 Backend Development
Backend Development
 XML/RSS Tutorial
XML/RSS Tutorial
 Case sharing on setting click events for View in XML layout
Case sharing on setting click events for View in XML layout
Case sharing on setting click events for View in XML layout
Setting up a click monitor for a View Event is a very common thing, such as
view.setOnClickListener(onClickListener);
Another way is to directly specify the View click in the XML layout When using the callback method, you first need to write the method for callback in the Activity, such as
public void onClickView(View view){
// do something
} and then set the android:onClick attribute of the View in XML
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:onClick="onClickView" />Sometimes it is more convenient to directly set the click event from the XML layout (especially when writing DEMO projects). Not many people usually use this method. You can roughly guess it from the usage method. The View should use reflection to find the "onClickView" method from the Activity and call it when it is running, because this approach does not use any interface.
Next, we can analyze how View triggers the callback method from the source code.
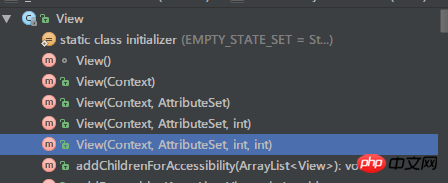
View has 5 construction methods. The first one is used internally. The second method is usually used to create View instances directly in Java code. The View instance rendered from the XML layout will eventually call the fifth method.
public View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
this(context);
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(
attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.View, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int attr = a.getIndex(i);
switch (attr) {
……
// 处理onClick属性
case R.styleable.View_onClick:
if (context.isRestricted()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The android:onClick attribute cannot "
+ "be used within a restricted context");
}
final String handlerName = a.getString(attr);
if (handlerName != null) {
// 给当前View实例设置一个DeclaredOnClickListener监听器
setOnClickListener(new DeclaredOnClickListener(this, handlerName));
}
break;
}
}
}When processing the onClick attribute, first determine whether the View's Context isRestricted, and if so, throw an IllegalStateException. Take a look at the isRestricted method
/**
* Indicates whether this Context is restricted.
*
* @return {@code true} if this Context is restricted, {@code false} otherwise.
*
* @see #CONTEXT_RESTRICTED
*/
public boolean isRestricted() {
return false;
}isRestricted is used to determine whether the current Context instance is in a restricted state. According to the official explanation, a Context in a restricted state will ignore certain features, such as XML. Certain properties, obviously the android:onClick property we're looking at are also ignored.
a restricted context may disable specific features. For instance, a View associated with a restricted context would ignore particular XML attributes.
However, the isRestricted method is one of the few in Context Most of them have concrete implementation methods (the rest are basically abstract methods), here they return false directly, and this method is only overridden in ContextWrapper and MockContext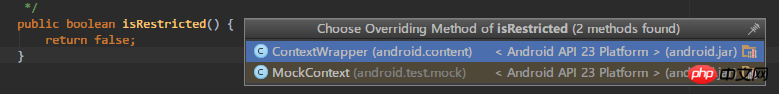
public class ContextWrapper extends Context {
Context mBase;
@Override
public boolean isRestricted() {
return mBase.isRestricted();
}
}
public class MockContext extends Context {
@Override
public boolean isRestricted() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}ContextWrapper is also only a proxy Call mBase's isRestricted, and MockContext is only used when writing unit tests, so isRestricted here will basically only return false, unless a custom ContextWrapper is used and isRestricted is rewritten.
Go back to View, then final String handlerName = a.getString(attr);In fact, we get the "onClickView" in android:onClick="onClickView" ##String, then use the instance of the current View and "onClickView" to create a DeclaredOnClickListener instance and set it as the click listener of the current View.
/**
* An implementation of OnClickListener that attempts to lazily load a
* named click handling method from a parent or ancestor context.
*/
private static class DeclaredOnClickListener implements OnClickListener {
private final View mHostView;
private final String mMethodName;
private Method mMethod;
public DeclaredOnClickListener(@NonNull View hostView, @NonNull String methodName) {
mHostView = hostView;
mMethodName = methodName;
}
@Override
public void onClick(@NonNull View v) {
if (mMethod == null) {
mMethod = resolveMethod(mHostView.getContext(), mMethodName);
}
try {
mMethod.invoke(mHostView.getContext(), v);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Could not execute non-public method for android:onClick", e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Could not execute method for android:onClick", e);
}
}
@NonNull
private Method resolveMethod(@Nullable Context context, @NonNull String name) {
while (context != null) {
try {
if (!context.isRestricted()) {
return context.getClass().getMethod(mMethodName, View.class);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
// Failed to find method, keep searching up the hierarchy.
}
if (context instanceof ContextWrapper) {
context = ((ContextWrapper) context).getBaseContext();
} else {
// Can't search up the hierarchy, null out and fail.
context = null;
}
}
final int id = mHostView.getId();
final String idText = id == NO_ID ? "" : " with id '"
+ mHostView.getContext().getResources().getResourceEntryName(id) + "'";
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not find method " + mMethodName
+ "(View) in a parent or ancestor Context for android:onClick "
+ "attribute defined on view " + mHostView.getClass() + idText);
}
}android:onClick is to find the callback method from the Context, so if for the View created in the Fragment's XML, It is impossible to bind the callback method in Fragment in this way, because Fragment itself is not a Context. The Context of the View here is actually FragmentActivity, which also means that this method can be used to quickly call back from Fragment to FragmentActivity.
android:onClick, mainly plays the role of lazy loading, only when the View is clicked , you will know which method is used for click callback.
android:onClick to set a click event for View means adding a non-interface public method to the Activity. The current Android development trend is "Don't write business logic in the Activity class." This is beneficial to project maintenance and prevents Activity explosion, so try not to have non-interface and non-lifecycle public methods in Activity. Therefore, rash use of android:onClick may "pollute" the Activity.
The above is the detailed content of Case sharing on setting click events for View in XML layout. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1655
1655
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1306
1306
 25
25
 1252
1252
 29
29
 1226
1226
 24
24
 How to add touch events to pictures in vue
May 02, 2024 pm 10:21 PM
How to add touch events to pictures in vue
May 02, 2024 pm 10:21 PM
How to add click event to image in Vue? Import the Vue instance. Create a Vue instance. Add images to HTML templates. Add click events using the v-on:click directive. Define the handleClick method in the Vue instance.
 What is the event-driven mechanism of C++ functions in concurrent programming?
Apr 26, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
What is the event-driven mechanism of C++ functions in concurrent programming?
Apr 26, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
The event-driven mechanism in concurrent programming responds to external events by executing callback functions when events occur. In C++, the event-driven mechanism can be implemented with function pointers: function pointers can register callback functions to be executed when events occur. Lambda expressions can also implement event callbacks, allowing the creation of anonymous function objects. The actual case uses function pointers to implement GUI button click events, calling the callback function and printing messages when the event occurs.
 How to use PHP functions to process XML data?
May 05, 2024 am 09:15 AM
How to use PHP functions to process XML data?
May 05, 2024 am 09:15 AM
Use PHPXML functions to process XML data: Parse XML data: simplexml_load_file() and simplexml_load_string() load XML files or strings. Access XML data: Use the properties and methods of the SimpleXML object to obtain element names, attribute values, and subelements. Modify XML data: add new elements and attributes using the addChild() and addAttribute() methods. Serialized XML data: The asXML() method converts a SimpleXML object into an XML string. Practical example: parse product feed XML, extract product information, transform and store it into a database.
 Why can't click events in js be executed repeatedly?
May 07, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Why can't click events in js be executed repeatedly?
May 07, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Click events in JavaScript cannot be executed repeatedly because of the event bubbling mechanism. To solve this problem, you can take the following measures: Use event capture: Specify an event listener to fire before the event bubbles up. Handing over events: Use event.stopPropagation() to stop event bubbling. Use a timer: trigger the event listener again after some time.
 How do you parse and process HTML/XML in PHP?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
How do you parse and process HTML/XML in PHP?
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:57 AM
This tutorial demonstrates how to efficiently process XML documents using PHP. XML (eXtensible Markup Language) is a versatile text-based markup language designed for both human readability and machine parsing. It's commonly used for data storage an
 What does div mean in css
Apr 28, 2024 pm 02:21 PM
What does div mean in css
Apr 28, 2024 pm 02:21 PM
A DIV in CSS is a document separator or container used for grouping content, creating layouts, adding style, and interactivity. In HTML, the DIV element uses the syntax <div></div>, where div represents an element to which attributes and content can be added. DIV is a block-level element that occupies an entire line in the browser.
 How to use void in java
May 01, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
How to use void in java
May 01, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
void in Java means that the method does not return any value and is often used to perform operations or initialize objects. The declaration format of void method is: void methodName(), and the calling method is methodName(). The void method is often used for: 1. Performing operations without returning a value; 2. Initializing objects; 3. Performing event processing operations; 4. Coroutines.
 How to bind events to tags in vue
May 02, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
How to bind events to tags in vue
May 02, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
Use the v-on directive in Vue.js to bind label events. The steps are as follows: Select the label to which the event is to be bound. Use the v-on directive to specify the event type and how to handle the event. Specify the Vue method to call in the directive value.



