 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 What are the four functions of prototype chain, closure, inheritance, namespace, and enumeration types in js?
What are the four functions of prototype chain, closure, inheritance, namespace, and enumeration types in js?
What are the four functions of prototype chain, closure, inheritance, namespace, and enumeration types in js?
The content of this article is to introduce the prototype chain, the four functions of closure, inheritance, namespace, and enumeration types in js? . It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Prototype Chain
JavaScript objects are dynamic "packages" of properties (referring to their own properties). JavaScript objects have a chain that points to a prototype object. When trying to access a property of an object, it not only searches on the object, but also searches on the prototype of the object, and the prototype of the prototype of the object, and searches upwards until it finds a property with a matching name or reaches the prototype. end of chain.
Create a target to copy the prototype chain of origin without affecting the prototype chain of origin
var inherit = (function(){
var F = function (){};
return function (Target, Origin){
F.prototype = Origin.prototype;
Target.prototype = new F();
Target.prototype.constructor = Target; //目标函数的原型的构造函数定义为目标函数
Target.prototype.uber = Origin.prototype; //uber超类,指的是目标函数的最终原型为Orign的原型
}
}())Inheritance
Generally companies often execute function writing functions immediately and call an init() initialization function
The function of call in callname() in the code is to change this pointer , change the this pointer of name to this under the current function
Note that return is used to return the function
<script>
var init=(function(){
var name ='辣鸡';
function callname(){
console.log(name);
}
return function(){
callname();
}
}())
init();
</script>Enumeration:
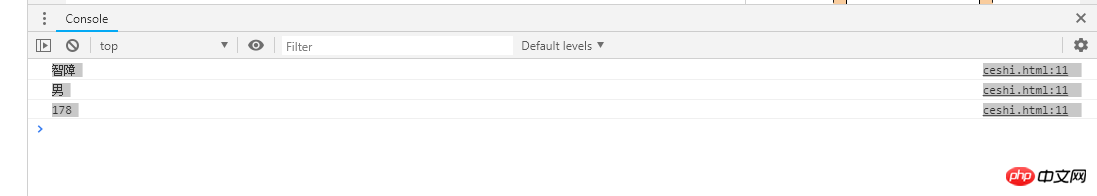
var org={
name:'智障',
sex:'男',
height:178
}
for ( var proto in org ){
console.log(org.proto)
}This will print undefined three times, because proto will be regarded as a property of the object. You need to change org.proto in the code to org[proto], otherwise it will default Understood as org['proto'].
The normal output is as follows. Three values are printed out. If you want to print the attributes, just console.log(proto)
Enumeration of objects, three methods:
for in -----> 1.instanceof 2.hasOwnProperty 3. in
1. Instance of
A instance of B
Determine whether the A object is constructed by the constructor of B
function Person(){}
var person = new Person();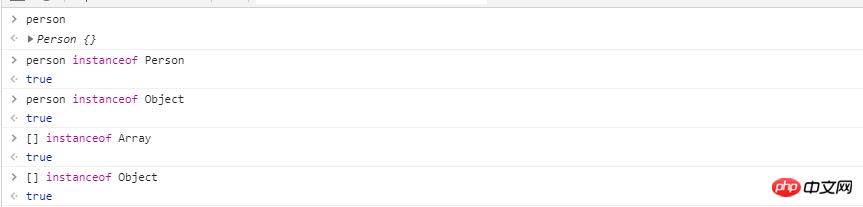
So the method of identifying arrays and objects------->1. instanceof 2. to String call 3.constructor
1) var obj={}

2) toString call
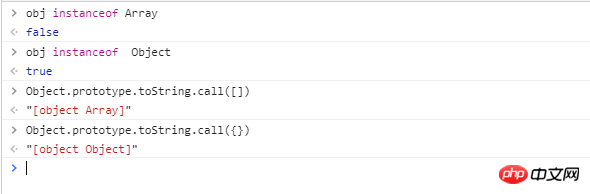
3) constructor
var obj = {}
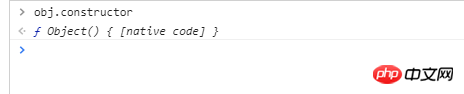
See if there is a prototype of B on the prototype chain of object A
2, hasOwnProperty, determine whether it belongs to your own method, you can exclude the prototype method __proto__
var org={
name:'智障',
sex:'男',
height:178,
__proto__:{
lastName:'zhang'
}
}for(var prop in org){ if(org.hasOwnProperty( prop )){
console.log(prop)
}
}var obj={};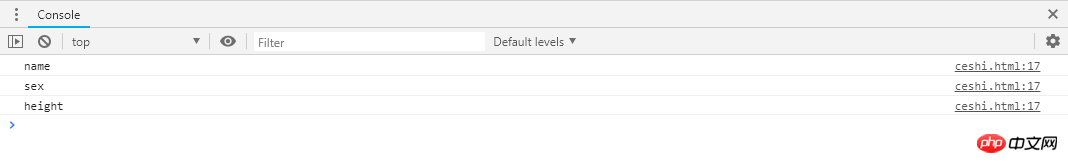
##3, in
in and hasOwnProperty case types, but methods in the prototype also exist in the method enumeration
Four functions of closure:
1. Implement public variables eg: accumulator2. Can be cached (storage structure)3. Implement encapsulation and attribute privatization 4. Modular development to prevent pollution of global variables (Holy Grail mode)/Use closures to define public functions and enable them to access private functions and variables . This method is also called module pattern (Holy Grail pattern)The above is the detailed content of What are the four functions of prototype chain, closure, inheritance, namespace, and enumeration types in js?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Detailed explanation of C++ function inheritance: How to use 'base class pointer' and 'derived class pointer' in inheritance?
May 01, 2024 pm 10:27 PM
Detailed explanation of C++ function inheritance: How to use 'base class pointer' and 'derived class pointer' in inheritance?
May 01, 2024 pm 10:27 PM
In function inheritance, use "base class pointer" and "derived class pointer" to understand the inheritance mechanism: when the base class pointer points to the derived class object, upward transformation is performed and only the base class members are accessed. When a derived class pointer points to a base class object, a downward cast is performed (unsafe) and must be used with caution.
 What is the meaning of closure in C++ lambda expression?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
What is the meaning of closure in C++ lambda expression?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
In C++, a closure is a lambda expression that can access external variables. To create a closure, capture the outer variable in the lambda expression. Closures provide advantages such as reusability, information hiding, and delayed evaluation. They are useful in real-world situations such as event handlers, where the closure can still access the outer variables even if they are destroyed.
 What are the advantages and disadvantages of closures in C++ functions?
Apr 25, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
What are the advantages and disadvantages of closures in C++ functions?
Apr 25, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
A closure is a nested function that can access variables in the scope of the outer function. Its advantages include data encapsulation, state retention, and flexibility. Disadvantages include memory consumption, performance impact, and debugging complexity. Additionally, closures can create anonymous functions and pass them to other functions as callbacks or arguments.
 What are the application scenarios of Java enumeration types in databases?
May 05, 2024 am 09:06 AM
What are the application scenarios of Java enumeration types in databases?
May 05, 2024 am 09:06 AM
Enumeration types in Java can be mapped to enumeration types in the database and are used to represent status, permissions or roles to maintain data integrity. Specific application scenarios include: indicating order status, such as creation, processing, delivery, etc. Indicates user permissions or roles, such as administrator, user, guest, etc. Used to limit user input data and ensure data consistency, such as the type of post is discussion, question or answer, etc.
 How to implement closure in C++ Lambda expression?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 05:50 PM
How to implement closure in C++ Lambda expression?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 05:50 PM
C++ Lambda expressions support closures, which save function scope variables and make them accessible to functions. The syntax is [capture-list](parameters)->return-type{function-body}. capture-list defines the variables to capture. You can use [=] to capture all local variables by value, [&] to capture all local variables by reference, or [variable1, variable2,...] to capture specific variables. Lambda expressions can only access captured variables but cannot modify the original value.
 Detailed explanation of C++ function inheritance: How to debug errors in inheritance?
May 02, 2024 am 09:54 AM
Detailed explanation of C++ function inheritance: How to debug errors in inheritance?
May 02, 2024 am 09:54 AM
Inheritance error debugging tips: Ensure correct inheritance relationships. Use the debugger to step through the code and examine variable values. Make sure to use the virtual modifier correctly. Examine the inheritance diamond problem caused by hidden inheritance. Check for unimplemented pure virtual functions in abstract classes.
 Detailed explanation of C++ function inheritance: How to understand the 'is-a' and 'has-a' relationship in inheritance?
May 02, 2024 am 08:18 AM
Detailed explanation of C++ function inheritance: How to understand the 'is-a' and 'has-a' relationship in inheritance?
May 02, 2024 am 08:18 AM
Detailed explanation of C++ function inheritance: Master the relationship between "is-a" and "has-a" What is function inheritance? Function inheritance is a technique in C++ that associates methods defined in a derived class with methods defined in a base class. It allows derived classes to access and override methods of the base class, thereby extending the functionality of the base class. "is-a" and "has-a" relationships In function inheritance, the "is-a" relationship means that the derived class is a subtype of the base class, that is, the derived class "inherits" the characteristics and behavior of the base class. The "has-a" relationship means that the derived class contains a reference or pointer to the base class object, that is, the derived class "owns" the base class object. SyntaxThe following is the syntax for how to implement function inheritance: classDerivedClass:pu
 The role of golang function closure in testing
Apr 24, 2024 am 08:54 AM
The role of golang function closure in testing
Apr 24, 2024 am 08:54 AM
Go language function closures play a vital role in unit testing: Capturing values: Closures can access variables in the outer scope, allowing test parameters to be captured and reused in nested functions. Simplify test code: By capturing values, closures simplify test code by eliminating the need to repeatedly set parameters for each loop. Improve readability: Use closures to organize test logic, making test code clearer and easier to read.





