 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 A calculator method implemented by python3.5 + PyQt5 +Eric6 (with code)
A calculator method implemented by python3.5 + PyQt5 +Eric6 (with code)
A calculator method implemented by python3.5 + PyQt5 +Eric6 (with code)
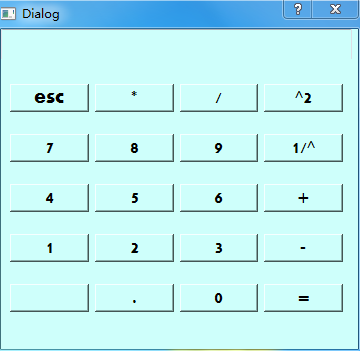
This article mainlyintroducespython3.5 + PyQt5 +Eric6 to implement a calculator method (with code), the calculator can run perfectly on the windows7 32-bit system, with Those who are interested can find out.
Simple calculations can currently be implemented. Please reset before calculating. The default number during design is 0. It took me a long time to get such a result, but there are many bugs. python3.5 + PyQt5 +Eric6 can run the calculator perfectly on Windows 7 32-bit system. It took me a long time to simply learn it and draw a picture to implement it. There are bugs. Some buttons have not been implemented yet and will be optimized in the future.
The code structure is as shown below:
jisuan.py
import re
#匹配整数或小数的乘除法,包括了开头存在减号的情况
mul_p=re.compile("(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?(\*|/)(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?")
#匹配整数或小数的加减法,包括了开头存在减号的情况
plus_minus = re.compile("(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?(-|\+)(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?")
#匹配括号
bracket=re.compile("\([^()]*\)")
#匹配乘法的时候出现乘以负数的情况,包括了开头存在减号的情况
mul_minus_minus = re.compile("(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?(\*-)(\d+)(\.\d+)?")
#匹配除法的时候出现乘以负数的情况,包括了开头存在减号的情况
p_minus_minus = re.compile("(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?(/-)(\d+)(\.\d+)?")
#定义一个两位数的加减乘除法的运算,匹配左边的右边的数字和左边的数字,然后进行计算
def touble_cale(str_expire):
if str_expire.count("+") == 1:
right_num = float(str_expire[(str_expire.find("+")+1):])
left_num = float(str_expire[:str_expire.find("+")])
return str(right_num+left_num)
elif str_expire[1:].count("-") == 1:
right_num = float(str_expire[:str_expire.find("-",1)])
left_num = float(str_expire[(str_expire.find("-", 1) + 1):])
return str(right_num - left_num)
elif str_expire.count("*") == 1:
right_num = float(str_expire[:str_expire.find("*")])
left_num = float(str_expire[(str_expire.find("*")+1):])
return str(right_num * left_num)
elif str_expire.count("/") == 1:
right_num = float(str_expire[:str_expire.find("/")])
left_num = float(str_expire[(str_expire.find("/") + 1):])
return str(right_num / left_num)
#定义一个方法用于判断是否存在乘以负数和除以负数的情况
def judge_mul_minus(str_expire):
#判断公式中乘以负数的部分
if len(re.findall("(\*-)", str_expire)) != 0:
#调用上面的正则取得*-的公式
temp_mul_minus = mul_minus_minus.search(str_expire).group()
#将匹配的部分的*-换成*并将-放到前面
temp_mul_minus_2 = temp_mul_minus.replace(temp_mul_minus,"-" + temp_mul_minus.replace("*-","*"))
#经更改的的部分与原来的部分进行替换
str_expire=str_expire.replace(temp_mul_minus,temp_mul_minus_2)
return judge_mul_minus(str_expire)
#return str_expire
# 判断公式中除以负数的部分
elif len(re.findall(r"(/-)", str_expire)) != 0:
# 调用上面的正则取得/-的公式
temp_dev_minus = p_minus_minus.search(str_expire).group()
# 将匹配的部分的/-换成/并将-放到前面
temp_dev_minus_2 = temp_dev_minus.replace(temp_dev_minus,"-" + temp_dev_minus.replace("/-","/"))
# 经更改的的部分与原来的部分进行替换
str_expire = str_expire.replace(temp_dev_minus,temp_dev_minus_2)
return judge_mul_minus(str_expire)
#调用change_sign将公式中的++换成= +-换成-
return change_sign(str_expire)
#定义一个方法取将--更改为+ +-改为-
def change_sign(str_expire):
if len(re.findall(r"(\+-)", str_expire)) != 0:
str_expire = str_expire.replace("+-", "-")
return change_sign(str_expire)
elif len(re.findall(r"(--)", str_expire)) != 0:
str_expire = str_expire.replace("--", "+")
return change_sign(str_expire)
return str_expire
#定义一个方法用于计算只有加减乘除的公式,优先处理乘法
def cale_mix(str_expire):
#如果公式中出现符号数字的情况即+5 -6 *8 /8的这种情况直接放回数字否则则先计算乘除在处理加减
while len(re.findall("[-+*/]",str_expire[1:])) != 0:
if len(re.findall("(\*|/)",str_expire)) != 0:
str_expire = str_expire.replace(mul_p.search(str_expire).group(),touble_cale(mul_p.search(str_expire).group()))
elif len(re.findall("(\+|-)",str_expire)) !=0:
str_expire = str_expire.replace(plus_minus.search(str_expire).group(),touble_cale(plus_minus.search(str_expire).group()))
return str_expire
#定义一个方法用于去括号,并调用上述的方法进行计算
def remove_bracket(str_expire):
#判断公式中是否有括号
if len(bracket.findall(str_expire)) == 0:
return cale_mix(judge_mul_minus(str_expire))
elif len(bracket.findall(str_expire))!=0:
while len(bracket.findall(str_expire)) !=0:
#print(bracket.search(str_expire).group())
#只有存在括号优先处理括号中的内容并对内容进行替换,直到没有括号位置
str_expire = str_expire.replace(bracket.search(str_expire).group(),cale_mix(judge_mul_minus(bracket.search(str_expire).group()[1:-1])))
str_expire = cale_mix(judge_mul_minus(str_expire))
return str_expire
if name == "main":
while True:
user_input_expire = input("请输入你的公式:(不要带空格,q表示退出):")
print("%s=%s" %(user_input_expire,remove_bracket(user_input_expire)))
continueuntitled.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
from Ui_untitled import Ui_Dialog
from jisuan import remove_bracket
class Dialog(QDialog, Ui_Dialog):
def init(self, parent=None):
super(Dialog, self).init(parent)
self.setupUi(self)
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_6_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('6')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_2_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('2')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_3_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('3')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_pingfang_clicked(self):
me=self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
m=int(me) *int(me)
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(str(m))
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_add_clicked(self):
h=self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(h+'+')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_jian_clicked(self):
h = self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(h + '-')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_9_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('9')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_chu_clicked(self):
h = self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(h + '/')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_cheng_clicked(self):
h = self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(h + '*')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_8_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('8')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_4_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('4')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_esc_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_7_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('7')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_1_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('1')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_5_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('5')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_xiaoshu_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('.')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_0_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('0')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_dengyu_clicked(self):
pe=self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
m=remove_bracket(pe)
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(str(m))
def on_Button_fenzhi_clicked(self):
pe = self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
if int(pe) ==0:
QMessageBox.information(self,u'提示',u'零不能作为分母')
Dialog()
else:
m=1/(int(pe))
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(str(m))
Dialog()
if name =="main":
import sys
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
app.processEvents()
ui = Dialog()
ui.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())Ui_untitled.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Form implementation generated from reading ui file 'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\pyqt5\untitled.ui'
#
# Created by: PyQt5 UI code generator 5.5
#
# WARNING! All changes made in this file will be lost!
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
class Ui_Dialog(object):
def setupUi(self, Dialog):
Dialog.setObjectName("Dialog")
Dialog.resize(357, 320)
Dialog.setStyleSheet("font: 75 16pt \"Aharoni\";\n"
"background-color: rgb(206, 255, 251);")
self.label = QtWidgets.QLabel(Dialog)
self.label.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(201, 210, 301, 21))
self.label.setText("")
self.label.setObjectName("label")
self.Edit_xianshi = QtWidgets.QTextEdit(Dialog)
self.Edit_xianshi.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 0, 351, 41))
self.Edit_xianshi.setStyleSheet("font: 75 16pt \"Aharoni\";")
self.Edit_xianshi.setObjectName("Edit_xianshi")
self.gridLayoutWidget = QtWidgets.QWidget(Dialog)
self.gridLayoutWidget.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 30, 351, 281))
self.gridLayoutWidget.setObjectName("gridLayoutWidget")
self.gridLayout = QtWidgets.QGridLayout(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.gridLayout.setObjectName("gridLayout")
self.Button_6 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_6.setObjectName("Button_6")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_6, 2, 2, 1, 1)
self.Button_2 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_2.setObjectName("Button_2")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_2, 3, 1, 1, 1)
self.Button_3 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_3.setObjectName("Button_3")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_3, 3, 2, 1, 1)
self.Button_fenzhi = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_fenzhi.setObjectName("Button_fenzhi")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_fenzhi, 1, 3, 1, 1)
self.Button_pingfang = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_pingfang.setObjectName("Button_pingfang")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_pingfang, 0, 3, 1, 1)
self.Button_add = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_add.setObjectName("Button_add")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_add, 2, 3, 1, 1)
self.Button_jian = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_jian.setObjectName("Button_jian")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_jian, 3, 3, 1, 1)
self.Button_9 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_9.setObjectName("Button_9")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_9, 1, 2, 1, 1)
self.Button_chu = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_chu.setObjectName("Button_chu")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_chu, 0, 2, 1, 1)
self.Button_cheng = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_cheng.setObjectName("Button_cheng")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_cheng, 0, 1, 1, 1)
self.Button_8 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_8.setObjectName("Button_8")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_8, 1, 1, 1, 1)
self.Button_4 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_4.setObjectName("Button_4")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_4, 2, 0, 1, 1)
self.Button_esc = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_esc.setObjectName("Button_esc")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_esc, 0, 0, 1, 1)
self.Button_7 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_7.setObjectName("Button_7")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_7, 1, 0, 1, 1)
self.Button_1 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_1.setObjectName("Button_1")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_1, 3, 0, 1, 1)
self.Button_5 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_5.setObjectName("Button_5")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_5, 2, 1, 1, 1)
self.pushButton_17 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.pushButton_17.setText("")
self.pushButton_17.setObjectName("pushButton_17")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.pushButton_17, 4, 0, 1, 1)
self.Button_xiaoshu = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_xiaoshu.setObjectName("Button_xiaoshu")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_xiaoshu, 4, 1, 1, 1)
self.Button_0 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_0.setStyleSheet("")
self.Button_0.setObjectName("Button_0")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_0, 4, 2, 1, 1)
self.Button_dengyu = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_dengyu.setObjectName("Button_dengyu")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_dengyu, 4, 3, 1, 1)
self.retranslateUi(Dialog)
QtCore.QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(Dialog)
def retranslateUi(self, Dialog):
_translate = QtCore.QCoreApplication.translate
Dialog.setWindowTitle(_translate("Dialog", "Dialog"))
self.Edit_xianshi.setHtml(_translate("Dialog", "<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0//EN\" \"http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-html40/strict.dtd\">\n"
"<html><head><meta name=\"qrichtext\" content=\"1\" /><style type=\"text/css\">\n"
"p, li { white-space: pre-wrap; }\n"
"</style></head><body style=\" font-family:\'Aharoni\'; font-size:16pt; font-weight:72; font-style:normal;\">\n"
"<p style=\" margin-top:0px; margin-bottom:0px; margin-left:0px; margin-right:0px; -qt-block-indent:0; text-indent:0px;\"><span style=\" font-family:\'SimSun\'; font-weight:400;\">0</span></p></body></html>"))
self.Button_6.setText(_translate("Dialog", "6"))
self.Button_2.setText(_translate("Dialog", "2"))
self.Button_3.setText(_translate("Dialog", "3"))
self.Button_fenzhi.setText(_translate("Dialog", "1/^"))
self.Button_pingfang.setText(_translate("Dialog", "^2"))
self.Button_add.setText(_translate("Dialog", "+"))
self.Button_jian.setText(_translate("Dialog", "-"))
self.Button_9.setText(_translate("Dialog", "9"))
self.Button_chu.setText(_translate("Dialog", "/"))
self.Button_cheng.setText(_translate("Dialog", "*"))
self.Button_8.setText(_translate("Dialog", "8"))
self.Button_4.setText(_translate("Dialog", "4"))
self.Button_esc.setText(_translate("Dialog", "esc"))
self.Button_7.setText(_translate("Dialog", "7"))
self.Button_1.setText(_translate("Dialog", "1"))
self.Button_5.setText(_translate("Dialog", "5"))
self.Button_xiaoshu.setText(_translate("Dialog", "."))
self.Button_0.setText(_translate("Dialog", "0"))
self.Button_dengyu.setText(_translate("Dialog", "="))
if name == "main":
import sys
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
Dialog = QtWidgets.QDialog()
ui = Ui_Dialog()
ui.setupUi(Dialog)
Dialog.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())Rendering:
The above is the detailed content of A calculator method implemented by python3.5 + PyQt5 +Eric6 (with code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1665
1665
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1321
1321
 25
25
 1269
1269
 29
29
 1249
1249
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".



