Summary of tips for using React high-order components
This time I will bring you a summary of the skills for using React high-end components. What are the precautions when using React high-end components? The following is a practical case, let’s take a look.
Some time ago when I was writing a Hybrid page at work, I encountered such a scenario. The company needed a series of active components, and when each component was registered, it needed to call an interface provided by the App. Several methods were considered at the beginning, including mixins, component inheritance, and react higher-order components. But after various considerations, we finally chose to use high-level components.
So what are advanced components? First of all, you must first understand that requesting classes in ES6 is just syntactic sugar, and the essence is prototypal inheritance. To better illustrate this, we will not modify the component's code. Instead, it provides components that wrap components and enhance them with additional functionality. We call such components higher-order components (Higher-Order Component).
1. Disadvantages of Mixins
React officially does not recommend the use of Mixins technology to achieve code reuse. Mixins technology has a series of shortcomings. First, Mixins will cause naming problems. Conflict, we inject Mixins in the following way:
var myMixins = require('myMixins');
var Button = React.createClass({
mixins: [myMixins],
// ...
})If you need to inject multiple mixins, one of them is your own and the other may be a third-party. It is possible to use a method with the same name in two mixins, which will cause one of them to not work, and all you can do is change the name of one of the methods. On the other hand, a mixins may be very simple at first, only needing to implement a certain function, but when the business becomes more complex and more methods need to be added, it will become very complicated. To learn more about the shortcomings of mixins, you can check out the official blog.
2. Component inheritance
For myself, this method has been used more often. First, create a BaseComponent and implement a series of public methods in it. Each subsequent component inherits from this component, but the disadvantage is that it is not flexible enough. Only some relatively fixed methods can be implemented in the basic components, and there are great restrictions on the customization of each component.
3. React high-order components
Due to a series of shortcomings of mixins, React officials also realized that the pain points caused by using mixins are far higher than those caused by the technology itself. Advantages, high-order components can replace mixins, and it has richer uses when you go deeper.
Higher-order components (HOC) are advanced technologies in React that reuse component logic. But higher-order components themselves are not React APIs. It's just a pattern that arises inevitably from the compositional nature of React itself.
Higher-order functions
Speaking of high-order components, we must first talk about high-order functions. High-order functions are functions that at least meet the following conditions:
1. Accept one or more functions as input
2. Output a function
In javascript, a language where functions are first-class citizens, higher-order functions There are still many uses, such as our usual callback function, etc., all of which use the knowledge of high-order functions. Let’s first look at a simple higher-order function
var fun = function(x, y) {
return x + y;
}fun is a function, let’s pass the entire function as a parameter to another function
var comp = function(x, y, f) {
return f(x,y);
}Verify it
comp(1,2,fun) // 3
High-order component definition
Analogous to the definition of a high-order function, a high-order component accepts a component as a parameter, performs a series of processes on the component in the function, and then returns a new component. as return value.
We first define a high-order component BaseActivity
const BaseActivity = (WrappedComponent) => {
return class extends Component {
render() {
return (
<section>
<p>我的包裹组件</p>
<WrappedComponent />
</section>
)
}
}
}The component accepts a wrapped component as a parameter and returns a processed anonymous component.
Use this high-order component in other components
class Example extends React.PureComponent {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
width: '100%',
height: '100%'
}
}
componentWillMount() {
if ((navigator.userAgent.match(/(phone|pad|pod|iPhone|iPod|ios|iPad|Android|Mobile|BlackBerry|IEMobile|MQQBrowser|JUC|Fennec|wOSBrowser|BrowserNG|WebOS|Symbian|Windows Phone)/i))) {
return;
} else {
this.setState({
width: '375px',
height: '640px'
})
}
}
render() {
let { width, height } = this.state;
return (
<p className="activity">
<p className="activity-content" style={{ width, height }}>
<button className="btn">参加活动</button>
</p>
</p>
)
}
}
export default BaseActivity(Example);The specific usage is to use the BaseActivity function to wrap the component when exporting the component, and look at the output react dom content
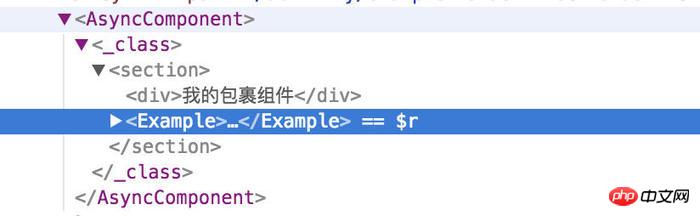
An anonymous component is wrapped outside the Example component.
Parameters
Since the higher-order component is a function, we can pass the parameters we need to it
const BaseActivity = (WrappedComponent, title) => {
return class extends Component {
render() {
return (
<section>
<p>{title}</p>
<WrappedComponent />
</section>
)
}
}
}Export like this in Example
export default BaseActivity(Example, '这是高阶组件的参数');
Let’s take a look at the output react dom
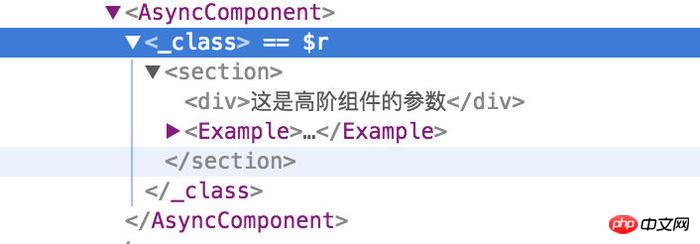
可以看到参数已经传递进去了。
当然还可以这样用(柯里化)
const BaseActivity (title) => (WrappedComponent) => {
return class extends Component {
render() {
return (
<section>
<p>{title}</p>
<WrappedComponent />
</section>
)
}
}
}在Example中这样export
export default BaseActivity('这是高阶组件的参数')(Example);这种用法在ant-design的表单以及redux的connect中我们都可以看到
// ant const WrappedDemo = Form.create()(Demo) // redux export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Counter)
高阶组件还可以扩展原组件的props属性,如下所示:
const BaseActivity (title) => (WrappedComponent) => {
return class extends Component {
render() {
const newProps = {
id: Math.random().toString(8)
}
return (
<section>
<p>{title}</p>
<WrappedComponent {...this.props} {...newProps}/>
</section>
)
}
}
}看下输出的react dom
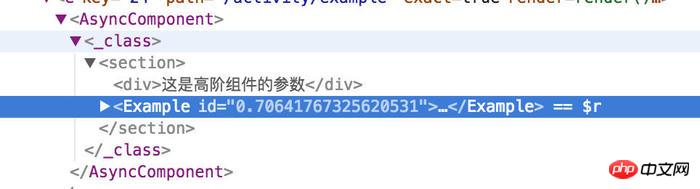
高阶组件的缺点
高阶组件也有一系列的缺点,首先是被包裹组件的静态方法会消失,这其实也是很好理解的,我们将组件当做参数传入函数中,返回的已经不是原来的组件,而是一个新的组件,原来的静态方法自然就不存在了。如果需要保留,我们可以手动将原组件的方法拷贝给新的组件,或者使用hoist-non-react-statics之类的库来进行拷贝。
相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of Summary of tips for using React high-order components. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1658
1658
 14
14
 1415
1415
 52
52
 1309
1309
 25
25
 1257
1257
 29
29
 1231
1231
 24
24
 Summarize the usage of system() function in Linux system
Feb 23, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Summarize the usage of system() function in Linux system
Feb 23, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
Summary of the system() function under Linux In the Linux system, the system() function is a very commonly used function, which can be used to execute command line commands. This article will introduce the system() function in detail and provide some specific code examples. 1. Basic usage of the system() function. The declaration of the system() function is as follows: intsystem(constchar*command); where the command parameter is a character.
 PHP, Vue and React: How to choose the most suitable front-end framework?
Mar 15, 2024 pm 05:48 PM
PHP, Vue and React: How to choose the most suitable front-end framework?
Mar 15, 2024 pm 05:48 PM
PHP, Vue and React: How to choose the most suitable front-end framework? With the continuous development of Internet technology, front-end frameworks play a vital role in Web development. PHP, Vue and React are three representative front-end frameworks, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. When choosing which front-end framework to use, developers need to make an informed decision based on project needs, team skills, and personal preferences. This article will compare the characteristics and uses of the three front-end frameworks PHP, Vue and React.
 Integration of Java framework and front-end React framework
Jun 01, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Integration of Java framework and front-end React framework
Jun 01, 2024 pm 03:16 PM
Integration of Java framework and React framework: Steps: Set up the back-end Java framework. Create project structure. Configure build tools. Create React applications. Write REST API endpoints. Configure the communication mechanism. Practical case (SpringBoot+React): Java code: Define RESTfulAPI controller. React code: Get and display the data returned by the API.
 Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific Considerations
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js is suitable for small and medium-sized projects and fast iterations, while React is suitable for large and complex applications. 1) Vue.js is easy to use and is suitable for situations where the team is insufficient or the project scale is small. 2) React has a richer ecosystem and is suitable for projects with high performance and complex functional needs.
 Master the advantages and operating techniques of the conda virtual environment
Feb 18, 2024 pm 07:46 PM
Master the advantages and operating techniques of the conda virtual environment
Feb 18, 2024 pm 07:46 PM
To understand the advantages and usage techniques of the conda virtual environment, specific code examples are required. Python is a very popular programming language that is widely used in fields such as scientific computing, data analysis, and artificial intelligence. In the Python ecosystem, there are many third-party libraries and tools, and different versions of the libraries may need to be used in different projects. In order to manage the dependencies of these libraries, the conda virtual environment becomes an important tool. conda is an open source package management system and environment management system that can easily create and
 React's Role in HTML: Enhancing User Experience
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
React's Role in HTML: Enhancing User Experience
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
React combines JSX and HTML to improve user experience. 1) JSX embeds HTML to make development more intuitive. 2) The virtual DOM mechanism optimizes performance and reduces DOM operations. 3) Component-based management UI to improve maintainability. 4) State management and event processing enhance interactivity.
 React vs. Vue: Which Framework Does Netflix Use?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
React vs. Vue: Which Framework Does Netflix Use?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Netflixusesacustomframeworkcalled"Gibbon"builtonReact,notReactorVuedirectly.1)TeamExperience:Choosebasedonfamiliarity.2)ProjectComplexity:Vueforsimplerprojects,Reactforcomplexones.3)CustomizationNeeds:Reactoffersmoreflexibility.4)Ecosystema
 React and the Frontend: Building Interactive Experiences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:02 AM
React and the Frontend: Building Interactive Experiences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:02 AM
React is the preferred tool for building interactive front-end experiences. 1) React simplifies UI development through componentization and virtual DOM. 2) Components are divided into function components and class components. Function components are simpler and class components provide more life cycle methods. 3) The working principle of React relies on virtual DOM and reconciliation algorithm to improve performance. 4) State management uses useState or this.state, and life cycle methods such as componentDidMount are used for specific logic. 5) Basic usage includes creating components and managing state, and advanced usage involves custom hooks and performance optimization. 6) Common errors include improper status updates and performance issues, debugging skills include using ReactDevTools and Excellent




