 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Summary and performance analysis of 11 methods for exchanging values between two variables in js (with code)
Summary and performance analysis of 11 methods for exchanging values between two variables in js (with code)
Summary and performance analysis of 11 methods for exchanging values between two variables in js (with code)
js exchanges the values of two variables. This is a topic that is worth understanding in depth. Now there are many methods to solve the problem of exchanging between js variables. In this article, I will share with you the js Several methods of variable exchange and performance analysis of js variable exchange.
When I was working on a project recently, one of the requirements was to exchange two elements in an array. The method used at that time was:
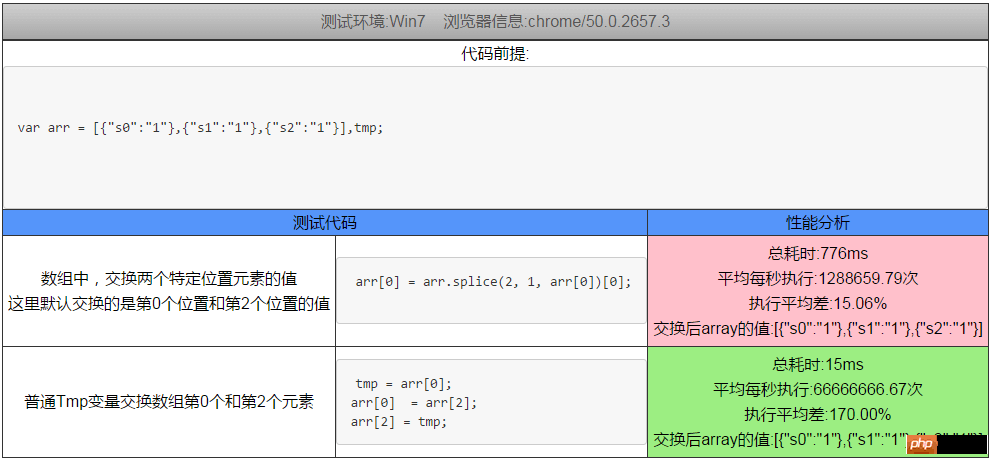
arr = [item0,item1,...,itemN]; //最初使用这段代码来交换第0个和第K(k<N)个元素 arr[0] = arr.splice(k, 1, arr[0])[0];
At that time, I thought this method was very good.
Later, I studied this in my spare time and wrote an analysis tool myself to compare with the ordinary method.
The result was far beyond my expectation. The efficiency of this method is much lower than I thought. The following is a picture of one of the test results
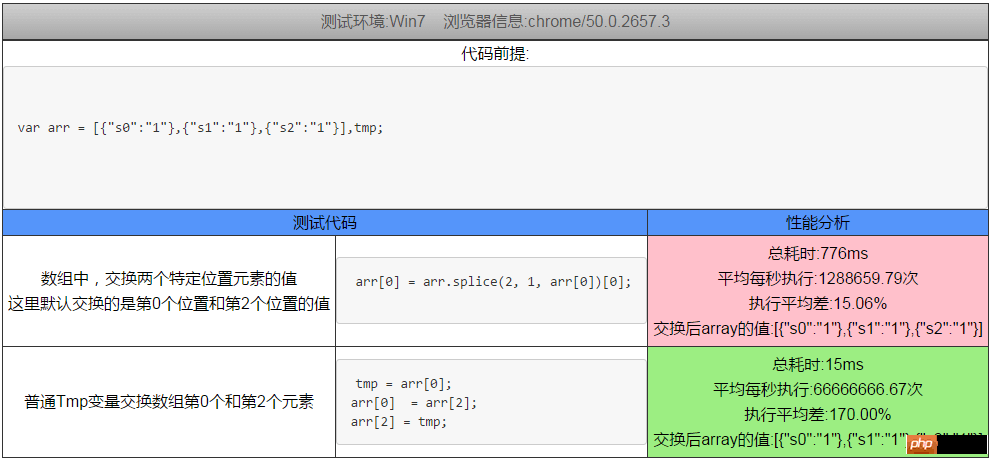
So, based on this, we studied several other methods of numerical exchange. , are integrated into the analysis tools together, and this is the summary of this article.
Several methods of JS variable exchange
In fact, regarding JS variable exchange, the most widely used methods are basically necessary skills for front-end personnel. This article just takes this opportunity of analysis and research to list several exchange methods used in this analysis:
The first: ordinary temporary variable exchange method
Applicability: Applicable to all types of codes as follows:
tmp = a; a = b; b = tmp;
Brief description: This is the most widely used method. After actual testing and analysis, the performance is also very high
(In JS, this method is indeed very efficient, and even in other languages, as long as the tmp variable If created in advance, the performance will not be very low. On the contrary, the performance of some acrobats and minorities is very low)
Basically we can say: the classic is the most elegant
The second type: Use a new object for data exchange
Applicability: Applicable to all types of codes as follows:
a = {a : b, b : a};
b = a.b
;a = a.a;Brief description: This method is rarely used in actual combat
Third method: Use a new array for data exchange
Applicability: Applicable to all types of codes as follows :
a = [b, b=a][0];
Brief description: This method has been seen being used in major forums, but the actual performance after testing is not high
Fourth method: Using arrays to exchange variables (requires EJS support)
Applicability: Applicable to all types of codes as follows:
`[a, b] = [b, a];
Brief description: This is what I saw some people using after ES6 came out. It was actually tested in existing browsers and the performance was very low
The fifth way: using try catch exchange
Applicability: Applicable to all types of codes as follows:
a=(function(){;
try{return b}
finally{b=a}}
)();Brief description: This method should be rarely used by anyone, and it has no practicality, and its performance is also at the bottom of various methods
Sixth method: XOR operation exchange variables The first method
Applicability: Suitable for numeric or string codes as follows:
a = (b = (a ^= b) ^ b) ^ a;
Brief description: The XOR method is more commonly used in numbers or strings, and its performance is not low
Seventh method: The second method of XOR operation to exchange variables
Applicability: Applicable to numeric or string codes as follows:
a ^=b; b ^=a; a ^=b;
Brief description: The XOR method is more commonly used for numbers or strings, and its performance is not low
The eighth method: the addition and subtraction between numbers is implemented, the first addition and subtraction method
Applicability: Only applicable to numeric codes as follows:
a = a + b; b = a - b; a = a - b;
Brief description: When this usage is only used for the exchange between numbers, the performance is not weak
The ninth method: the addition and subtraction between numbers is implemented, the first addition and subtraction method
Applicability: Only applicable to numeric codes as follows:
a = b -a +(b = a);
Brief description: When this usage is only used for the exchange of numbers, the performance is not weak
Tenth: Use eval calculation
Applicability: Only applicable to numbers and sums The string code is as follows:
eval("a="+b+";b="+a);Brief description: This method is only for research, and should be used with caution in actual combat.
The time it takes to execute this mode 10,000 times is equal to 100 million times for other modes...
Type 11: In an array, Use splice to exchange the positions of two elements
Applicability: Only applicable to array elements The code is as follows:
arr[0] = arr.splice(2, 1, arr[0])[0];
Brief description: This method looks quite elegant, but in fact the performance is far inferior to that of temporary variables.
Performance comparison of various exchange methods
The above listed methods all have one Once we have done a comparative analysis, we can basically draw the conclusion:
Let’s just use temporary variable exchange honestly, it is classic, elegant, and guaranteed not to cause any trouble
Performance comparison screenshots
Analysis results 1
The data in the screenshots below are the conclusions drawn after running 100 million times in chrome (each run is 100 Ten thousand times, a total of 100 loops, the analysis results obtained) can be seen that tmp variable exchange is the fastest, try catch is the slowest
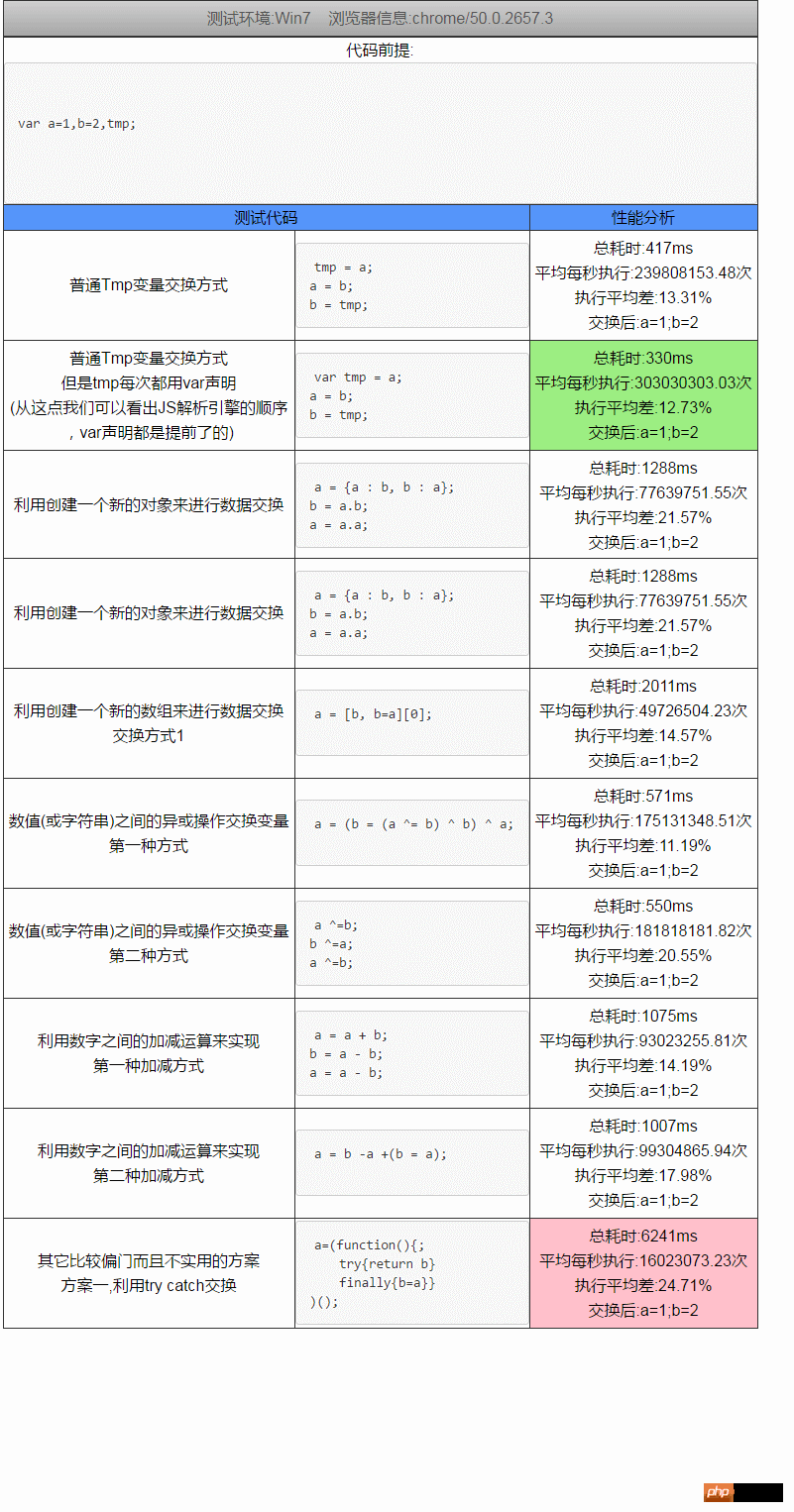
Analysis results 2
The following screenshot data is the conclusion drawn after running 1 million times in chrome (supports es6) (each run 10,000 times, a total of 100 cycles, the analysis results obtained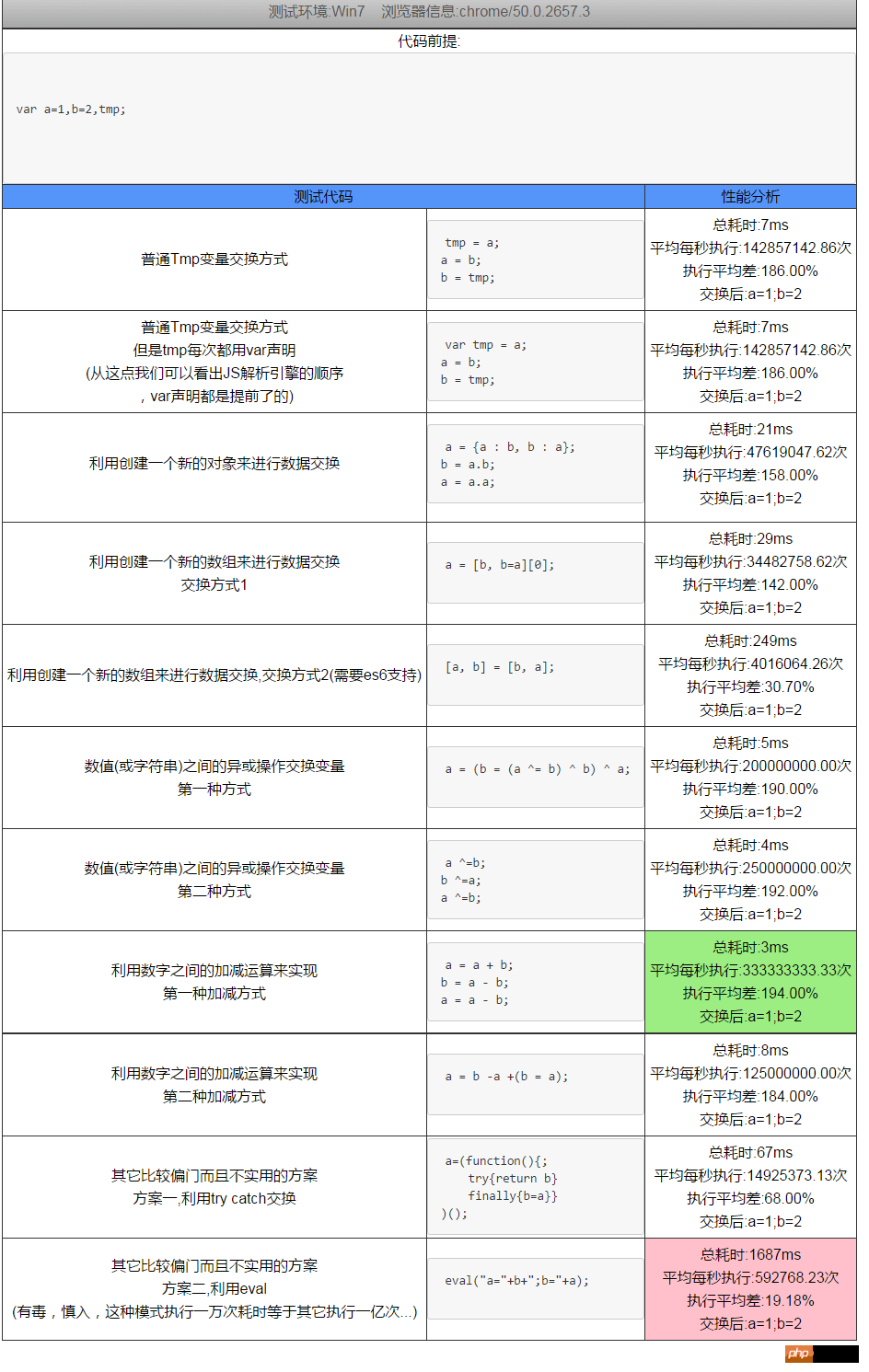
It can be seen that eval is the slowest, splice performance is low, and tmp variable exchange is very stable
Related recommendations:
The above is the detailed content of Summary and performance analysis of 11 methods for exchanging values between two variables in js (with code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1657
1657
 14
14
 1415
1415
 52
52
 1309
1309
 25
25
 1257
1257
 29
29
 1229
1229
 24
24
 Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript is the cornerstone of modern web development, and its main functions include event-driven programming, dynamic content generation and asynchronous programming. 1) Event-driven programming allows web pages to change dynamically according to user operations. 2) Dynamic content generation allows page content to be adjusted according to conditions. 3) Asynchronous programming ensures that the user interface is not blocked. JavaScript is widely used in web interaction, single-page application and server-side development, greatly improving the flexibility of user experience and cross-platform development.
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Different JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript is the core language of modern web development and is widely used for its diversity and flexibility. 1) Front-end development: build dynamic web pages and single-page applications through DOM operations and modern frameworks (such as React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Server-side development: Node.js uses a non-blocking I/O model to handle high concurrency and real-time applications. 3) Mobile and desktop application development: cross-platform development is realized through ReactNative and Electron to improve development efficiency.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
This article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 How do I install JavaScript?
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:16 AM
How do I install JavaScript?
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:16 AM
JavaScript does not require installation because it is already built into modern browsers. You just need a text editor and a browser to get started. 1) In the browser environment, run it by embedding the HTML file through tags. 2) In the Node.js environment, after downloading and installing Node.js, run the JavaScript file through the command line.



