How to query MySQL concurrently with PHP
I have been studying PHP recently and I like it very much. I encountered the problem of concurrent query of MySQL by PHP. This article mainly introduces the example code of concurrent query of MySQL by PHP. I think it is quite good. Now I will share it with you and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor to take a look, I hope it can help everyone.
Synchronous query
This is our most common calling mode. The client calls Query[function], initiates a query command, waits for the result to be returned, and reads the result; Send the second query command, wait for the result to be returned, and read the result. The total time taken will be the sum of the time of the two queries. Simplify the process, for example, as shown in the figure below:
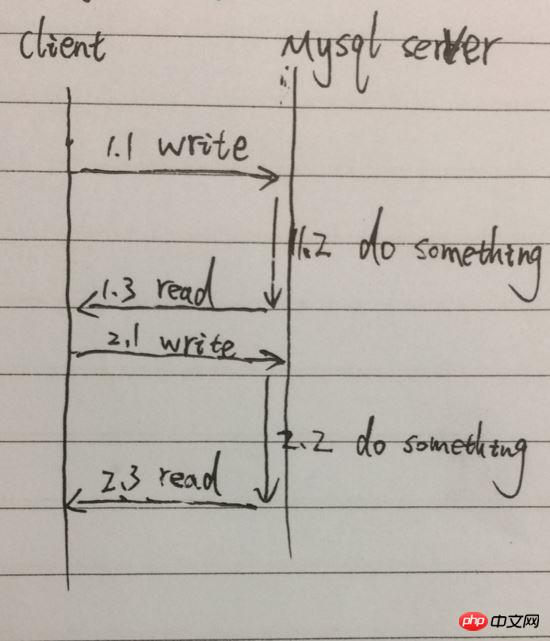
As shown in the figure, from 1.1 to 1.3 is the call of a Query [function]. Two queries require serialization of 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, especially 1.2 and 2.2 will block waiting, and the process cannot do other things.
The advantage of synchronous calling is that it conforms to our intuitive thinking and is simple to call and process. The disadvantage is that the process is blocked waiting for the result to be returned, adding extra running time.
If there are multiple query requests, or the process has other things to deal with, then it is obviously possible to make reasonable use of the waiting time and improve the processing capacity of the process.
Split
Now, we break the Query[function] into pieces. The client returns immediately after 1.1. The client skips 1.2 and has data in 1.3. Read the data after reaching it. In this way, the process is freed from the original 1.2 stage and can do more things, such as...initiate another sql query [2.1], have you seen the prototype of concurrent query?
Concurrent query
Compared to the synchronous query, the next query is initiated after the previous query is completed. Concurrent queries can be initiated immediately after the previous query request is initiated. Initiate the next query request. Simplify the process, as shown below:
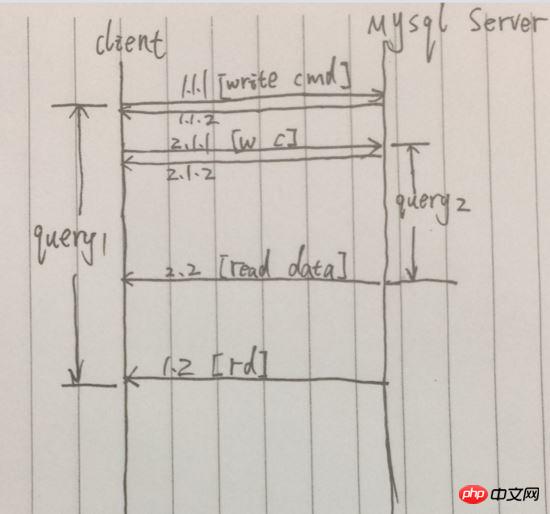
Example picture, after successfully sending the request in 1.1.1, [1.1.2] is returned immediately, and the final query result is returned in Distant 1.2. However, between 1.1.1 and 1.2, another query request was initiated. During this time period, two query requests were initiated at the same time. 2.2 arrived before 1.2, so the total time of the two queries was only equivalent to The time of the first query.
The advantage of concurrent query is that it can improve the utilization rate of the process, avoid blocking waiting for the server to process the query, and shorten the time of multiple queries. But the shortcomings are also obvious. To initiate N concurrent queries, you need to establish N database links. For applications with database connection pools, this situation can be avoided.
Degeneration
Ideally, we want to concurrently run N queries, and the total time consumption is equal to the query with the longest query time. But it is also possible that concurrent queries will [degenerate] into [synchronous queries]. What? In the example diagram, if 1.2 is returned before 2.1.1, then the concurrent query will [degenerate] into [synchronous query], but the cost will be higher than that of synchronous query.
Multiplexing
Initiate query1
Initiate query2
Initiate query3
......
Waiting for query1, query2, query3
-
Read query2 results
Read query1 results
Read query3 results
So, how to wait and know when the query results are returned, and which query results are returned?
Call read on each query IO? If it encounters blocking IO, it will be blocked on one IO, and other IOs will have results returned and cannot be processed. So, if it is non-blocking IO, there is no need to worry about being blocked on one of the IOs. It is indeed the case, but it will cause continuous polling and judgment and waste CPU resources.
For this situation, multiplexing can be used to poll multiple IOs.
PHP implements concurrent query MySQL
PHP's mysqli (mysqlnd driver) provides multiplexed polling IO (mysqli_poll) and asynchronous query (MYSQLI_ASYNC, mysqli_reap_async_query), Use these two features to implement concurrent queries, sample code:
<?php
$sqls = array(
'SELECT * FROM `mz_table_1` LIMIT 1000,10',
'SELECT * FROM `mz_table_1` LIMIT 1010,10',
'SELECT * FROM `mz_table_1` LIMIT 1020,10',
'SELECT * FROM `mz_table_1` LIMIT 10000,10',
'SELECT * FROM `mz_table_2` LIMIT 1',
'SELECT * FROM `mz_table_2` LIMIT 5,1'
);
$links = [];
$tvs = microtime();
$tv = explode(' ', $tvs);
$start = $tv[1] * 1000 + (int)($tv[0] * 1000);
// 链接数据库,并发起异步查询
foreach ($sqls as $sql) {
$link = mysqli_connect('127.0.0.1', 'root', 'root', 'dbname', '3306');
$link->query($sql, MYSQLI_ASYNC); // 发起异步查询,立即返回
$links[$link->thread_id] = $link;
}
$llen = count($links);
$process = 0;
do {
$r_array = $e_array = $reject = $links;
// 多路复用轮询IO
if(!($ret = mysqli_poll($r_array, $e_array, $reject, 2))) {
continue;
}
// 读取有结果返回的查询,处理结果
foreach ($r_array as $link) {
if ($result = $link->reap_async_query()) {
print_r($result->fetch_row());
if (is_object($result))
mysqli_free_result($result);
} else {
}
// 操作完后,把当前数据链接从待轮询集合中删除
unset($links[$link->thread_id]);
$link->close();
$process++;
}
foreach ($e_array as $link) {
die;
}
foreach ($reject as $link) {
die;
}
}while($process < $llen);
$tvs = microtime();
$tv = explode(' ', $tvs);
$end = $tv[1] * 1000 + (int)($tv[0] * 1000);
echo $end - $start,PHP_EOL;mysqli_poll source code:
#ifndef PHP_WIN32
#define php_select(m, r, w, e, t) select(m, r, w, e, t)
#else
#include "win32/select.h"
#endif
/* {{{ mysqlnd_poll */
PHPAPI enum_func_status
mysqlnd_poll(MYSQLND **r_array, MYSQLND **e_array, MYSQLND ***dont_poll, long sec, long usec, int * desc_num)
{
struct timeval tv;
struct timeval *tv_p = NULL;
fd_set rfds, wfds, efds;
php_socket_t max_fd = 0;
int retval, sets = 0;
int set_count, max_set_count = 0;
DBG_ENTER("_mysqlnd_poll");
if (sec < 0 || usec < 0) {
php_error_docref(NULL, E_WARNING, "Negative values passed for sec and/or usec");
DBG_RETURN(FAIL);
}
FD_ZERO(&rfds);
FD_ZERO(&wfds);
FD_ZERO(&efds);
// 从所有mysqli链接中获取socket链接描述符
if (r_array != NULL) {
*dont_poll = mysqlnd_stream_array_check_for_readiness(r_array);
set_count = mysqlnd_stream_array_to_fd_set(r_array, &rfds, &max_fd);
if (set_count > max_set_count) {
max_set_count = set_count;
}
sets += set_count;
}
// 从所有mysqli链接中获取socket链接描述符
if (e_array != NULL) {
set_count = mysqlnd_stream_array_to_fd_set(e_array, &efds, &max_fd);
if (set_count > max_set_count) {
max_set_count = set_count;
}
sets += set_count;
}
if (!sets) {
php_error_docref(NULL, E_WARNING, *dont_poll ? "All arrays passed are clear":"No stream arrays were passed");
DBG_ERR_FMT(*dont_poll ? "All arrays passed are clear":"No stream arrays were passed");
DBG_RETURN(FAIL);
}
PHP_SAFE_MAX_FD(max_fd, max_set_count);
// select轮询阻塞时间
if (usec > 999999) {
tv.tv_sec = sec + (usec / 1000000);
tv.tv_usec = usec % 1000000;
} else {
tv.tv_sec = sec;
tv.tv_usec = usec;
}
tv_p = &tv;
// 轮询,等待多个IO可读,php_select是select的宏定义
retval = php_select(max_fd + 1, &rfds, &wfds, &efds, tv_p);
if (retval == -1) {
php_error_docref(NULL, E_WARNING, "unable to select [%d]: %s (max_fd=%d)",
errno, strerror(errno), max_fd);
DBG_RETURN(FAIL);
}
if (r_array != NULL) {
mysqlnd_stream_array_from_fd_set(r_array, &rfds);
}
if (e_array != NULL) {
mysqlnd_stream_array_from_fd_set(e_array, &efds);
}
// 返回可操作的IO数量
*desc_num = retval;
DBG_RETURN(PASS);
}Concurrent query operation results
In order to see the effect more intuitively, I found a table with 130 million data volumes and has not been optimized for operation.
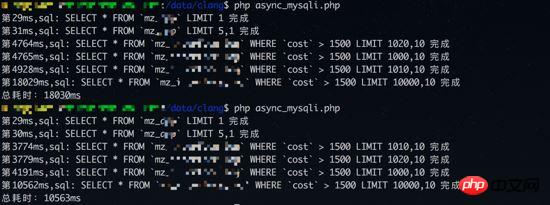
Concurrent query results:
Synchronous query results:
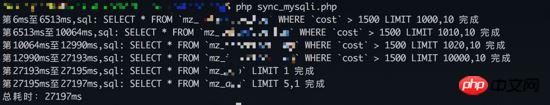
From From the results, the total time consumption of synchronous query is the accumulation of the time of all queries; and the total time consumption of concurrent query is actually the query with the longest time (the fourth query time of synchronous query is a few seconds) , consistent with the total time consumption of concurrent queries), and the query order of concurrent queries and the order in which results arrive are different.
Comparison of multiple queries with shorter query times
Use multiple sql queries with shorter query times for comparison
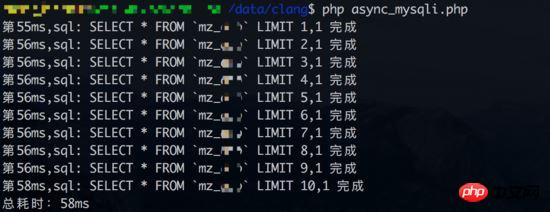
Concurrent query test 1 Result (database link time is also counted):
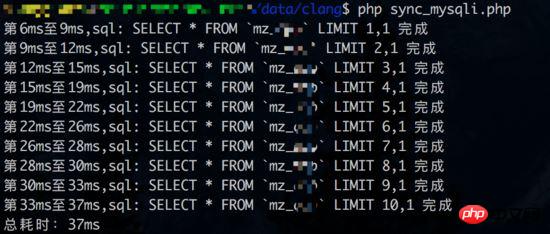
Result of synchronous query (database link time is also counted):
Concurrent query test 2 results (database link time is not counted):
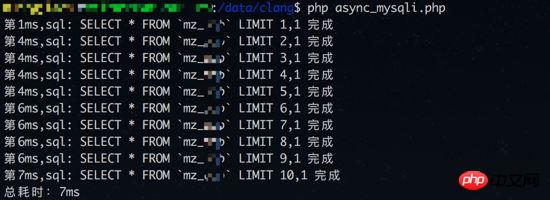
Judging from the results, concurrent query test 1 did not benefit. From the perspective of synchronous queries, each query takes about 3-4ms. But if the database connection time is not included in the statistics (synchronous query only has one database connection), the advantages of concurrent query can be reflected again.
Conclusion
Here we discussed the implementation of concurrent query MySQL in PHP, and intuitively understood the advantages and disadvantages of concurrent query from the experimental results. The time to establish a database connection still accounts for a large proportion of an optimized SQL query. #There is no connection pool, what use do you have?
Related recommendations:
Questions about MySQL concurrent queries
The above is the detailed content of How to query MySQL concurrently with PHP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
I encountered a tricky problem when developing a small application: the need to quickly integrate a lightweight database operation library. After trying multiple libraries, I found that they either have too much functionality or are not very compatible. Eventually, I found minii/db, a simplified version based on Yii2 that solved my problem perfectly.
 The Continued Use of PHP: Reasons for Its Endurance
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The Continued Use of PHP: Reasons for Its Endurance
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:23 AM
What’s still popular is the ease of use, flexibility and a strong ecosystem. 1) Ease of use and simple syntax make it the first choice for beginners. 2) Closely integrated with web development, excellent interaction with HTTP requests and database. 3) The huge ecosystem provides a wealth of tools and libraries. 4) Active community and open source nature adapts them to new needs and technology trends.
 Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Article summary: This article provides detailed step-by-step instructions to guide readers on how to easily install the Laravel framework. Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that speeds up the development process of web applications. This tutorial covers the installation process from system requirements to configuring databases and setting up routing. By following these steps, readers can quickly and efficiently lay a solid foundation for their Laravel project.
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Compared with other programming languages, MySQL is mainly used to store and manage data, while other languages such as Python, Java, and C are used for logical processing and application development. MySQL is known for its high performance, scalability and cross-platform support, suitable for data management needs, while other languages have advantages in their respective fields such as data analytics, enterprise applications, and system programming.






