Use of Mybatis (mapper interface method)
Using the Mapper interface, there is no need to write an interface implementation class, and the database operation can be completed directly, which is simple and convenient. In order to help everyone learn the Mapper interface better, the editor has summarized some knowledge points about the Mapper interface, hoping to help those in need.
First go to the structure diagram: 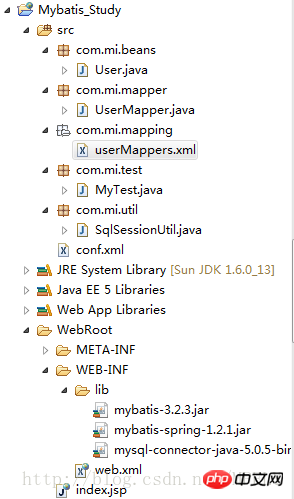
The following is the specific code:
1. User.java
实体类中的的get/set方法以及构造方法及toString方法就不贴了
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
}2. UserMapper.java
This is the mapper interface, and the idea of interface-oriented programming is still very important. It is also the most important part of this blog post.
The interface definition has the following characteristics:
The Mapper interface method name has the same name as the id of each sql defined in UserMapper.xml.
The input parameter type of the Mapper interface method is the same as the parameterType type of sql defined in UserMapper.xml.
The return type of the Mapper interface is the same as the resultType of sql defined in UserMapper.xml
Pay attention to the method of creating the table, There is annotation @Param
package com.mi.mapper;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;import com.mi.beans.User;public interface UserMapper {
void createTable (@Param("tableName") String tableName); void add(User user); void del(int id); void update(User user);
User getUser(int id);
User[] list();
} 3. userMappers.xml
Need to pay attention here
1. The namespace of the xml file must be written as mapper interface The path is as follows.
<mapper namespace="com.mi.mapper.UserMapper">
2. When writing the statement to dynamically create a table, write ${tableName} instead of #{}. Click to view the difference between the two
create table ${tableName}...The following is the complete code: including table creation, CRUD
<mapper namespace="com.mi.mapper.UserMapper">
create table ${tableName} (id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(20),age int)
insert into t_user(name,age) value(#{name},#{age})
delete from t_user where id = #{id}
update t_user set name=#{name},age=#{age} where id=#{id}
4, conf.xml
Two things need to be configured here
Configuration JDBC connection
Configuration mapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 配置数据库连接信息 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 注册userMapper.xml文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/mi/mapping/userMappers.xml"/>
</mappers></configuration>5. SqlSessionUtil.java
I write here A tool class is created, the main purpose is to get the sqlSession, because every time the database is operated in the future, it needs to be written once, so it is encapsulated once.
package com.mi.util;import java.io.InputStream;import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;import org.apache.ibatis.
session.SqlSessionFactory;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;public class SqlSessionUtil
{
public static SqlSession getSqlSession() throws Exception{
String resource = "conf.xml";
//使用类加载器加载mybatis的配置文件(它也加载关联的映射文件)
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//构建sqlSession的工厂
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
//创建能执行映射文件中sql的sqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession();
return sqlSession;
}
}6. MyTest.java
This is a test class. Through the above tool class sqlSession, the most important thing is the following sentence
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
MyBatis implements the mapper interface through dynamic proxy. After that, it will be easy to handle. Execute the interface Just use the prepared method.
Be careful not to forget sqlSession.commit() and sqlSession.close(). Otherwise, although no error will be reported during execution, there will be no changes in the database.
这里我只执行了创建表的方法.
package com.mi.test;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;import com.mi.beans.User;import com.mi.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.mi.util.SqlSessionUtil;public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
userMapper.createTable("t_user");
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
}
Using the Mapper interface, there is no need to write an interface implementation class, and the database operation can be completed directly, which is simple and convenient.
First go to the structure diagram: 
The following is the specific code:
1. User.java
实体类中的的get/set方法以及构造方法及toString方法就不贴了public class User { private int id; private String name; private int age;2. UserMapper .java
This is the mapper interface, and the idea of interface-oriented programming is still very important. It is also the most important part of this blog post.
The interface definition has the following characteristics:
The Mapper interface method name has the same name as the id of each sql defined in UserMapper.xml.
The input parameter type of the Mapper interface method is the same as the parameterType type of sql defined in UserMapper.xml.
The return type of the Mapper interface is the same as the resultType of sql defined in UserMapper.xml
Pay attention to the method of creating the table, There is annotation @Param
package com.mi.mapper;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;import com.mi.beans.User;public interface UserMapper {
void createTable (@Param("tableName") String tableName); void add(User user); void del(int id); void update(User user);
User getUser(int id);
User[] list();
} 3. userMappers.xml
Need to pay attention here
1. The namespace of the xml file must be written as mapper interface The path is as follows.
<mapper namespace="com.mi.mapper.UserMapper">
2. When writing the statement to dynamically create a table, write ${tableName} instead of #{}. Click to view the difference between the two
create table ${tableName}...The following is the complete code: including table creation, CRUD
<mapper namespace="com.mi.mapper.UserMapper">
create table ${tableName} (id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(20),age int)
insert into t_user(name,age) value(#{name},#{age})
delete from t_user where id = #{id}
update t_user set name=#{name},age=#{age} where id=#{id}
4, conf.xml
Two things need to be configured here
Configuration JDBC connection
Configuration mapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 配置数据库连接信息 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 注册userMapper.xml文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/mi/mapping/userMappers.xml"/>
</mappers></configuration>5. SqlSessionUtil.java
I write here A tool class is created, the main purpose is to get the sqlSession, because every time the database is operated in the future, it needs to be written once, so it is encapsulated once.
package com.mi.util;import java.io.InputStream;import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;public class SqlSessionUtil
{
public static SqlSession getSqlSession() throws Exception{
String resource = "conf.xml";
//使用类加载器加载mybatis的配置文件(它也加载关联的映射文件)
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//构建sqlSession的工厂
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
//创建能执行映射文件中sql的sqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession();
return sqlSession;
}
}6. MyTest.java
This is a test class. Through the above tool class sqlSession, the most important thing is the following sentence
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
MyBatis implements the mapper interface through dynamic proxy. After that, it will be easy to handle. Execute the interface Just use the prepared method.
Be careful not to forget sqlSession.commit() and sqlSession.close(). Otherwise, although no error will be reported during execution, there will be no changes in the database.
这里我只执行了创建表的方法.
package com.mi.test;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;import com.mi.beans.User;import com.mi.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.mi.util.SqlSessionUtil;public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
userMapper.createTable("t_user");
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
}Related recommendations:
Mybatis paging plug-in pageHelper example detailed explanation
##Oracle combines Mybatis to implement 10 pieces of data from the table
Spring Boot, Mybatis, Redis quickly build modern Web projects
The above is the detailed content of Use of Mybatis (mapper interface method). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1670
1670
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1274
1274
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Detailed explanation of the Set tag function in MyBatis dynamic SQL tags
Feb 26, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Interpretation of MyBatis dynamic SQL tags: Detailed explanation of Set tag usage MyBatis is an excellent persistence layer framework. It provides a wealth of dynamic SQL tags and can flexibly construct database operation statements. Among them, the Set tag is used to generate the SET clause in the UPDATE statement, which is very commonly used in update operations. This article will explain in detail the usage of the Set tag in MyBatis and demonstrate its functionality through specific code examples. What is Set tag Set tag is used in MyBati
 What are the internal interfaces of a computer motherboard? Recommended introduction to the internal interfaces of a computer motherboard
Mar 12, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
What are the internal interfaces of a computer motherboard? Recommended introduction to the internal interfaces of a computer motherboard
Mar 12, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
When we assemble the computer, although the installation process is simple, we often encounter problems in the wiring. Often, users mistakenly plug the power supply line of the CPU radiator into the SYS_FAN. Although the fan can rotate, it may not work when the computer is turned on. There will be an F1 error "CPUFanError", which also causes the CPU cooler to be unable to adjust the speed intelligently. Let's share the common knowledge about the CPU_FAN, SYS_FAN, CHA_FAN, and CPU_OPT interfaces on the computer motherboard. Popular science on the CPU_FAN, SYS_FAN, CHA_FAN, and CPU_OPT interfaces on the computer motherboard 1. CPU_FANCPU_FAN is a dedicated interface for the CPU radiator and works at 12V
 Common programming paradigms and design patterns in Go language
Mar 04, 2024 pm 06:06 PM
Common programming paradigms and design patterns in Go language
Mar 04, 2024 pm 06:06 PM
As a modern and efficient programming language, Go language has rich programming paradigms and design patterns that can help developers write high-quality, maintainable code. This article will introduce common programming paradigms and design patterns in the Go language and provide specific code examples. 1. Object-oriented programming In the Go language, you can use structures and methods to implement object-oriented programming. By defining a structure and binding methods to the structure, the object-oriented features of data encapsulation and behavior binding can be achieved. packagemaini
 Analyze the caching mechanism of MyBatis: compare the characteristics and usage of first-level cache and second-level cache
Feb 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
Analyze the caching mechanism of MyBatis: compare the characteristics and usage of first-level cache and second-level cache
Feb 25, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
Analysis of MyBatis' caching mechanism: The difference and application of first-level cache and second-level cache In the MyBatis framework, caching is a very important feature that can effectively improve the performance of database operations. Among them, first-level cache and second-level cache are two commonly used caching mechanisms in MyBatis. This article will analyze the differences and applications of first-level cache and second-level cache in detail, and provide specific code examples to illustrate. 1. Level 1 Cache Level 1 cache is also called local cache. It is enabled by default and cannot be turned off. The first level cache is SqlSes
 Introduction to PHP interfaces and how to define them
Mar 23, 2024 am 09:00 AM
Introduction to PHP interfaces and how to define them
Mar 23, 2024 am 09:00 AM
Introduction to PHP interface and how it is defined. PHP is an open source scripting language widely used in Web development. It is flexible, simple, and powerful. In PHP, an interface is a tool that defines common methods between multiple classes, achieving polymorphism and making code more flexible and reusable. This article will introduce the concept of PHP interfaces and how to define them, and provide specific code examples to demonstrate their usage. 1. PHP interface concept Interface plays an important role in object-oriented programming, defining the class application
 Solution to NotImplementedError()
Mar 01, 2024 pm 03:10 PM
Solution to NotImplementedError()
Mar 01, 2024 pm 03:10 PM
The reason for the error is in python. The reason why NotImplementedError() is thrown in Tornado may be because an abstract method or interface is not implemented. These methods or interfaces are declared in the parent class but not implemented in the child class. Subclasses need to implement these methods or interfaces to work properly. How to solve this problem is to implement the abstract method or interface declared by the parent class in the child class. If you are using a class to inherit from another class and you see this error, you should implement all the abstract methods declared in the parent class in the child class. If you are using an interface and you see this error, you should implement all methods declared in the interface in the class that implements the interface. If you are not sure which
 Application of interfaces and abstract classes in design patterns in Java
May 01, 2024 pm 06:33 PM
Application of interfaces and abstract classes in design patterns in Java
May 01, 2024 pm 06:33 PM
Interfaces and abstract classes are used in design patterns for decoupling and extensibility. Interfaces define method signatures, abstract classes provide partial implementation, and subclasses must implement unimplemented methods. In the strategy pattern, the interface is used to define the algorithm, and the abstract class or concrete class provides the implementation, allowing dynamic switching of algorithms. In the observer pattern, interfaces are used to define observer behavior, and abstract or concrete classes are used to subscribe and publish notifications. In the adapter pattern, interfaces are used to adapt existing classes. Abstract classes or concrete classes can implement compatible interfaces, allowing interaction with original code.
 Real-time monitoring of SQL output in the MyBatis console
Feb 25, 2024 pm 03:48 PM
Real-time monitoring of SQL output in the MyBatis console
Feb 25, 2024 pm 03:48 PM
MyBatis is a popular persistence layer framework that provides convenient SQL mapping and database operation functions, allowing developers to interact with the database more efficiently. In the actual development process, we sometimes need to print out the SQL statements executed by MyBatis on the console in real time to better debug and optimize SQL queries. This article will introduce how to realize real-time printing of SQL on the console in MyBatis and provide specific code examples. First, we need to add My




