PHP7 Kernel Analysis 3 Variables
The content of this article introduces CGI and FastCGI about PHP7 kernel analysis 1. Now I share it with everyone. Friends in need can refer to it
1. Variable structure
typedef struct _zval_struct zval;
typedef union _zend_value {
zend_long lval; //int整形
double dval; //浮点型
zend_string *str; //string字符串
zend_array *arr; //array数组
zend_object *obj; //object对象
zend_resource *res; //resource资源类型
zend_reference *ref; //引用类型,通过&$var_name定义的
} zend_value;
struct _zval_struct {
zend_value value; //变量实际的value
union {
struct {
ZEND_ENDIAN_LOHI_4(
zend_uchar type, //变量类型
zend_uchar type_flags, //类型掩码,不同的类型会有不同的几种属性,内存管理会用到
zend_uchar const_flags,
zend_uchar reserved)
} v;
uint32_t type_info; //上面4个值的组合值,可以直接根据type_info取到4个对应位置的值
} u1;
union {
uint32_t var_flags;
uint32_t next; //哈希表中解决哈希冲突时用到
uint32_t cache_slot;
uint32_t lineno;
uint32_t num_args;
uint32_t fe_pos;
uint32_t fe_iter_idx;
} u2;
};2. Variable type
#define IS_UNDEF 0 #define IS_NULL 1 #define IS_FALSE 2 #define IS_TRUE 3 #define IS_LONG 4 #define IS_DOUBLE 5 #define IS_STRING 6 #define IS_ARRAY 7 #define IS_OBJECT 8 #define IS_RESOURCE 9 #define IS_REFERENCE 10
Among them, undef, true, false and null have no value and are directly distinguished according to type, while long , the value of double is stored directly in value, and other types are pointers
3. String
typedef struct _zend_string zend_string;
struct _zend_string {
zend_refcounted_h gc; //变量引用信息,比如当前value的引用数
size_t len; //字符串长度,通过这个值保证二进制安全
char val[1]; //字符串内容,变长struct,分配时按len长度申请内存
};4. Array
typedef struct _zend_array HashTable;
typedef struct _zend_array zend_array;
typedef struct _Bucket {
zval val; //存储的具体value,这里嵌入了一个zval,而不是一个指针
zend_ulong h; //哈希值
zend_string *key; //key值
} Bucket;
struct _zend_array {
zend_refcounted_h gc; //引用计数信息
uint32_t nTableMask; //计算bucket索引时的掩码,用于散列表的计算nIndex
Bucket *arData; //bucket数组
uint32_t nNumUsed; //已用bucket数
uint32_t nNumOfElements; //已有元素数,nNumOfElements <= nNumUsed,因为删除的并不是直接从arData中移除
uint32_t nTableSize; //数组的大小,为2^n,默认为8
uint32_t nInternalPointer; //数值索引,用于HashTable遍历
zend_long nNextFreeElement;//下一个空闲可用位置的数字索引
dtor_func_t pDestructor;//析构函数,销毁时调用的函数指针
};HashTable mainly relies on arData to realize the storage and indexing of elements. When inserting an element, first insert the element into the Bucket array in order, the position is idx, and then map it to a certain position nIndex in the hash table according to the hash value of the key, and store idx in this position; when searching, first in the hash table Map to nIndex, get the position idx of value in the Bucket array, and then take out the element from the Bucket array.
$arr["a"] = 1; $arr["b"] = 2; $arr["c"] = 3; $arr["d"] = 4; unset($arr["c"]);
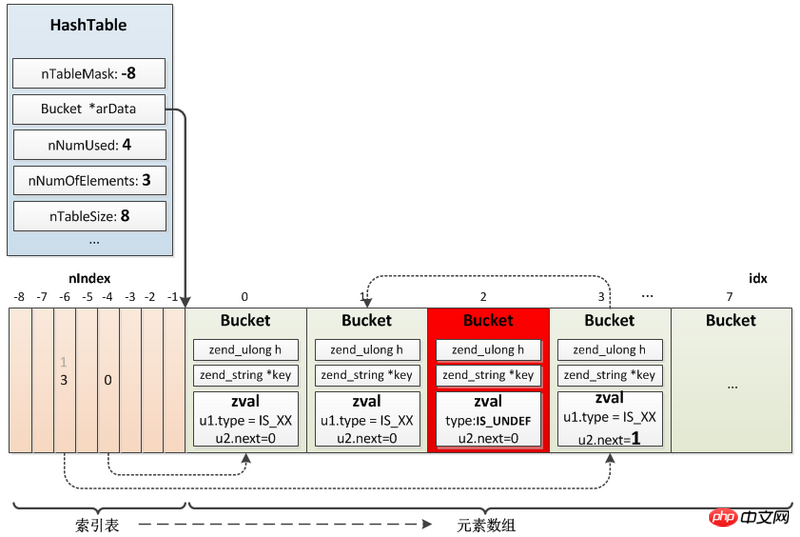
Hash collision: When a conflict occurs, save the position of the original value to zval.u2.next of the new value, and then add the new value value replaces the original value position
Expansion: The size of the PHP hash table is 2^n. If the capacity is not enough during insertion, the proportion of deleted elements will be first checked. If the threshold is reached, the deleted elements will be removed. Rebuild the index. If the threshold is not reached, perform an expansion operation to double the current size, copy the current Bucket array to the new space, and then rebuild the index.
Rebuild the hash table: When the deleted elements reach a certain number or the capacity is expanded, the hash table needs to be rebuilt because the value has moved in the Bucket position or the hash array nTableSize has changed, causing the mapping relationship between key and value to change. The reconstruction process The actual process is to traverse the values in the Bucket array, then recalculate the mapping value and update it to the hash table, remove the deleted value, and move the subsequent undeleted values forward in sequence
5. Reference
Reference is a special type in PHP. It actually points to another PHP variable. Modifying it will directly change the zval actually pointed to. You can simply Understood as a pointer in C, a reference variable is generated through the & operator in PHP. That is to say, no matter what the previous type is, & will first create a zend_reference structure with a zval embedded in it. The value of this zval points to the original The value of zval (if it is a Boolean, integer, or floating point, copy the original value directly), and then change the type of the original zval to IS_REFERENCE, and the value of the original zval points to the newly created zend_reference structure.
typedef struct _zend_reference zend_reference;
struct _zend_reference {
zend_refcounted_h gc;
zval val;
};6. Reference counting
typedef struct _zend_refcounted_h {
uint32_t refcount;
union {
struct {
ZEND_ENDIAN_LOHI_3(
zend_uchar type,
zend_uchar flags,
uint16_t gc_info)
} v;
uint32_t type_info;
} u;
} zend_refcounted_h;$a = "time:" . time(); //$a -> zend_string_1(refcount=1) $b = $a; //$a,$b -> zend_string_1(refcount=2) $c = $b; //$a,$b,$c -> zend_string_1(refcount=3) unset($b); //$b = IS_UNDEF $a,$c -> zend_string_1(refcount=2)
Not all data types use reference counting, long and double directly It is a hard copy, and only those types whose value is a pointer (except interned string, immutable array) can use reference counting. Can be judged by zval.u1.type_flag
7. Copy on write
$a = array(1,2); $b = &$a; $c = $a; //发生分离 $b[] = 3;
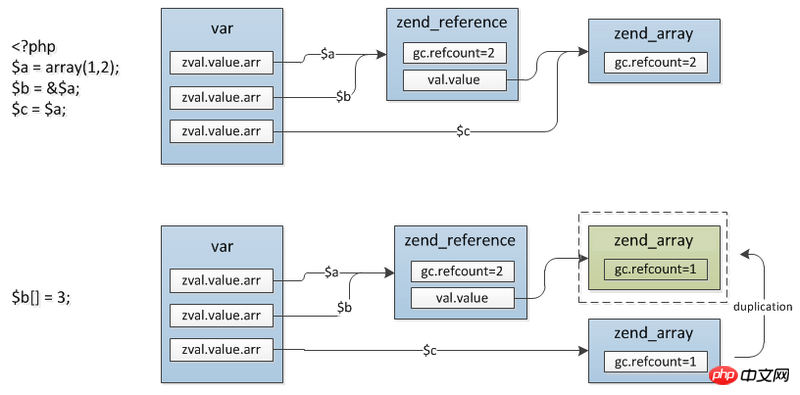
In fact, only string and array are supported,
8. Garbage collection
Recycling of PHP variables There are two main types: active destruction and automatic destruction. Active destruction refers to unset, and automatic destruction is PHP's automatic management mechanism. When returning, the refcount of local variables is subtracted. Even if there is no explicit return, PHP will automatically add this operation. The other is copy-on-write. When the original value is pointed to, the refcount of the old value after the disconnection will also be checked.
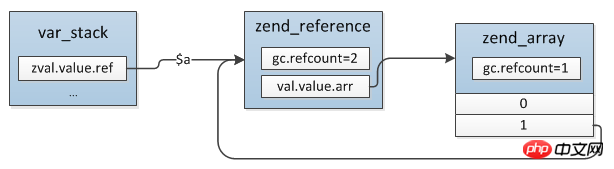
$a = [1]; $a[] = &$a; unset($a);
Reference relationship before unset($a):
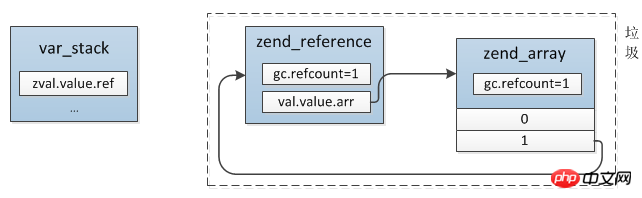
Related recommendations:
PHP7 Kernel Analysis 1 CGI and FastCGI
PHP7 Kernel Analysis 2 I/O Model
The above is the detailed content of PHP7 Kernel Analysis 3 Variables. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1663
1663
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1313
1313
 25
25
 1263
1263
 29
29
 1236
1236
 24
24
 Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JWT is an open standard based on JSON, used to securely transmit information between parties, mainly for identity authentication and information exchange. 1. JWT consists of three parts: Header, Payload and Signature. 2. The working principle of JWT includes three steps: generating JWT, verifying JWT and parsing Payload. 3. When using JWT for authentication in PHP, JWT can be generated and verified, and user role and permission information can be included in advanced usage. 4. Common errors include signature verification failure, token expiration, and payload oversized. Debugging skills include using debugging tools and logging. 5. Performance optimization and best practices include using appropriate signature algorithms, setting validity periods reasonably,
 Explain late static binding in PHP (static::).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain late static binding in PHP (static::).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Static binding (static::) implements late static binding (LSB) in PHP, allowing calling classes to be referenced in static contexts rather than defining classes. 1) The parsing process is performed at runtime, 2) Look up the call class in the inheritance relationship, 3) It may bring performance overhead.
 Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Causes and solutions for errors when using PECL to install extensions in Docker environment When using Docker environment, we often encounter some headaches...
 What are PHP magic methods (__construct, __destruct, __call, __get, __set, etc.) and provide use cases?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:03 AM
What are PHP magic methods (__construct, __destruct, __call, __get, __set, etc.) and provide use cases?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:03 AM
What are the magic methods of PHP? PHP's magic methods include: 1.\_\_construct, used to initialize objects; 2.\_\_destruct, used to clean up resources; 3.\_\_call, handle non-existent method calls; 4.\_\_get, implement dynamic attribute access; 5.\_\_set, implement dynamic attribute settings. These methods are automatically called in certain situations, improving code flexibility and efficiency.
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is widely used in e-commerce, content management systems and API development. 1) E-commerce: used for shopping cart function and payment processing. 2) Content management system: used for dynamic content generation and user management. 3) API development: used for RESTful API development and API security. Through performance optimization and best practices, the efficiency and maintainability of PHP applications are improved.
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.




