(PHP7 Kernel Analysis-1) CGI and FastCGI
CGI: It is a protocol for data exchange between Web Server and Web Application.
FastCGI: Same as CGI, it is a communication protocol, but it has some optimizations in efficiency than CGI.
PHP-CGI: It is the interface program of PHP (Web Application) to the CGI protocol provided by Web Server.
PHP-FPM: It is the interface program of the FastCGI protocol provided by PHP (Web Application) to the Web Server. In addition, it also provides relatively intelligent task management
CGI workflow
1. If the client requests index.html, then the Web Server will find this file in the file system and send it to the browser. What is distributed here is static data.
2. When the Web Server receives the index.php request, it will start the corresponding CGI program, which is the PHP parser. Next, the PHP parser will parse the php.ini file, initialize the execution environment, then process the request, return the processed result in the format specified by CGI, exit the process, and the Web server will return the result to the browser.
FastCGI workflow
1. If the client requests index.html, then the Web Server will find this file in the file system and send it to the browser. What is distributed here is static data.
2. When the Web Server receives the index.php request, the FastCGI program (FastCGI initializes the execution environment when it starts, and each CGI process pool shares the execution environment) is in the CGI process pool. Select a CGI process to process the request, return the processed result in the format specified by CGI, and continue to wait for the next request.
Basic implementation of PHP-FPM
1. The implementation of PHP-FPM is to create a master process, create a worker pool in the master process and let it listen to the socket, and then Fork multiple sub-processes (work), and each of these sub-processes accepts the request. The processing of the sub-process is very simple. It blocks on accept after startup. When a request arrives, it starts to read the request data. After the reading is completed, it starts processing and then Return, no other requests will be received during this period, which means that the sub-process of PHP-FPM can only respond to one request at the same time. Only after this request is processed, the next request will be accepted
2. There is no direct communication between the PHP-FPM master process and the worker process. The master obtains the information of the worker process through shared memory, such as the current status of the worker process, the number of processed requests, etc. When the master process wants to kill a worker process, Notify the worker process by sending a signal.
3.PHP-FPM can monitor multiple ports at the same time. Each port corresponds to a worker pool, and each pool corresponds to multiple worker processes
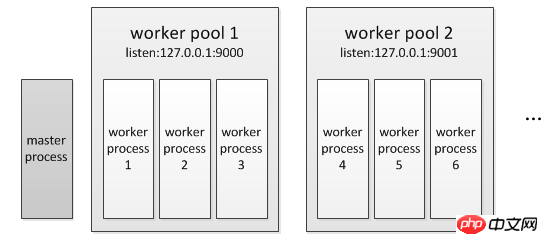
Worker workflow
1. Waiting for the request: The worker process is blocked in fcgi_accept_request() waiting for the request;
2. Parsing the request: After the fastcgi request arrives, it is The worker receives, then starts to receive and parse the request data until the request data is completely arrived;
3. Request initialization: Execute php_request_startup(), this stage will call each extension: PHP_RINIT_FUNCTION();
4. Compile, Execution: The compilation and execution of the PHP script is completed by php_execute_script();
5. Shut down the request: After the request is completed, execute php_request_shutdown(). This stage will call each extension: PHP_RSHUTDOWN_FUNCTION(), and then enter step (1) to wait. Next request.
Master process management
1.static: This method is relatively simple. At startup, the master forks out the corresponding number of worker processes according to the pm.max_children configuration, that is, worker The number of processes is fixed
2.dynamic: Dynamic process management, first initialize a certain number of workers according to pm.start_servers when fpm starts. During operation, if the master finds that the number of idle workers is lower than the pm.min_spare_servers configuration number (indicating that there are too many requests and the worker cannot handle them), the worker process will be forked, but the total number of workers cannot exceed pm.max_children. If the master finds that the number of idle workers exceeds pm.max_spare_servers (indicating that there are too many idle workers) ) will kill some workers to avoid taking up too many resources. The master uses these 4 values to control the number of workers
3.ondemand: This method is generally rarely used and does not allocate worker processes at startup. Wait until there is a request and then notify the master process to fork the worker process. The total number of workers does not exceed pm.max_children. The worker process will not exit immediately after the processing is completed. It will exit when the idle time exceeds pm.process_idle_timeout
PHP-FPM Event Manager
1.sp[1] Pipeline readable event: This event is used by master to process signals
2.fpm_pctl_perform_idle_server_maintenance_heartbeat(): This It is the main event in the implementation of process management. The master starts a timer, which is triggered every 1s. It is mainly used for worker management in dynamic and ondemand modes. The master will regularly check the number of worker processes in each worker pool and implement it through this timer. Control of the number of workers
3.fpm_pctl_heartbeat(): This event is used to limit the maximum time it takes for a worker to process a single request. There is a request_terminate_timeout configuration item in php-fpm.conf. If the total time it takes for a worker to process a request exceeds this value, then The master will send the kill -TERM signal to the worker process to kill the worker process. The unit of this configuration is seconds. The default value is 0, which means turning off this mechanism.
4.fpm_pctl_on_socket_accept(): The new value monitored by the master in ondemand mode The event of request arrival, because in ondemand mode fpm will not pre-create workers when it starts, and a child process will be generated only when there is a request, so the master process needs to be notified when the request arrives
The above is the detailed content of (PHP7 Kernel Analysis-1) CGI and FastCGI. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1425
1425
 52
52
 1328
1328
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1253
1253
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is widely used in e-commerce, content management systems and API development. 1) E-commerce: used for shopping cart function and payment processing. 2) Content management system: used for dynamic content generation and user management. 3) API development: used for RESTful API development and API security. Through performance optimization and best practices, the efficiency and maintainability of PHP applications are improved.
 The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
PHP is still dynamic and still occupies an important position in the field of modern programming. 1) PHP's simplicity and powerful community support make it widely used in web development; 2) Its flexibility and stability make it outstanding in handling web forms, database operations and file processing; 3) PHP is constantly evolving and optimizing, suitable for beginners and experienced developers.
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP is used to build dynamic websites, and its core functions include: 1. Generate dynamic content and generate web pages in real time by connecting with the database; 2. Process user interaction and form submissions, verify inputs and respond to operations; 3. Manage sessions and user authentication to provide a personalized experience; 4. Optimize performance and follow best practices to improve website efficiency and security.




