 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Extension of custom annotations based on shiro - detailed explanation with pictures and text
Extension of custom annotations based on shiro - detailed explanation with pictures and text
Extension of custom annotations based on shiro - detailed explanation with pictures and text
Extension based on shiro's custom annotations
Here we mainly adopt shiro's custom annotation solution. This article mainly solves the following problems.
How to associate the page with the api interface through logic.
Usage of shiro’s own annotations.
How to write custom annotations.
How to associate pages with api interfaces through logic
In the structural relationship between tables, the page and interface tables are ultimately associated with the permissions table (For details, please see my previous article "Miscellaneous Talk about Permission Design"). 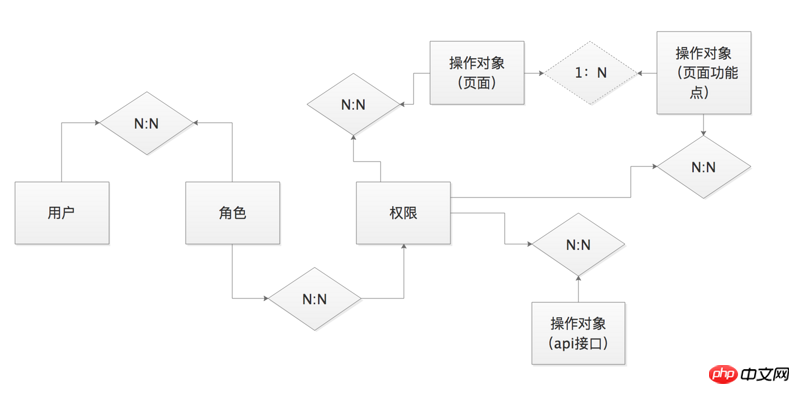 We now hope to replace it with another solution to achieve a low cost while taking into account a certain degree of permission control. Here we introduce two concepts. Business module, Operation type.
We now hope to replace it with another solution to achieve a low cost while taking into account a certain degree of permission control. Here we introduce two concepts. Business module, Operation type.
Business module
Concept: Abstracting the business module in the system into a kind of data, we can Express it in the form of a string, for example: role management corresponds to role-manage, user management corresponds to user-manage, etc. We divide the business modules existing in the system through the "principle of least privilege" and finally form a batch of distributable data.
Principles of use: The api interface, page and function are essentially logically related to the business module. Therefore, we can use the api interface and page ( and function points) to perform logical matching to determine the relationship between the page and the interface.
Operation type
Concept: Abstract all operation types in the system into one We can also express this kind of data in the form of strings, for example: add corresponds to new addition, allot corresponds to allocation, etc. We divide all operation types in the system through "data licenses" according to business modules, and finally form a batch of distributable data.
Usage Principle: The page is the display, the function point is the action, and the interface is the resource provision for the final action. The resources to be called are determined through the "business module" , the "operation type" determines how the resource is used. Through the two, you can roughly and accurately determine whether the interface triggered by the function point of the page is within the authentication.
Now that these two concepts are proposed, what is their final actual use? Let us first think about it from the following perspectives.
Is the data in the page table in the database or the api interface table true and valid?
The actual use of the page or interface is based on the existence of functions or the existence of data in the database table.
In the permission structure, is the only way to store "control objects" is the database?
Let's look at these issues from the conclusion. First of all, the "control object" can be stored not only in the database but also in the code or in the configuration file. It does not necessarily have to be In the database; then to answer the second question, when the interface information exists in the database but the server has not developed this interface, there is a problem with the database information itself, or the new interface in the database must be the server side The interface that has been deployed can take effect; then there is the first question, then the data in the "control object" table in the database is not necessarily true and valid. So we can come up with the following solution
We can use the annotation form to supplement the data information of "Business Module" and "Operation Type" on the interface, Both types of information can be stored in constant classes.
When adding and creating the page table structure and page function table structure in the database, add the "Business Module" and "Operation Type" fields .
You can store the "business module" and "operation type" information in the dictionary table of the database.
The addition of modules or operations will inevitably bring about the addition of interfaces, which will lead to a system deployment activity. This operation and maintenance cost cannot be reduced. It cannot be reduced by table structure.
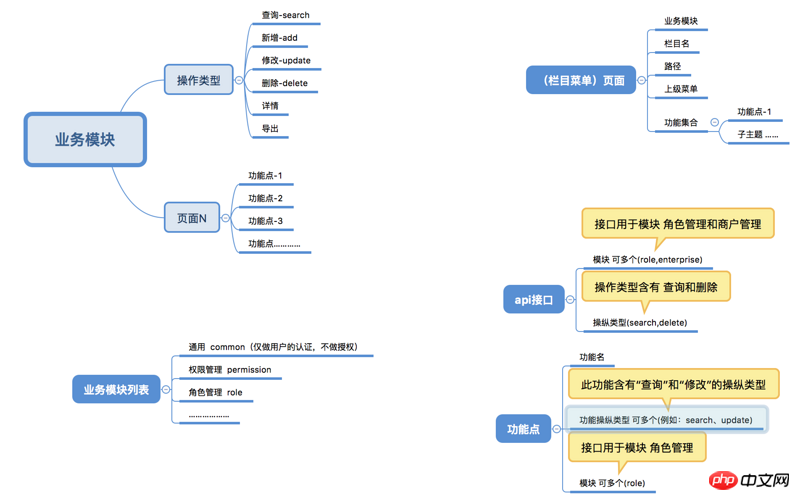
However, this solution is only suitable for non-strong control interface projects. In strong control interface projects, the page and the interface must still be bound, although this will bring huge operation and maintenance costs. In addition, it can also be divided by interface routing rules, for example: /api/page/xxxx/ (only used for pages), /api/mobile/xxxxx (only used for mobile terminals) will classify interfaces that are only used by pages. This The class interface only performs authentication but not authorization, which can also achieve the purpose.
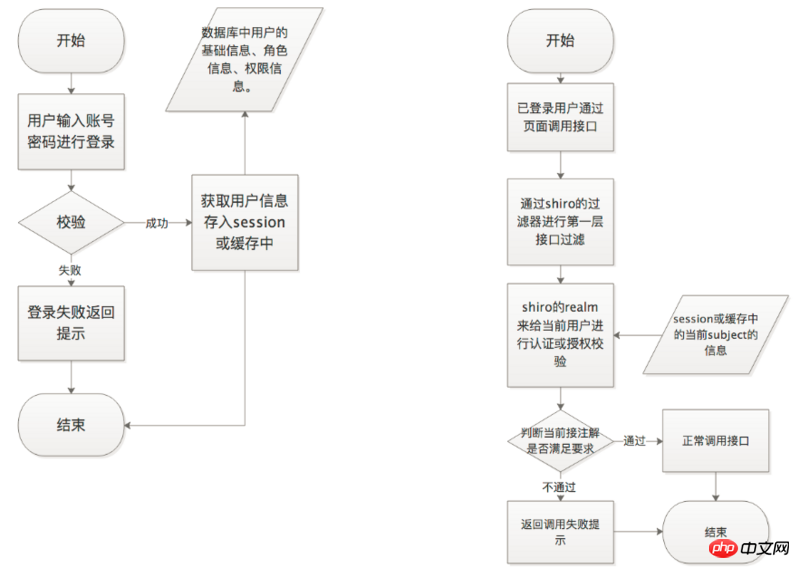
Usage of Shiro’s own annotations
After a theoretical idea is approved, the rest is put into technical practice. We use the security framework of Apache Shiro here. , applied in Spring Boot environment. Briefly explain the following annotations of Shiro.
| Annotation name | Function |
|---|---|
| Acts on classes, methods, and instances. When called, the current subject must be authenticated. | |
| acts on classes, methods, and instances. When called, the subject can be in the guest state. | |
| Acts on classes, methods, and instances. When calling, you need to determine whether the project contains the Permission (permission information) in the current interface. | |
| acts on classes, methods, and instances. When calling, you need to determine whether the subject contains the Role (role information) in the current interface. | |
| acts on classes, methods, and instances. When calling, it is necessary to determine whether the subject is a user currently in the application. |
- Define annotation class
/**
* 用于认证的接口的注解,组合形式默认是“或”的关系
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Auth {
/**
* 业务模块
* @return
*/
String[] module();
/**
* 操作类型
*/
String[] action();
}- Define annotation processing class
/**
* Auth注解的操作类
*/
public class AuthHandler extends AuthorizingAnnotationHandler {
public AuthHandler() {
//写入注解
super(Auth.class);
}
@Override
public void assertAuthorized(Annotation a) throws AuthorizationException {
if (a instanceof Auth) {
Auth annotation = (Auth) a;
String[] module = annotation.module();
String[] action = annotation.action();
//1.获取当前主题
Subject subject = this.getSubject();
//2.验证是否包含当前接口的权限有一个通过则通过
boolean hasAtLeastOnePermission = false;
for(String m:module){
for(String ac:action){
//使用hutool的字符串工具类
String permission = StrFormatter.format("{}:{}",m,ac);
if(subject.isPermitted(permission)){
hasAtLeastOnePermission=true;
break;
}
}
}
if(!hasAtLeastOnePermission){
throw new AuthorizationException("没有访问此接口的权限");
}
}
}
}- Define shiro interception processing class
/**
* 拦截器
*/
public class AuthMethodInterceptor extends AuthorizingAnnotationMethodInterceptor {
public AuthMethodInterceptor() {
super(new AuthHandler());
}
public AuthMethodInterceptor(AnnotationResolver resolver) {
super(new AuthHandler(), resolver);
}
@Override
public void assertAuthorized(MethodInvocation mi) throws AuthorizationException {
// 验证权限
try {
((AuthHandler) this.getHandler()).assertAuthorized(getAnnotation(mi));
} catch (AuthorizationException ae) {
if (ae.getCause() == null) {
ae.initCause(new AuthorizationException("当前的方法没有通过鉴权: " + mi.getMethod()));
}
throw ae;
}
}
}- Define shiro’s aop aspect class
/**
* shiro的aop切面
*/
public class AuthAopInterceptor extends AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor {
public AuthAopInterceptor() {
super();
// 添加自定义的注解拦截器
this.methodInterceptors.add(new AuthMethodInterceptor(new SpringAnnotationResolver()));
}
}- Define shiro's custom annotation startup class
/**
* 启动自定义注解
*/
public class ShiroAdvisor extends AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor {
public ShiroAdvisor() {
// 这里可以添加多个
setAdvice(new AuthAopInterceptor());
}
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked"})
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class targetClass) {
Method m = method;
if (targetClass != null) {
try {
m = targetClass.getMethod(m.getName(), m.getParameterTypes());
return this.isFrameAnnotation(m);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ignored) {
}
}
return super.matches(method, targetClass);
}
private boolean isFrameAnnotation(Method method) {
return null != AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, Auth.class);
}
}annotation class (define variables that can be used by the business) ->Defineannotation processing class(do business logic processing through variables in the annotation)->Defineannotation interceptor->defineaop aspect class->Finally define Shiro’s custom annotation enablement class. The writing ideas for other custom annotations are similar to this one.Related recommendations:
Custom annotation mapping thinkPHP21 custom tag library import method detailed explanation
About custom annotations in Java Detailed introduction
Detailed explanation of shiro authorization implementation
The above is the detailed content of Extension of custom annotations based on shiro - detailed explanation with pictures and text. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1245
1245
 24
24
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.



