Detailed explanation of Angularjs Promise examples
Promise is a constructor. It has all, reject, and resolve methods for asynchronously processing values. The prototype has then, catch, and other familiar methods. Let’s explain angularjs promise through example code. Related knowledge, interested friends should take a look together
1. What is Promise
Promise is an object, representing the final possibility of a function The return value or exception thrown is used to process the value asynchronously.
Promise is a constructor. It has all, reject, and resolve methods for asynchronously processing values. The prototype has then, catch, and other familiar methods.
2. Why use Promise
With the Promise object, asynchronous operations can be expressed as a synchronous operation process, avoiding the need for layers Nested callback functions. In addition, Promise objects provide a unified interface, making it easier to control asynchronous operations.
The Promise object has the following two characteristics:
1. The state of the object is not affected by the outside world.
The Promise object represents an asynchronous operation and has three states: Pending (in progress), Resolved (completed) and Rejected (failed). Only the result of the asynchronous operation can determine the current state, and no other operation can change this state.
2. Once the status changes, it will not change again, and this result can be obtained at any time.
There are only two possibilities for the state change of the Promise object: from Pending to Resolved; from Pending to Rejected. As long as these two situations occur, the state will be solidified and will not change again, and will maintain this result.
3. How to create a Promise
First paste a piece of code:
define([
'angularModule'
],function (app) {
app.register.service('httpRequestService', ['$http', '$q', function ($http, $q) {
return{
request: function (params) {
var deferred = $q.defer();
$http({
method : params.method,
url : params.url
}).success(
function (data) {
deferred.resolve(data);
}
).error(
function(data){
deferred.reject(data);
}
);
return deferred.promise;
}
}
}])
});Let’s talk about $q service
q service is a Promise implementation that is encapsulated and implemented in AngularJS.
To create a deferred object, you can call the defer() method:
var deferred = $q.defer(); //deffered上面暴露了三个方法,以及一个可以用于处理promise的promise属性。 //promise属性里面又包含了then、catch、finally三个方法
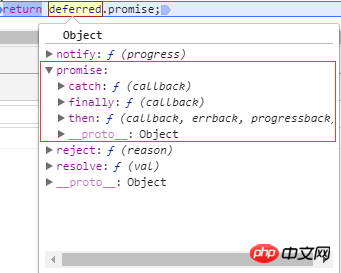
In Promise , three states are defined: waiting state, completion state, and rejection state.
deffered API
1.deffered object method
1.resolve(value) : At the declaration of resolve(), it indicates that the promise object changes from the pending state to resolve.
2.reject(reason): At the point where resolve() is declared, it indicates that the promise object changes from the pending state to rejected.
3.notify(value): When notify() is declared, it indicates the unfulfilled status of the promise object and can be called multiple times before resolve or reject.
2.deffered object attribute
promise: What is finally returned is a new deferred object promise attribute, not the original deferred object. This new Promise object can only observe the state of the original Promise object, and cannot modify the internal state of the deferred object to prevent the task state from being modified externally.
3.Promise API
When a deferred instance is created, a new promise object is created, and the reference can be obtained through deferred.promise.
The purpose of the promise object is to allow the interested part to obtain its execution results when the deferred task is completed.
4.Promise object methods
1.then(errorHandler, fulfilledHandler, progressHandler): The then method is used to monitor the different states of a Promise. The errorHandler monitors the failed status, the fulfilledHandler monitors the fulfilled status, and the progressHandler monitors the unfulfilled (incomplete) status. Additionally, the notify callback may be called zero to more times, providing an indication of progress before resolving or rejecting (resolve and rejected).
2.catch(errorCallback) - a shortcut for promise.then(null, errorCallback)
3.finally(callback) - allows you to observe whether a promise is executed or not Rejected, but doing so does not modify the last value. This can be used to do some work of releasing resources or cleaning up unused objects, regardless of whether the promise is rejected or resolved.
q Several commonly used methods:
defer() creates a deferred object, which can execute several common methods, such as resolve, reject, notify, etc.
all() Pass in the array of Promise, execute it in batches, and return a promise object
when() pass Enter an uncertain parameter, and if it meets the Promise standard, return a promise object.
all() method
This method can be used when executing certain methods in batches. With all, you can perform multiple asynchronous operations in parallel and process all return data in a callback.
Use Promise.all to execute. all receives an array parameter, and the values inside are eventually returned to the Promise object. In this way, three asynchronous operations are executed in parallel, and they will not enter then until they are all executed.
那么,三个异步操作返回的数据哪里去了呢?都在then里面呢,all会把所有异步操作的结果放进一个数组中传给then,就是 下面的results。所以下面代码的输出结果就是:
var funcA = function(){
console.log("funcA");
return "hello,funA";
}
var funcB = function(){
console.log("funcB");
return "hello,funB";
}
$q.all([funcA(),funcB()])
.then(function(result){
console.log(result);
});执行的结果:
funcA funcB Array [ "hello,funA", "hello,funB" ]
when()方法
when方法中可以传入一个参数,这个参数可能是一个值,可能是一个符合promise标准的外部对象。
var funcA = function(){
console.log("funcA");
return "hello,funA";
}
$q.when(funcA())
.then(function(result){
console.log(result);
});当传入的参数不确定时,可以使用这个方法。
hello,funA
四、链式请求
通过then()方法可以实现promise链式调用,因为then方法总是返回一个新的promise。
runAsync1()
.then(function(data){
console.log(data);
return runAsync2();
})
.then(function(data){
console.log(data);
return runAsync3();
})
.then(function(data){
console.log(data);
});
function runAsync1(){
var p = new Promise(function(resolve, reject){
//做一些异步操作
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('异步任务1执行完成');
resolve('随便什么数据1');
}, 1000);
});
return p;
}
function runAsync2(){
var p = new Promise(function(resolve, reject){
//做一些异步操作
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('异步任务2执行完成');
resolve('随便什么数据2');
}, 2000);
});
return p;
}
function runAsync3(){
var p = new Promise(function(resolve, reject){
//做一些异步操作
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('异步任务3执行完成');
resolve('随便什么数据3');
}, 2000);
});
return p;
}运行结果:

上面是我整理给大家的,希望今后会对大家有帮助。
相关文章:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Angularjs Promise examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1655
1655
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1306
1306
 25
25
 1252
1252
 29
29
 1226
1226
 24
24
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 Keeping your word: The pros and cons of delivering on your promises
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:06 PM
Keeping your word: The pros and cons of delivering on your promises
Feb 18, 2024 pm 08:06 PM
In daily life, we often encounter problems between promises and fulfillment. Whether in a personal relationship or a business transaction, delivering on promises is key to building trust. However, the pros and cons of commitment are often controversial. This article will explore the pros and cons of commitments and give some advice on how to keep your word. The promised benefits are obvious. First, commitment builds trust. When a person keeps his word, he makes others believe that he is a trustworthy person. Trust is the bond established between people, which can make people more
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 Learn more about Promise.resolve()
Feb 18, 2024 pm 07:13 PM
Learn more about Promise.resolve()
Feb 18, 2024 pm 07:13 PM
Detailed explanation of Promise.resolve() requires specific code examples. Promise is a mechanism in JavaScript for handling asynchronous operations. In actual development, it is often necessary to handle some asynchronous tasks that need to be executed in sequence, and the Promise.resolve() method is used to return a Promise object that has been fulfilled. Promise.resolve() is a static method of the Promise class, which accepts a




