 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 CSS Tutorial
CSS Tutorial
 Analysis of the difference between display:none and visibility:hidden in css
Analysis of the difference between display:none and visibility:hidden in css
Analysis of the difference between display:none and visibility:hidden in css
The content of this article is about the analysis of the difference between display:none and visibility:hidden in CSS. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Do you still remember being asked during the interview, "Please tell me the difference between display:none and visibility:hidden"? Will the interviewer smile after answering that display:none does not occupy the original position and visibility:hidden retains the original position? It’s actually more than that! In this article, we will delve into their grievances and resentments together, so that we can give better answers in the next interview!
In-depth display:none
We all know that when an element is set to display:none, the element will not be displayed on the interface, and the element will not occupy the layout space. But we can still manipulate the element through JavaScript. But why is this so?
This involves the rendering principle of the browser: the browser will parse HTML tags to generate DOM
Tree, parses CSS to generate CSSOM, then synthesizes DOM Tree and CSSOM to generate Render Tree, elements in Render
Tree corresponds to 0 or more boxes, and then the browser layouts and renders the interface with the information of the box model. Elements set to display:none do not generate corresponding box models in the Render Tree, so subsequent layout and rendering work naturally has nothing to do with it. As for DOM operations, it is still possible.
But in addition to the above knowledge points, there are also the following 8 points that we need to pay attention to
1. Elements with native default display:none
In fact, many native browser elements have display:none Elements, such as link, script, style, dialog, input [type=hidden], etc.
2. The hidden Boolean attribute is added to HTML5, allowing developers to customize the hiddenness of elements
/* 兼容原生不支持hidden属性的浏览器 */
[hidden]{
display: none;
}
<span>Hide and Seek: You can't see me!</span>3. The parent element is display:none, and the descendant elements cannot escape
.hidden{
display: none;
}
.visible{
display: block;
}
*** START ***
<div>
I'm parent!
<div> I'm son! </div>
</div>
*** END ***The browser directly displays it as
*** START *** *** END ***
4. Unable to obtain focus
There is no box originally. Where is the focus? ^_^ Even through the tab key, there is no way
<!-- 真心不会获得焦点 --> <input> <div>hidden</div>
5. Unable to respond to any event, whether it is capturing, hitting the target, or bubbling stage
Due to display:none The element will not be rendered on the interface at all, it does not even occupy 1 pixel, so naturally it cannot be hit by mouse click, and the element cannot obtain focus, so it cannot be the target of keyboard events; and the display of the parent element When it is none, the display of the child element must be none, so the element has no chance to be on the path of the event capture or bubbling stage, so the element with display:none cannot respond to the event.
6. Do not delay form form submission data
Although we cannot see the display:none element, the value of the hidden input element will still be submitted when the form is submitted.
7. The counter in CSS will ignore the elements of display:none
.start{
counter-reset: son 0;
}
.son{
counter-increment: son 1;
}
.son::before{
content: counter(son) ". ";
}
<div>
<div>son1</div>
<div>son2</div>
<div>son3</div>
</div>The result is:
1. son1 2. son3
8.Transition changes to display Don’t catch a cold
9. Reflow will be triggered when display changes
Leaving aside display:none, let’s see that display:block means that the element is located in BFC, while display:inline means that the element is located in IFC. In other words, the purpose of display is to set the layout context to which the element belongs. If the display value is modified, it means that the layout method adopted by the element has changed. It would be strange if reflow is not triggered!
In-depth visibility
Visibility has two different functions
It is used to hide the rows and columns of the table
It is used without triggering layout Hidden element
4 valid values
1.visible
There is nothing to say, it is just displayed on the interface.
2.hidden
Make the element invisible on the screen, but retain the original position of the element.
3.collapse
When used on table sub-elements (such as tr, tbody, col, colgroup), the effect is the same as display:none. When used on other elements, the effect is the same as visibility:hidden. However, since the implementation effects of each browser are different, this value is generally not used.
4.inherit
Inherit the visibility value of the parent element.
Clearly compare display:none and visibility:hidden
We have listed 8 points for attention on display:none above, so we only need to compare it and list the visibility one by one, and it will be clearly visible. Yet?
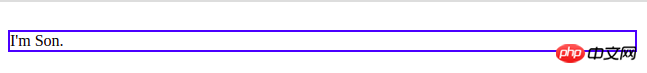
1. The parent element is visibility:hidden, and the child element can be set to visibility:visible and it will take effect
div{
border: solid 2px blue;
}
.visible{
visibility: visible;
}
.hidden{
visibility: hidden;
}
<div>
I'm Parent.
<div>
I'm Son.
</div>
</div>Result:
2. Can't get focus like display:none
3. Can respond to events in the bubbling stage
Since the child elements of an element set to visibility:hidden can be visibility:visible, it is hidden The element may be located on the path of the event bubbling. Therefore, in the following code, when the mouse is moved to .visible, .hidden will be displayed in response to the hover event.
div{
border: solid 2px blue;
}
.visible{
visibility: visible;
}
.hidden{
visibility: hidden;
}
.hidden:hover{
visibility: visible;
}
<div class="hidden">
I'm Parent.
<div class="visible">
I'm Son.
</div>
</div>4. Like display:none, it does not prevent form submission
5.The counter in CSS will not be ignored
6.Transition is effective for changes in visibility
7. Visibility changes will not trigger reflow
Since the attributes related to the element layout will not be changed when it is set from visible to hidden, reflow will not be triggered, and it will just quietly wait for browsing with other rendering changes. The controller redraws the interface regularly.
The above is the detailed content of Analysis of the difference between display:none and visibility:hidden in css. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1421
1421
 52
52
 1316
1316
 25
25
 1266
1266
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
There are several ways to insert images in Bootstrap: insert images directly, using the HTML img tag. With the Bootstrap image component, you can provide responsive images and more styles. Set the image size, use the img-fluid class to make the image adaptable. Set the border, using the img-bordered class. Set the rounded corners and use the img-rounded class. Set the shadow, use the shadow class. Resize and position the image, using CSS style. Using the background image, use the background-image CSS property.
 How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
There are two ways to create a Bootstrap split line: using the tag, which creates a horizontal split line. Use the CSS border property to create custom style split lines.
 How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
To set up the Bootstrap framework, you need to follow these steps: 1. Reference the Bootstrap file via CDN; 2. Download and host the file on your own server; 3. Include the Bootstrap file in HTML; 4. Compile Sass/Less as needed; 5. Import a custom file (optional). Once setup is complete, you can use Bootstrap's grid systems, components, and styles to create responsive websites and applications.
 How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
To adjust the size of elements in Bootstrap, you can use the dimension class, which includes: adjusting width: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust height: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-
 How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use the Bootstrap button? Introduce Bootstrap CSS to create button elements and add Bootstrap button class to add button text



