Encountering low performance issues with PHP's in_array
PHP performance is constantly improving. However, if you use it improperly or if you are not careful, you may still step into the pitfalls of PHP's internal implementation. I encountered a performance problem a few days ago
The performance of PHP has been improving. However, if you use it improperly or if you are not careful, you may still step into the pitfalls of PHP's internal implementation. I encountered a performance problem a few days ago.
The thing is like this. A colleague reported that one of our interfaces took 5 seconds to return each time. We reviewed the code together, and we were "surprised" to find that it was called in a loop (about 900 times). A read cache operation was performed, and the cache key did not change, so we moved this code outside the loop and tested again. The interface return time dropped to 2 seconds, woohoo! Although it has doubled, it is obviously not a result we can accept!
The amount of code that caused the performance problem was not large. After we eliminated the IO problem, we wrote a test code, and sure enough, the problem reappeared quickly.
Copy code The code is as follows:
<?php
$y="1800";
$x = array();
for($j=0;$j<2000;$j++){
$x[]= "{$j}";
}
for($i=0;$i<3000;$i++){
if(in_array($y,$x)){
continue;
}
}
?>
shell$ time /usr/local/php/bin/php test.php
real 0m1.132s
user 0m1.118s
sys 0m0.015s
Yes, we are using string numbers, and this is what they look like when taken out from the cache La! So here it is specially converted into a string (if it is a number directly, this problem will not occur, you can verify it by yourself). It can be seen that the time consumed is 1 second, which is only 3000 cycles. The subsequent sys time is also destined that we will not get any effective information using strace.
shell$ strace -ttt -o xxx /usr/local/php/bin/php test.php
shell$ less xxx 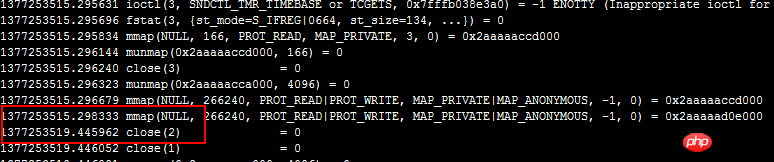
us I only saw that the delay between these two system calls was very large, but I didn't know what was done? I am at a loss. Fortunately, in addition to strace, the debugging tools under Linux also include ltrace (of course, there are also dtrace and ptrace, which are beyond the scope of this article and will be omitted).
Quote: strace is used to track the system calls or signal generation of a process, while ltrace is used to track the process of calling library functions (via IBM developerworks).
In order to eliminate interference factors, we directly assign $x to the form of array(“0″,”1″,”2″,…) to avoid excessive malloc calls affecting the results. Execute
shell$ ltrace -c /usr/local/php/bin/php test.php
As shown in Figure 2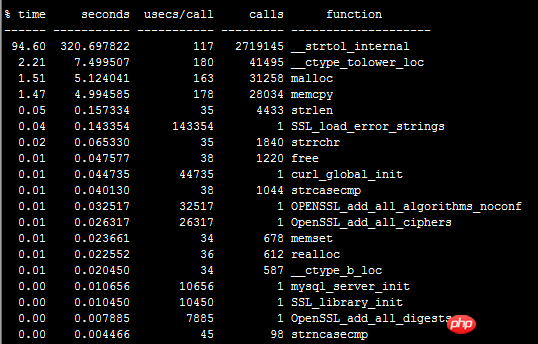
We saw that the library function __strtol_internal is called very frequently, reaching 94%, which is too exaggerated. Then I checked what this library function __strtol_internal does. It turns out to be an alias for strtol. Simply put, it is Convert the string into a long integer. It can be guessed that the PHP engine has detected that this is a string number, so it expects to convert them into a long integer for comparison. This conversion process consumes too much time, we execute again:
Copy code The code is as follows:
shell$ ltrace -e "__strtol_internal" /usr/local/php/bin/php test. php
can easily catch a large number of calls like the one below. At this point, the problem has been found. The loose comparison of in_array will convert two character numeric strings first. Compare the long integer type again, but I don’t know that the performance is consumed on this. 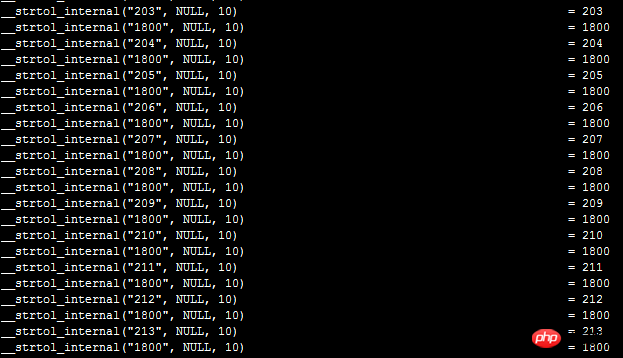
Knowing the crux of the problem, we have many solutions. The simplest one is to add the third parameter to in_array to true, which becomes a strict comparison, while also To compare types, this avoids PHP's clever conversion types, and it runs much faster. The code is as follows:
Copy code The code is as follows:
<?php
$y="1800";
$x = array();
for($j=0;$j<2000;$j++){
$x[]= "{$j}";
}
for($i=0;$i<3000;$i++){
if(in_array($y,$x,true)){
continue;
}
}
?>Copy code The code is as follows:
shell$ time /usr/local/php/bin/php test.php
real 0m0 .267s
user 0m0.247s
sys 0m0.020s
Many times faster! ! ! It can be seen that the sys time consumption has hardly changed much. When we ltrace again, we still need to assign $x directly to eliminate the interference of malloc calls. Because in our actual application, we pull it out from the cache at once, so there is no such loop in the sample code to apply for memory.
Execute again
Copy code The code is as follows:
shell$ ltrace -c /usr/local/php/bin /php test.php
#As shown below:
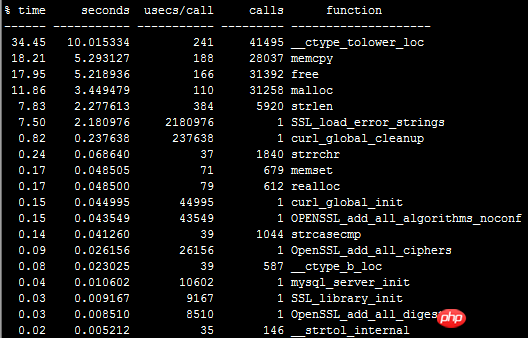
__ctype_tolower_loc takes up the most time! I checked what the library function __ctype_tolower_loc does: the simple understanding is to convert strings into lowercase, so does this mean that in_array comparison strings are not case-sensitive? In fact, this function call has little connection with our in_array. Regarding the implementation of in_array, it is better to take a look at the source code of PHP. I will probably understand it more thoroughly. Okay, I can’t go on. Welcome to communicate with me. , please correct me if I write something wrong.
——————2013.08.29 dividing line——————————
I read the following source code of PHP 5.4.10 in the evening, and I am interested in in_array It’s so big, haha. It’s located at line 1248 of ./ext/standard/array.c. You can see that it calls the php_search_array function. The array_serach below also adjusts this, but the last parameter is different! After some tracking, in the case of in_array loose comparison, he finally called the function zendi_smart_strcmp (really a "smart" function) for comparison, located in ./Zend/zend_operators.c. We used ltrace to convert a large number of captured data into integers. The operation is the behavior of is_numeric_string_ex. 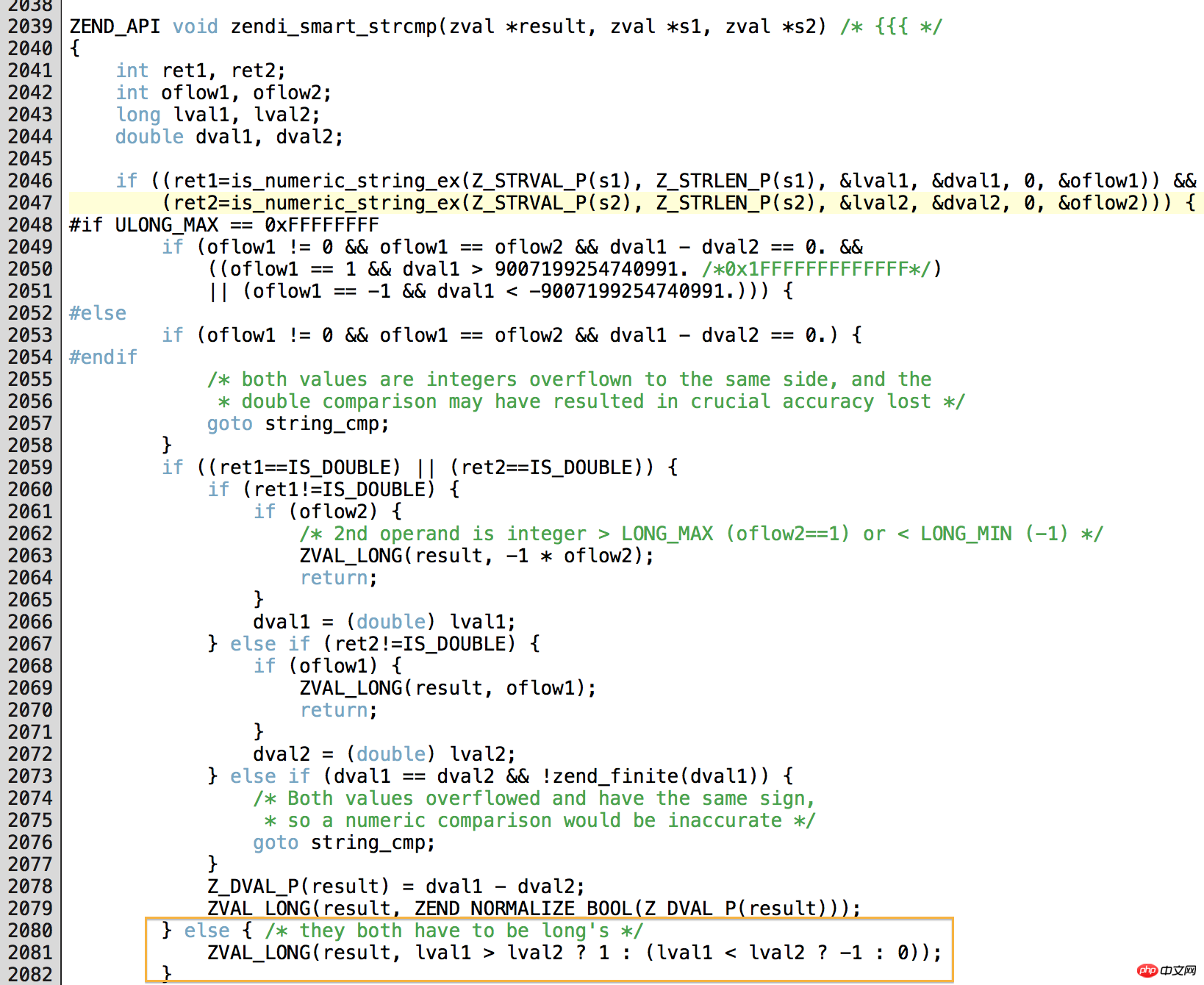
The function is_numeric_string_ex is defined in ./Zend/zend_operators.h. After a bunch of judgments and conversions, strtol is called on line 232, that is The system function we mentioned in the article converts a string into a long integer. There are pictures and the truth
Related recommendations:
Once again, I encountered garbled characters
when PHP inserted Chinese into MYSQL and displayed it.
The above is the detailed content of Encountering low performance issues with PHP's in_array. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1672
1672
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1332
1332
 25
25
 1277
1277
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is widely used in e-commerce, content management systems and API development. 1) E-commerce: used for shopping cart function and payment processing. 2) Content management system: used for dynamic content generation and user management. 3) API development: used for RESTful API development and API security. Through performance optimization and best practices, the efficiency and maintainability of PHP applications are improved.
 The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
PHP is still dynamic and still occupies an important position in the field of modern programming. 1) PHP's simplicity and powerful community support make it widely used in web development; 2) Its flexibility and stability make it outstanding in handling web forms, database operations and file processing; 3) PHP is constantly evolving and optimizing, suitable for beginners and experienced developers.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 PHP: Handling Databases and Server-Side Logic
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP: Handling Databases and Server-Side Logic
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP uses MySQLi and PDO extensions to interact in database operations and server-side logic processing, and processes server-side logic through functions such as session management. 1) Use MySQLi or PDO to connect to the database and execute SQL queries. 2) Handle HTTP requests and user status through session management and other functions. 3) Use transactions to ensure the atomicity of database operations. 4) Prevent SQL injection, use exception handling and closing connections for debugging. 5) Optimize performance through indexing and cache, write highly readable code and perform error handling.




