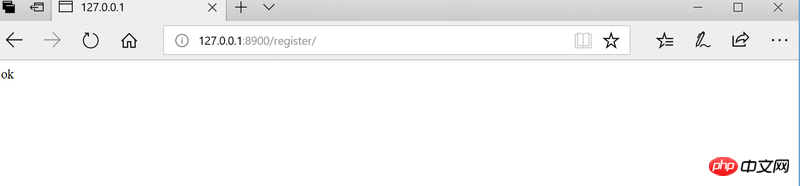
When the registration is successful, ' OK'
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to flask_bootstrap decorating web pages in python (with code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 Does Python projects need to be layered?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Does Python projects need to be layered?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Discussion on Hierarchical Structure in Python Projects In the process of learning Python, many beginners will come into contact with some open source projects, especially projects using the Django framework...
 How to safely store JavaScript objects containing functions and regular expressions to a database and restore?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
How to safely store JavaScript objects containing functions and regular expressions to a database and restore?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
Safely handle functions and regular expressions in JSON In front-end development, JavaScript is often required...
 HTML5 and H5: Understanding the Common Usage
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
HTML5 and H5: Understanding the Common Usage
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
There is no difference between HTML5 and H5, which is the abbreviation of HTML5. 1.HTML5 is the fifth version of HTML, which enhances the multimedia and interactive functions of web pages. 2.H5 is often used to refer to HTML5-based mobile web pages or applications, and is suitable for various mobile devices.
 How to correctly divide business logic and non-business logic in hierarchical architecture in back-end development?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to correctly divide business logic and non-business logic in hierarchical architecture in back-end development?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Discussing the hierarchical architecture problem in back-end development. In back-end development, common hierarchical architectures include controller, service and dao...
 Python vs. C : Which Language to Choose for Your Project?
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Python vs. C : Which Language to Choose for Your Project?
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Choosing Python or C depends on project requirements: 1) If you need rapid development, data processing and prototype design, choose Python; 2) If you need high performance, low latency and close hardware control, choose C.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Use Cases and Applications Compared
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Use Cases and Applications Compared
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python is more suitable for data science and automation, while JavaScript is more suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 1. Python performs well in data science and machine learning, using libraries such as NumPy and Pandas for data processing and modeling. 2. Python is concise and efficient in automation and scripting. 3. JavaScript is indispensable in front-end development and is used to build dynamic web pages and single-page applications. 4. JavaScript plays a role in back-end development through Node.js and supports full-stack development.
 Choosing Between Python and C : The Right Language for You
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Choosing Between Python and C : The Right Language for You
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is suitable for beginners and data science, and C is suitable for system programming and game development. 1. Python is simple and easy to use, suitable for data science and web development. 2.C provides high performance and control, suitable for game development and system programming. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.





