 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 Recommended 10 commonly used ways to view user usage, welcome to download!
Recommended 10 commonly used ways to view user usage, welcome to download!
Recommended 10 commonly used ways to view user usage, welcome to download!
1. View the currently logged in user information who command: The default output of who includes user name, terminal type, login date and remote host. who /var/log/wtmp You can view every login since the wtmp file was created (1) -b: View the latest startup time of the system (2) -H: Print the title of each column users command: Print the currently logged in users, each displayed user name corresponds to a login session. 2. Check the command history. Each user has a command history. Check $HOME/.bash_history or enter: history3. last command in the terminal to check the user login history. This command will read the /var/log/wtmp file; /var/log/btmp can display remote login information. &n
1. Linux User Management (3) Detailed explanation on how to view user login time and command history

Introduction: 1. View the currently logged in user information who command: The default output of who includes user name, terminal type, login date and remote host. who /var/log/wtmp You can view every login since the wtmp file was created (1) -b: View the latest startup time of the system (2) -H: Print the title of each column users command: Print the currently logged in user , each displayed username corresponds to a login session. 2. View the command history. Each user has
2. How to use the php explode() function
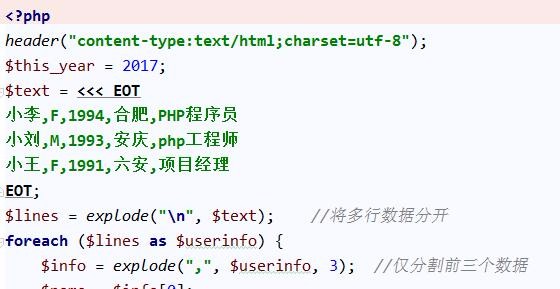
Introduction: To split a string in php, we can use the function explode() to achieve it. Usually in development projects, we want to see what users submit through forms or other methods. Each part of the string for easy classification storage and use. For example, looking at words in a sentence, or splitting a URL or email address into its component parts. At this time we can use the explode() function. This article will introduce how to use the php explode() function
3. [php] 7. Student management System-Administrator View User

## Introduction:: This article mainly introduces [php] 7. Student Management System - Administrators view users. Students who are interested in PHP tutorials can refer to it.
4. PHP5 calls the win system com component to view user information
Introduction: PHP5 calls the win system com component to view User information php5
5. [php] 3. Student Management System-View User


7.
Oracle query table belongs to which user

8.
Modification of expired Oracle user login password #Introduction: Modification of expired Oracle user login password 1. Check which user's proifle is, usually default: sqlgt;SELECT username,PROFILE FROM dba_use 9. Oracle 11g forced password change ORA-28001 processing method Introduction: I received an alarm that the monitoring user could not connect to the database. Oracle prompted the error message ORA-28001: the password has expired. When I went up to check the user status, it turned out to be exp 10. Oracle basic knowledge: View users, user permissions, user table spaces, user default table spaces Introduction: 1. View the corresponding relationship between users and default tablespace www.linuxidc.com@ORCLgt; select username,default_tablespace from dba_users; 2. View table results [Related Q&A recommendations]: mysql - Problems with connecting to Mongod using the monogdb visualization tool robomongo linux - How to view it with the administrator All operations of the user How to use php or thinkphp to record user operations in the mysql database?


The above is the detailed content of Recommended 10 commonly used ways to view user usage, welcome to download!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1669
1669
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 Maintenance Mode in Linux: When and Why to Use It
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Maintenance Mode in Linux: When and Why to Use It
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AM
The timing and reasons for using Linux maintenance mode: 1) When the system starts up, 2) When performing major system updates or upgrades, 3) When performing file system maintenance. Maintenance mode provides a safe and controlled environment, ensuring operational safety and efficiency, reducing impact on users, and enhancing system security.
 Linux Operations: System Administration and Maintenance
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Linux Operations: System Administration and Maintenance
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:10 AM
The key steps in Linux system management and maintenance include: 1) Master the basic knowledge, such as file system structure and user management; 2) Carry out system monitoring and resource management, use top, htop and other tools; 3) Use system logs to troubleshoot, use journalctl and other tools; 4) Write automated scripts and task scheduling, use cron tools; 5) implement security management and protection, configure firewalls through iptables; 6) Carry out performance optimization and best practices, adjust kernel parameters and develop good habits.
 Linux: A Look at Its Fundamental Structure
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Linux: A Look at Its Fundamental Structure
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The basic structure of Linux includes the kernel, file system, and shell. 1) Kernel management hardware resources and use uname-r to view the version. 2) The EXT4 file system supports large files and logs and is created using mkfs.ext4. 3) Shell provides command line interaction such as Bash, and lists files using ls-l.
 Linux: How to Enter Recovery Mode (and Maintenance)
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Linux: How to Enter Recovery Mode (and Maintenance)
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The steps to enter Linux recovery mode are: 1. Restart the system and press the specific key to enter the GRUB menu; 2. Select the option with (recoverymode); 3. Select the operation in the recovery mode menu, such as fsck or root. Recovery mode allows you to start the system in single-user mode, perform file system checks and repairs, edit configuration files, and other operations to help solve system problems.
 Linux's Essential Components: Explained for Beginners
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Linux's Essential Components: Explained for Beginners
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:08 AM
The core components of Linux include the kernel, file system, shell and common tools. 1. The kernel manages hardware resources and provides basic services. 2. The file system organizes and stores data. 3. Shell is the interface for users to interact with the system. 4. Common tools help complete daily tasks.
 Linux Operations: Utilizing the Maintenance Mode
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Linux Operations: Utilizing the Maintenance Mode
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Linux maintenance mode can be entered through the GRUB menu. The specific steps are: 1) Select the kernel in the GRUB menu and press 'e' to edit, 2) Add 'single' or '1' at the end of the 'linux' line, 3) Press Ctrl X to start. Maintenance mode provides a secure environment for tasks such as system repair, password reset and system upgrade.
 Linux: A Deep Dive into Its Fundamental Parts
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Linux: A Deep Dive into Its Fundamental Parts
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:03 AM
The core components of Linux include kernel, file system, shell, user and kernel space, device drivers, and performance optimization and best practices. 1) The kernel is the core of the system, managing hardware, memory and processes. 2) The file system organizes data and supports multiple types such as ext4, Btrfs and XFS. 3) Shell is the command center for users to interact with the system and supports scripting. 4) Separate user space from kernel space to ensure system stability. 5) The device driver connects the hardware to the operating system. 6) Performance optimization includes tuning system configuration and following best practices.



