 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 JavaScript closure interview questions that many programmers do wrong
JavaScript closure interview questions that many programmers do wrong
JavaScript closure interview questions that many programmers do wrong
Interview questions evolved from work
This is a question I encountered at work. It seemed very interesting, so I treated it as a question for the interview and found that Almost no one can answer them all correctly and tell the reasons, so let’s talk about them.
Look at the question code first:
function fun(n,o) {
console.log(o)
return {
fun:function(m){
return fun(m,n);
}
};
}
var a = fun(0); a.fun(1); a.fun(2); a.fun(3);//undefined,?,?,?
var b = fun(0).fun(1).fun(2).fun(3);//undefined,?,?,?
var c = fun(0).fun(1); c.fun(2); c.fun(3);//undefined,?,?,?
//问:三行a,b,c的输出分别是什么?This is a very typical JS closure problem. There are three levels of fun functions nested in it. It is particularly important to figure out which fun function the fun function of each level is.
You can first write down the results you think on paper or other places, and then expand to see what the correct answer is?
//答案: //a: undefined,0,0,0 //b: undefined,0,1,2 //c: undefined,0,1,1
Are you all correct? If you got all the answers right, congratulations. There is almost nothing that can stump you in the js closure question; if you don’t get the answer right, continue to analyze.
There are several functions in JS
First of all, what you need to understand before this is that functions in JS can be divided into two types, named functions (named functions) and anonymous functions.
The method of distinguishing these two functions is very simple. It can be judged by outputting fn.name. The one with a name is a named function, and the one without a name is an anonymous function.
Note: The name of the named function cannot be obtained on lower versions of IE, and undefined will be returned. It is recommended to test on Firefox or Google Chrome
or use the IE-compatible method of getting the function name to obtain the function name:
/**
* 获取指定函数的函数名称(用于兼容IE)
* @param {Function} fun 任意函数
*/
function getFunctionName(fun) {
if (fun.name !== undefined)
return fun.name;
var ret = fun.toString();
ret = ret.substr('function '.length);
ret = ret.substr(0, ret.indexOf('('));
return ret;
}Then use the above function to test whether it is an anonymous function:

You can know that the variable fn1 is a named function and fn2 is an anonymous function
Several ways to create functions
After talking about the types of functions, you also need to understand that there are several ways to create functions in JS.
1. Declare a function
The most common and standard way to declare a function, including function name and function body.
function fn1(){}2. Create an anonymous function expression
Create a variable whose content is a function
var fn1=function (){}Note that the function created using this method is an anonymous function, that is, there is no function name
var fn1=function (){};
getFunctionName(fn1).length;//03. Create a named function expression
Create a variable whose content is a function with a name
var fn1=function xxcanghai(){};Note: The function name of the named function expression can only be used inside the creation function
That is, it is created using this method The function can only use fn1 in the outer layer of the function and cannot use the function name of xxcanghai. The naming of xxcanghai can only be used inside the created function
Test:
var fn1=function xxcanghai(){
console.log("in:fn1<",typeof fn1,">xxcanghai:<",typeof xxcanghai,">");
};
console.log("out:fn1<",typeof fn1,">xxcanghai:<",typeof xxcanghai,">");
fn1();
//out:fn1< function >xxcanghai:< undefined >
//in:fn1< function >xxcanghai:< function >You can see that the function name of xxcanghai cannot be used outside the function (out) and is undefined.
Note: Functions defined within an object such as var o={ fn : function (){…} } are also function expressions
4, Function constructor
You can pass a function string to the Function constructor and return a function containing this string command. This method creates an anonymous function.
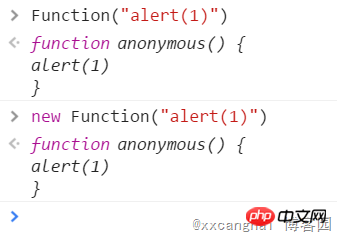
5. Self-executing functions
(function(){alert(1);})();
(function fn1(){alert(1);})();Self-executing functions belong to the above "Function expression", the rules are the same
6. Other methods of creating functions
Of course there are other methods of creating functions or executing functions, which I won’t go into more here, such as using eval, SetTimeout, setInterval and other very common methods will not be introduced here. They are non-standard methods. We will not expand too much here.
What is the relationship between the three fun functions?
After talking about function types and methods of creating functions, we can return to the topic and look at this interview question.
There are three fun functions in this code, so the first step is to figure out the relationship between these three fun functions and which function is the same as which function.
function fun(n,o) {
console.log(o)
return {
fun:function(m){
//...
}
};
}Let’s first look at the first fun function, which belongs to the standard named function declaration and is a newly created function. Its return value is an object literal expression and belongs to a new object.
This new object contains an attribute also called fun. From the above introduction, we can know that it is an anonymous function expression, that is, the attribute fun stores a newly created anonymous function expression.
Note: All declared anonymous functions are new functions.
So the first fun function and the second fun function are different, they are both newly created functions.
The problem of function scope chain
Before talking about the third fun function, we need to talk about whether the variable storing the current function can be accessed inside the function expression.
Test 1, function expression inside the object:
var o={
fn:function (){
console.log(fn);
}
};
o.fn();//ERROR报错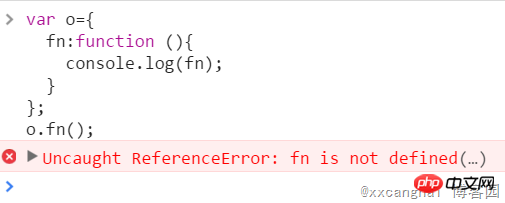
Test 2, function expression inside non-object:
var fn=function (){
console.log(fn);
};
fn();//function (){console.log(fn);};正确
结论是:使用var或是非对象内部的函数表达式内,可以访问到存放当前函数的变量;在对象内部的不能访问到。
原因也非常简单,因为函数作用域链的问题,采用var的是在外部创建了一个fn变量,函数内部当然可以在内部寻找不到fn后向上册作用域查找fn,而在创建对象内部时,因为没有在函数作用域内创建fn,所以无法访问。
所以综上所述,可以得知,最内层的return出去的fun函数不是第二层fun函数,是最外层的fun函数。
所以,三个fun函数的关系也理清楚了,第一个等于第三个,他们都不等于第二个。
到底在调用哪个函数?
再看下原题,现在知道了程序中有两个fun函数(第一个和第三个相同),遂接下来的问题是搞清楚,运行时他执行的是哪个fun函数?
function fun(n,o) {
console.log(o)
return {
fun:function(m){
return fun(m,n);
}
};
}
var a = fun(0); a.fun(1); a.fun(2); a.fun(3);//undefined,?,?,?
var b = fun(0).fun(1).fun(2).fun(3);//undefined,?,?,?
var c = fun(0).fun(1); c.fun(2); c.fun(3);//undefined,?,?,?
//问:三行a,b,c的输出分别是什么?1、第一行a
var a = fun(0); a.fun(1); a.fun(2); a.fun(3);
可以得知,第一个fun(0)是在调用第一层fun函数。第二个fun(1)是在调用前一个fun的返回值的fun函数,所以:
第后面几个fun(1),fun(2),fun(3),函数都是在调用第二层fun函数。
遂:
在第一次调用fun(0)时,o为undefined;
第二次调用fun(1)时m为1,此时fun闭包了外层函数的n,也就是第一次调用的n=0,即m=1,n=0,并在内部调用第一层fun函数fun(1,0);所以o为0;
第三次调用fun(2)时m为2,但依然是调用a.fun,所以还是闭包了第一次调用时的n,所以内部调用第一层的fun(2,0);所以o为0
第四次同理;
即:最终答案为undefined,0,0,0
2、第二行b
var b = fun(0).fun(1).fun(2).fun(3);//undefined,?,?,?
先从fun(0)开始看,肯定是调用的第一层fun函数;而他的返回值是一个对象,所以第二个fun(1)调用的是第二层fun函数,后面几个也是调用的第二层fun函数。
遂:
在第一次调用第一层fun(0)时,o为undefined;
第二次调用 .fun(1)时m为1,此时fun闭包了外层函数的n,也就是第一次调用的n=0,即m=1,n=0,并在内部调用第一层fun函数fun(1,0);所以o为0;
第三次调用 .fun(2)时m为2,此时当前的fun函数不是第一次执行的返回对象,而是第二次执行的返回对象。而在第二次执行第一层fun函数时时(1,0)所以n=1,o=0,返回时闭包了第二次的n,遂在第三次调用第三层fun函数时m=2,n=1,即调用第一层fun函数fun(2,1),所以o为1;
第四次调用 .fun(3)时m为3,闭包了第三次调用的n,同理,最终调用第一层fun函数为fun(3,2);所以o为2;
即最终答案:undefined,0,1,2
3、第三行c
var c = fun(0).fun(1); c.fun(2); c.fun(3);//undefined,?,?,?
根据前面两个例子,可以得知:
fun(0)为执行第一层fun函数,.fun(1)执行的是fun(0)返回的第二层fun函数,这里语句结束,遂c存放的是fun(1)的返回值,而不是fun(0)的返回值,所以c中闭包的也是fun(1)第二次执行的n的值。c.fun(2)执行的是fun(1)返回的第二层fun函数,c.fun(3)执行的也是fun(1)返回的第二层fun函数。
遂:
在第一次调用第一层fun(0)时,o为undefined;
第二次调用 .fun(1)时m为1,此时fun闭包了外层函数的n,也就是第一次调用的n=0,即m=1,n=0,并在内部调用第一层fun函数fun(1,0);所以o为0;
第三次调用 .fun(2)时m为2,此时fun闭包的是第二次调用的n=1,即m=2,n=1,并在内部调用第一层fun函数fun(2,1);所以o为1;
第四次.fun(3)时同理,但依然是调用的第二次的返回值,遂最终调用第一层fun函数fun(3,1),所以o还为1
即最终答案:undefined,0,1,1
后话
这段代码原本是在做一个将异步回调改写为同步调用的组件时的代码,发现了这个坑,对JS的闭包有了更深入的了解。
关于什么是闭包,网上的文章数不胜数,但理解什么是闭包还是要在代码中自己去发现与领悟。
如果要我说什么是闭包,我认为,广义上的闭包就是指一个变量在他自身作用域外被使用了,就叫发生了闭包。
希望读者能通过本文对闭包现象有进一步的了解,如有其它见解或看法,欢迎指正或留言讨论。(完)
The above is the detailed content of JavaScript closure interview questions that many programmers do wrong. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1663
1663
 14
14
 1420
1420
 52
52
 1313
1313
 25
25
 1266
1266
 29
29
 1237
1237
 24
24
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript is a programming language widely used in web development, while WebSocket is a network protocol used for real-time communication. Combining the powerful functions of the two, we can create an efficient real-time image processing system. This article will introduce how to implement this system using JavaScript and WebSocket, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to clarify the requirements and goals of the real-time image processing system. Suppose we have a camera device that can collect real-time image data



