 Backend Development
Backend Development
 XML/RSS Tutorial
XML/RSS Tutorial
 Detailed introduction to XML DTD and XML Schema sample code (picture and text)
Detailed introduction to XML DTD and XML Schema sample code (picture and text)
Detailed introduction to XML DTD and XML Schema sample code (picture and text)
XML(eXtensible Markup Language) extensible markup language. xml is particularly important in web service programming. It can be used as a carrier to transmit data in network transmission. As a metalanguage, xml can be used to mark data and define data types. It is a metalanguage that allows users to define their own markup languages. It is ideally suited for network transport, providing a unified approach to describing and exchanging structured data independent of applications or vendors. Interaction between heterogeneous languages and heterogeneous platforms can be realized. XML document definition methods include: document type definition (DTD) and XML Schema. DTD (Document Type Definition) defines the overall structure of the document and the syntax of the document (there are corresponding examples below for understanding). It is widely used and has rich tool support. XML Schema is more powerful and is used to define more powerful and richer features such as management information. XML can declare content in a more fine-grained manner, define constraints, and facilitate more meaningful transmission of content across multiple platforms. It provides a format for describing structured data, simplifies data exchange and representation in the network, separates code, data and representation, and serves as a standard format for data exchange, so it is often called an intelligent data document. DTD can be compared to a shovel, while XML Schema can be said to be an excavator, which is more powerful. Although XML is called a markup language, it is different from HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) in that its format is stricter, tags must be closed, and display and content are separated. XML describes the content and semantics of the document rather than how the document should be displayed. HTML has fixed tags, the display and content are together, and you cannot create your own tags, while XML is extensible, and the content and display are separated. Each element appears in pairs, and the beginning and end of XML elements are embedded. The nesting relationship must be kept correct (the tags that start later in the nesting must end first, and the tags that start first must end last). There is only one root element (Root Element) in each XML document, and the root element contains all other elements. An XML document that conforms to XML syntax is called well-formed when it is not verified by DTD or XML Schema. If a well-formed XML document is verified by DTD or XML Schema, this kind of XML document is called valid (Valid). of.
The following uses the xml of a student roster as an example
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<学生名册>
<学生 学号="A1">
<姓名>CIACs</姓名>
<性别>男</性别>
<年龄>22</年龄>
</学生>
<学生 学号="A2">
<姓名>zhihao</姓名>
<性别>男</性别>
<年龄>23</年龄>
</学生>
</学生名册>For a well-formatted xml document, the XMLSpy output window will output the following results

The first line of xml must be Processing instructions, and there must be no blank space between "xml elements are strict Case-sensitive , the document encoding format defaults to "UTF-8", and the version is only 1.0. The above xml document can only be said to be a well-formatted xml document, not a valid (Vaild) xml document. Below we use two methods to verify it.
First, verify it through DTD
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE 学生名册 [
<!ELEMENT 学生名册 (学生+)>
<!ELEMENT 学生 (名字,性别,年龄)>
<!ELEMENT 名字 (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 性别 (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT 年龄 (#PCDATA)>
<!ATTLIST 学生 学号 ID #REQUIRED>
<!ENTITY sex "男">
]>
<学生名册>
<学生 学号="A1">
<名字>CIACs</名字>
<性别>&sex;</性别>
<年龄>22</年龄>
</学生>
<学生 学号="A2">
<名字>zhihao</名字>
<性别>&sex;</性别>
<年龄>23</年龄>
</学生>
</学生名册>If the verification passes, the XMLSpy output window will display the following results

Otherwise, even if there is an extra space, it will not pass the verification. Here I wrote the dtd verification into xml. Of course, you can also write it into another file. The suffix of the file is ".dtd", and then associate it with the xml document to be verified. The syntax is as follows
1 DOCTYPE root element name SYSTEM "*.dtd">
The ID value here seems to start with a character. If it is just a number, it will not pass the verification.
Gender in student information, I define it as an entity, and then reference its value through the entity . Please note that the syntax of entity reference is "&entity name;".
The following is used to verify the XML Schema method
The xml document to be verified
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<学生名册 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="学生名册.xsd">
<学生 学号="A1">
<姓名>CIACs</姓名>
<性别>男</性别>
<年龄>22</年龄>
</学生>
<学生 学号="A2">
<姓名>zhihao</姓名>
<性别>男</性别>
<年龄>23</年龄>
</学生>
</学生名册>XML Schema verification document
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="学生名册">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="学生"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="学生">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="姓名" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="性别">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="男"/>
<xs:enumeration value="女"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="年龄">
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:integer">
<xs:minExclusive value="0"/>
<xs:maxExclusive value="120"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="学号" type="xs:string" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>The output result of the XMLSpy output window
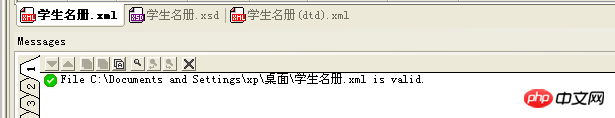
The xml document to be verified is associated with the XML Schema document by adding the following information to the root element start tag
1 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="学生名册.xsd"
The above document They are all placed in the same path, so just quote the file name directly.
From the above two verification methods, we can clearly see the difference between DTD and XML Schema verification. Both of them also verify xml documents. XML Schema provides more powerful features than DTD. functions and more fine-grained data types, and Schema can also customize data types. It itself is an xml file, but the syntax of dtd is different from the syntax of xml. Although Schema is larger than DTD in terms of code size, once you learn Schema you will prefer to use Schema.
Learning xml and its verification methods well is very important for learning web service programming later.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to XML DTD and XML Schema sample code (picture and text). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Can I open an XML file using PowerPoint?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Can I open an XML file using PowerPoint?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Can XML files be opened with PPT? XML, Extensible Markup Language (Extensible Markup Language), is a universal markup language that is widely used in data exchange and data storage. Compared with HTML, XML is more flexible and can define its own tags and data structures, making the storage and exchange of data more convenient and unified. PPT, or PowerPoint, is a software developed by Microsoft for creating presentations. It provides a comprehensive way of
 Using Python to merge and deduplicate XML data
Aug 07, 2023 am 11:33 AM
Using Python to merge and deduplicate XML data
Aug 07, 2023 am 11:33 AM
Using Python to merge and deduplicate XML data XML (eXtensibleMarkupLanguage) is a markup language used to store and transmit data. When processing XML data, sometimes we need to merge multiple XML files into one, or remove duplicate data. This article will introduce how to use Python to implement XML data merging and deduplication, and give corresponding code examples. 1. XML data merging When we have multiple XML files, we need to merge them
 Convert XML data to CSV format in Python
Aug 11, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Convert XML data to CSV format in Python
Aug 11, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Convert XML data in Python to CSV format XML (ExtensibleMarkupLanguage) is an extensible markup language commonly used for data storage and transmission. CSV (CommaSeparatedValues) is a comma-delimited text file format commonly used for data import and export. When processing data, sometimes it is necessary to convert XML data to CSV format for easy analysis and processing. Python is a powerful
 Filtering and sorting XML data using Python
Aug 07, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
Filtering and sorting XML data using Python
Aug 07, 2023 pm 04:17 PM
Implementing filtering and sorting of XML data using Python Introduction: XML is a commonly used data exchange format that stores data in the form of tags and attributes. When processing XML data, we often need to filter and sort the data. Python provides many useful tools and libraries to process XML data. This article will introduce how to use Python to filter and sort XML data. Reading the XML file Before we begin, we need to read the XML file. Python has many XML processing libraries,
 Python implements conversion between XML and JSON
Aug 07, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Python implements conversion between XML and JSON
Aug 07, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Python implements conversion between XML and JSON Introduction: In the daily development process, we often need to convert data between different formats. XML and JSON are common data exchange formats. In Python, we can use various libraries to convert between XML and JSON. This article will introduce several commonly used methods, with code examples. 1. To convert XML to JSON in Python, we can use the xml.etree.ElementTree module
 Handling errors and exceptions in XML using Python
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
Handling errors and exceptions in XML using Python
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
Handling Errors and Exceptions in XML Using Python XML is a commonly used data format used to store and represent structured data. When we use Python to process XML, sometimes we may encounter some errors and exceptions. In this article, I will introduce how to use Python to handle errors and exceptions in XML, and provide some sample code for reference. Use try-except statement to catch XML parsing errors When we use Python to parse XML, sometimes we may encounter some
 Python parsing special characters and escape sequences in XML
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:46 PM
Python parsing special characters and escape sequences in XML
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:46 PM
Python parses special characters and escape sequences in XML XML (eXtensibleMarkupLanguage) is a commonly used data exchange format used to transfer and store data between different systems. When processing XML files, you often encounter situations that contain special characters and escape sequences, which may cause parsing errors or misinterpretation of the data. Therefore, when parsing XML files using Python, we need to understand how to handle these special characters and escape sequences. 1. Special characters and
 How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development requires specific code examples. In modern software development, XML and JSON are two widely used data formats. XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a markup language used to store and transmit data, while JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data exchange format. In C# development, we often need to process and operate XML and JSON data. This article will focus on how to use C# to process these two data formats, and attach





