Introduce the differences and usage of MVC, MVP and MVVM
What are MVC, MVP and MVVM? MVC (Model-View-Controller) is one of the most common software architectures and is widely used in the industry. It's easy to understand on its own, but it's not so easy to explain how it differs from the derived MVP and MVVM architectures.
1. MVC
The MVC pattern means that the software can be divided into three parts.
View: User interface.
Controller: business logic
Model: data storage
The communication method between each part is as follows.
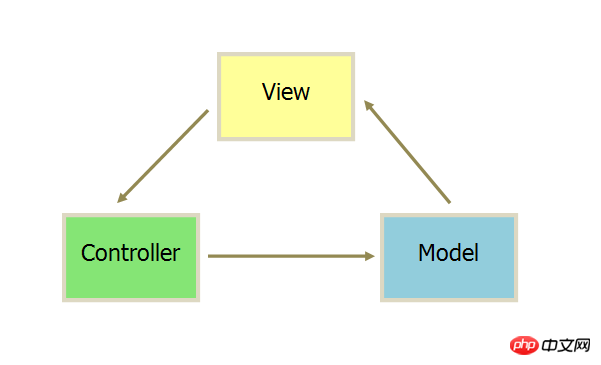
1.View sends instructions to Controller
2.After Controller completes the business logic, it requires Model to change state
3.Model will New data is sent to the View, and the user gets feedback
All communication is one-way.
2. Interactive mode
When accepting user instructions, MVC can be divided into two methods. One is to accept instructions through the View and pass them to the Controller.

The other is to accept instructions directly through the controller.

3. Example: Backbone
Actual projects often adopt a more flexible approach, taking Backbone.js as an example.
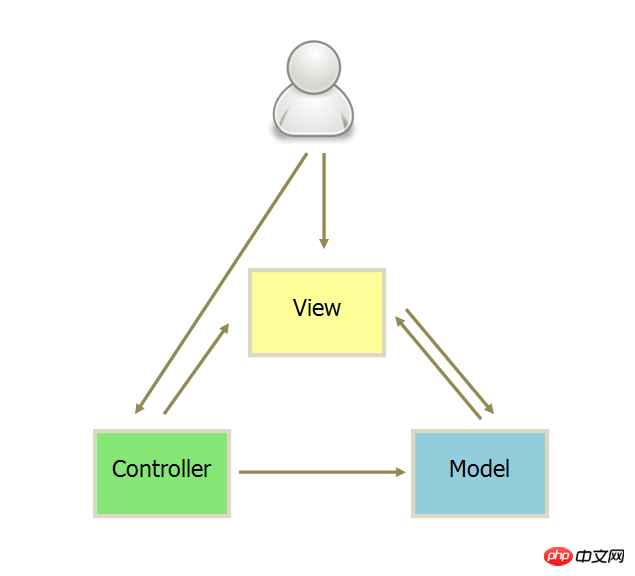
#1. The user can send instructions (DOM events) to the View, and then the View directly requests the Model to change state.
2. The user can also directly send instructions to the Controller (changing the URL triggers the hashChange event), and then the Controller sends it to the View.
3. Controller is very thin and only plays a routing role, while View is very thick and business logic is deployed in View. Therefore, Backbone simply canceled the Controller and only retained a Router.
4. MVP
MVP mode renames Controller to Presenter and changes the communication direction.
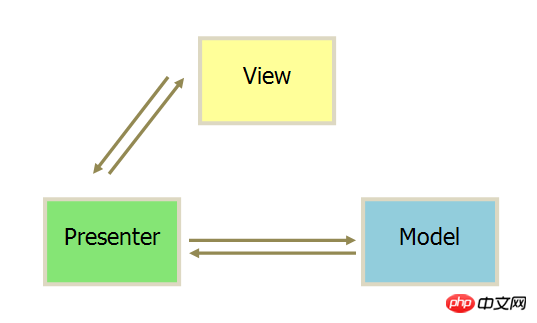
#1. The communication between various parts is two-way.
2. View and Model are not connected, and are passed through Presenter.
3. View is very thin and does not deploy any business logic. It is called "Passive View" (Passive View), that is, it does not have any initiative, while Presenter is very thick and all logic is deployed there.
5. MVVM
The MVVM mode renames Presenter to ViewModel, which is basically the same as the MVP mode.
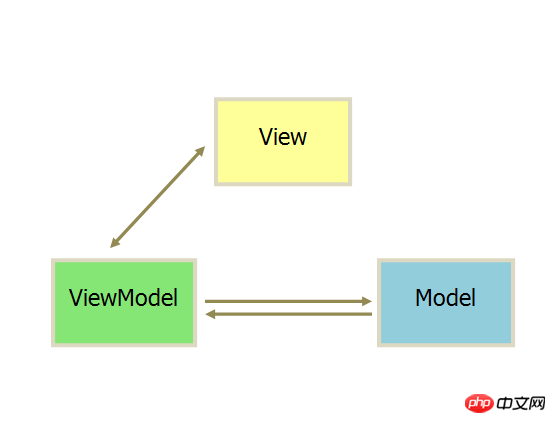
The only difference is that it uses two-way binding (data-binding): changes in View are automatically reflected in ViewModel, and vice versa. Both angular and ember adopt this pattern.
The above is the detailed content of Introduce the differences and usage of MVC, MVP and MVVM. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1425
1425
 52
52
 1327
1327
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1252
1252
 24
24
 How to set password protection for export PDF on PS
Apr 06, 2025 pm 04:45 PM
How to set password protection for export PDF on PS
Apr 06, 2025 pm 04:45 PM
Export password-protected PDF in Photoshop: Open the image file. Click "File"> "Export"> "Export as PDF". Set the "Security" option and enter the same password twice. Click "Export" to generate a PDF file.
 The difference between H5 and mini-programs and APPs
Apr 06, 2025 am 10:42 AM
The difference between H5 and mini-programs and APPs
Apr 06, 2025 am 10:42 AM
H5. The main difference between mini programs and APP is: technical architecture: H5 is based on web technology, and mini programs and APP are independent applications. Experience and functions: H5 is light and easy to use, with limited functions; mini programs are lightweight and have good interactiveness; APPs are powerful and have smooth experience. Compatibility: H5 is cross-platform compatible, applets and APPs are restricted by the platform. Development cost: H5 has low development cost, medium mini programs, and highest APP. Applicable scenarios: H5 is suitable for information display, applets are suitable for lightweight applications, and APPs are suitable for complex functions.
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 Why do you need to call Vue.use(VueRouter) in the index.js file under the router folder?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Why do you need to call Vue.use(VueRouter) in the index.js file under the router folder?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
The necessity of registering VueRouter in the index.js file under the router folder When developing Vue applications, you often encounter problems with routing configuration. Special...
 How to use XPath to search from a specified DOM node in JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
How to use XPath to search from a specified DOM node in JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
Detailed explanation of XPath search method under DOM nodes In JavaScript, we often need to find specific nodes from the DOM tree based on XPath expressions. If you need to...
 What is the difference between syntax for adding columns in different database systems
Apr 09, 2025 pm 02:15 PM
What is the difference between syntax for adding columns in different database systems
Apr 09, 2025 pm 02:15 PM
不同数据库系统添加列的语法为:MySQL:ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name data_type;PostgreSQL:ALTER TABLE table_name ADD COLUMN column_name data_type;Oracle:ALTER TABLE table_name ADD (column_name data_type);SQL Server:ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name data_
 The difference between laravel and thinkphp
Apr 18, 2025 pm 01:09 PM
The difference between laravel and thinkphp
Apr 18, 2025 pm 01:09 PM
Laravel and ThinkPHP are both popular PHP frameworks and have their own advantages and disadvantages in development. This article will compare the two in depth, highlighting their architecture, features, and performance differences to help developers make informed choices based on their specific project needs.
 What are the different ways of promoting H5 and mini programs?
Apr 06, 2025 am 11:03 AM
What are the different ways of promoting H5 and mini programs?
Apr 06, 2025 am 11:03 AM
There are differences in the promotion methods of H5 and mini programs: platform dependence: H5 depends on the browser, and mini programs rely on specific platforms (such as WeChat). User experience: The H5 experience is poor, and the mini program provides a smooth experience similar to native applications. Communication method: H5 is spread through links, and mini programs are shared or searched through the platform. H5 promotion methods: social sharing, email marketing, QR code, SEO, paid advertising. Mini program promotion methods: platform promotion, social sharing, offline promotion, ASO, cooperation with other platforms.




