Some introductions to MySQL data types
The types of data fields defined in MySQL are very important for the optimization of your database;
MySQL supports multiple types, which can be roughly divided into three categories: numerical values, date/time and strings (characters) Type;
Integer type

The meaning of N in Int(N)
defines init(5 ) zerofill When joining int (10), the display width does not match, and a temporary table may appear.
N means that the display width is N, but it still occupies 4 bytes of storage, and the storage range remains unchanged;
>create table int_test(a int zerofill NOT NULL auto_increment, PRIMARY KEY (a)); >createtable int_test_4(a int(4) zerofill NOT NULL auto_increment, PRIMARY KEY (a)); >select * from int_test_4; +------------+ |a | +------------+ | 0001 | | 0002 | |2147483648 | +------------+ >select * from int_test; +------------+ |a | +------------+ |0000000001 | |0000000002 | |2147483648 | +------------+
About floating point number types: 1) Try not to use them if possible, 2) Floating point numbers cannot be used in equal sign comparison scenarios
It is recommended that TINYINT replace enum
Date and Time type
The date and time types representing time values are DATETIME, DATE, TIMESTAMP, TIME and YEAR.
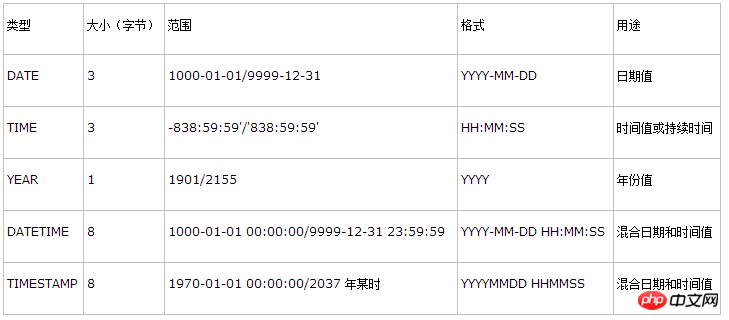
MySQL5.6 does not support year(2)
Date type Note
Timestamp, datatime supports automatic update to the current time from MySQL5.6.5: current timestamp
Date conversion: cast (datatime_col as DATE)
> ;select now()+0;
5.6 US support
>select now(4),MICROSECOND(now(4)); +--------------------------+---------------------+ |now(4) |MICROSECOND(now(4)) | +--------------------------+---------------------+ |2016-04-16 08:50:01.6589 | 658900 | +--------------------------+---------------------+
timestamp supports null after 5.6.6
It is recommended that datetime replace timestamp
String type
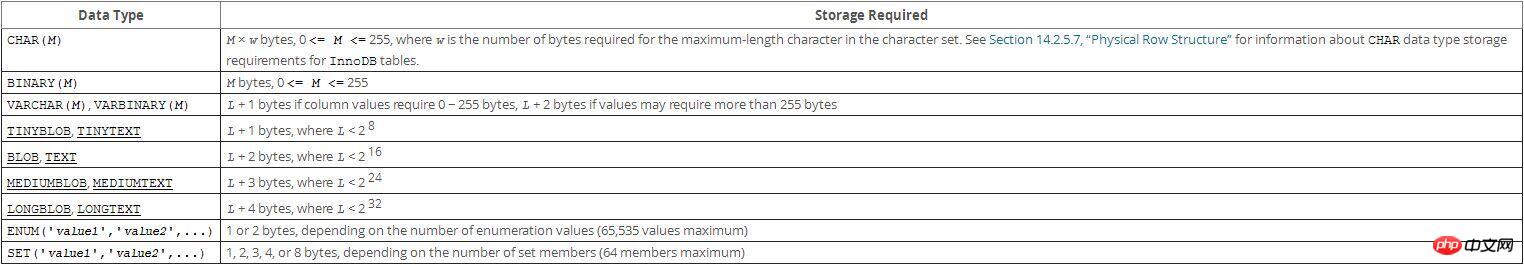
String type refers to CHAR, VARCHAR, BINARY, VARBINARY, BLOB, TEXT, ENUM and SET. This section describes how these types work and how to use them in queries;
Character type
The difference between varchar and char
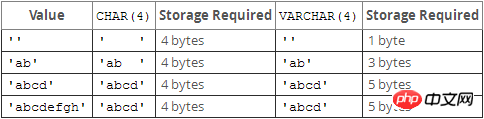
char is a fixed-length type, and varchar is a variable-length type. The difference between them is: In the data column of type char(M), each value occupies M bytes. If a certain length is less than M, MySQL will pad it with space characters on the right. (Padding space characters will be removed during the search operation.) In a varchar(M) type data column, each value only takes up just enough bytes plus one byte to record its length ( That is, the total length is L+1 bytes) varchar stores variable-length strings. When it is less than 255 bytes, it requires 1 extra byte (more than 255 requires 2 extra bytes) to store the length. The maximum length is 65532 bytes (all Column sum);
char is stored in fixed length, and the trailing spaces will be truncated when reading. The maximum length is 255 characters;
1) The meaning of CHAR (M):
The actual allocated length is: M * character encoding length = storage space
For example: 255 characters are stored and Chinese characters occupy 3 bytes
255*3 = 765 A total of 765 characters Section
2) The meaning of N in varchar(N)
can store up to N characters; varchar(5) and varchar(200) occupy the same space for storing hello, but the latter is sorted It will consume more memory because order by col uses fixed_length to calculate the col length (the same is true for the memory engine)
For example:
varchar(200)How many bytes are occupied by utf8
200*3+ 2
varchar(64) utf8
64*3=192<255
192+1=193
Recommendation:
Usually use MySQL as the innodb engine. The innodb engine is originally a variable-length storage.
Row storage:
trx_id, row-id,rollback, filed_pointer, null-flag, filed1,....
innodb storage engine recommended varchar
Char is faster because fixed-length allocation of char in a heap table like MyISAM will be faster
Calculation example
Give two examples to illustrate the calculation of the actual length.
a) If a table has only one varchar type, such as defined as
createtable t4(c varchar(N)) charset=gbk;
The maximum value of N here is The value is (65535-1-2)/2= 32766.
The reason for subtracting 1 is that the actual row storage starts from the second byte;
The reason for subtracting 2 is that the 2 bytes of the varchar header represent the length;
The reason for dividing by 2 is that the character encoding is gbk.
b) If a table is defined as
createtable t4(c int, c2 char(30), c3 varchar(N)) charset=utf8;
then here The maximum value of N is (65535-1-2-4-30*3)/3=21812
Subtracting 1 and subtracting 2 is the same as the above example;
The reason for subtracting 4 is int Type c occupies 4 bytes;
The reason for subtracting 30*3 is that char(30) occupies 90 bytes, and the encoding is utf8.
The above is the detailed content of Some introductions to MySQL data types. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1426
1426
 52
52
 1328
1328
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1255
1255
 24
24
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Compared with other programming languages, MySQL is mainly used to store and manage data, while other languages such as Python, Java, and C are used for logical processing and application development. MySQL is known for its high performance, scalability and cross-platform support, suitable for data management needs, while other languages have advantages in their respective fields such as data analytics, enterprise applications, and system programming.
 Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
In MySQL, the function of foreign keys is to establish the relationship between tables and ensure the consistency and integrity of the data. Foreign keys maintain the effectiveness of data through reference integrity checks and cascading operations. Pay attention to performance optimization and avoid common errors when using them.
 Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
The main difference between MySQL and MariaDB is performance, functionality and license: 1. MySQL is developed by Oracle, and MariaDB is its fork. 2. MariaDB may perform better in high load environments. 3.MariaDB provides more storage engines and functions. 4.MySQL adopts a dual license, and MariaDB is completely open source. The existing infrastructure, performance requirements, functional requirements and license costs should be taken into account when choosing.
 SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL is a standard language for managing relational databases, while MySQL is a database management system that uses SQL. SQL defines ways to interact with a database, including CRUD operations, while MySQL implements the SQL standard and provides additional features such as stored procedures and triggers.
 What software is better for yi framework? Recommended software for yi framework
Apr 18, 2025 pm 11:03 PM
What software is better for yi framework? Recommended software for yi framework
Apr 18, 2025 pm 11:03 PM
Abstract of the first paragraph of the article: When choosing software to develop Yi framework applications, multiple factors need to be considered. While native mobile application development tools such as XCode and Android Studio can provide strong control and flexibility, cross-platform frameworks such as React Native and Flutter are becoming increasingly popular with the benefits of being able to deploy to multiple platforms at once. For developers new to mobile development, low-code or no-code platforms such as AppSheet and Glide can quickly and easily build applications. Additionally, cloud service providers such as AWS Amplify and Firebase provide comprehensive tools
 MySQL: The Database, phpMyAdmin: The Management Interface
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:44 AM
MySQL: The Database, phpMyAdmin: The Management Interface
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:44 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin can be effectively managed through the following steps: 1. Create and delete database: Just click in phpMyAdmin to complete. 2. Manage tables: You can create tables, modify structures, and add indexes. 3. Data operation: Supports inserting, updating, deleting data and executing SQL queries. 4. Import and export data: Supports SQL, CSV, XML and other formats. 5. Optimization and monitoring: Use the OPTIMIZETABLE command to optimize tables and use query analyzers and monitoring tools to solve performance problems.
 How to safely store JavaScript objects containing functions and regular expressions to a database and restore?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
How to safely store JavaScript objects containing functions and regular expressions to a database and restore?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
Safely handle functions and regular expressions in JSON In front-end development, JavaScript is often required...




