 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Clarify the lexical, static, dynamic, function, and block scopes in JS
Clarify the lexical, static, dynamic, function, and block scopes in JS
Clarify the lexical, static, dynamic, function, and block scopes in JS
Well, I just wrote a lot, but it was overwritten by my mistake. My hard work╥﹏╥…
It’s okay to write it again. I also remind you to blog on this platform and be like me. For students who also like to use markdown language to code words
"Save online to draft" is a good habit, hmm
Today is Double Eleven, I feel like it’s time to buy something. .
When many students learn JavaScript, they may hear about "various" scopes
What are lexical scope, static scope, dynamic scope, function scope, Block scope
I can’t tell the difference
Let me clarify my thoughts for everyone
Scope mode
The scope’s working mode is divided into two types, static function Domain and dynamic scope
Static scope includes function scope and block scope
Students may ask what about lexical scope
In fact, lexical scope and static scope are the same thing
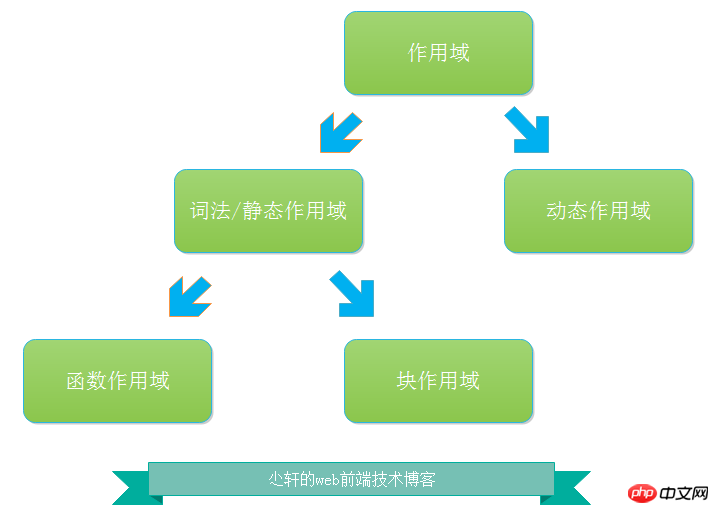
The picture is not good, everyone understands what I mean
Now that we have clarified this point, let’s go into detail
There is one more question to add, That is, is there dynamic scope in JavaScript?
Regarding this, I got completely opposite answers in the two books I have read
Whether it is the with statement or the catch clause of the try-catch statement, or it contains The eval() functions are all considered dynamic scopes. Dynamic scope only exists during code execution and therefore cannot be detected by static analysis (looking at the code structure). ——"High-Performance JavaScript" /p24
What needs to be clear is that in fact JavaScript does not have dynamic scope. It has only lexical scope, plain and simple. But this mechanism is somewhat like dynamic scope. ——"JavaScript You Don't Know (Volume 1)" /p59
These two books are very new, and both are very authoritative books, highly recommended
especially "JavaScript You Don't Know" series, when the middle volume just came out last month, I couldn't wait to buy a copy from the Internet
I was not disappointed
Ahem, I digressed, back to the topic
I think the great authors of the original book have different understandings of dynamic scope
That’s why this seemingly contradictory point of view
Here I want to talk about my position
Through my understanding, I also think There is no dynamic scope in JavaScript
What is the difference between static and dynamic scope
Look down↓
Lexical scope and dynamic scope
Let me start with a piece of code
function foo(){
var a = 1;
bar();
}function bar(){
console.log(a);
}var a = 100;
foo();Through our in-depth understanding of precompilation and scope
In the lexical scope of our JavaScript, the final result prints 100
But if we If the scope is a dynamic scope, the printed value will become 1
Why is this?
The most important feature of lexical scope is that its definition process occurs during the writing phase (if eval() and with are not used)
Dynamic scope enables the scope to be dynamically determined at runtime
Lexical scope cares about where the function is declared, and the scope chain is based on scope nesting
Dynamic scope cares about where the function is called, and the scope chain is based on the call stack
I translated the above words to The code is
Lexical scope: Because the bar function is declared globally, I output the value of the global variable a
Dynamic scope: Because the bar function is called within the foo function, so I output foo The value of variable a in
This is my understanding
The programming languages I have come into contact with are limited, all of which are lexical scopes. I have never seen a language based on dynamic scopes
C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, and php are all lexical scopes
JavaScript and php are based on function scope, and others are based on block scope
Function scope and block scope
In my understanding
The function scope is the scope generated by the function code block, and the block scope is the scope generated by the curly bracket code block
I have seen this written in many blogs. In JavaScript, there is only Function scope (big mistake)
This is completely incorrect, there is no dispute
JavaScript is indeed based on function scope, but it does not mean that we do not have block scope
There are many special cases, There are the with keyword, the catch clause of the try-catch statement, the let keyword (ES6), and the const keyword (ES6)
Here I will just briefly talk about it
Both the keyword with and the catch clause can be generated Block scope
I should have written about this in detail in an article
If you are interested, you can check it out
Portal->JavaScript deceptive lexical eval, with and catch and its performance issues
The let keyword is very similar to var. They both declare variables. However, the let keyword can bind the variable to any scope.
And using let to declare will not be promoted in the block scope.
The const keyword also declares variables, but it declares constants and binds variables to the block scope.
This is almost the same as our const keyword in C/C++
More about me I’ll talk about it in detail later when I write about ES6 knowledge
Now we only need to know “There is a block scope in JavaScript”
Summary
As usual, let me summarize for you
Scope working mode: Lexical/static scope, dynamic scope
Lexical scope : Function scope, block scope
JavaScript does not have dynamic scope
JavaScript has block scope
with, catch clause, let (ES6), const (ES6) generate block scope
Lexical scope cares where the function is declared
Dynamic scope cares about where the function is called
Lexical scope scope chaining is based on scope nesting
Dynamic scope scope chain is based on the call stack
The above is to clarify the content of lexical, static, dynamic, function, and block scope in JS. For more related content, please pay attention to PHP Chinese Net (www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1318
1318
 25
25
 1269
1269
 29
29
 1248
1248
 24
24
 Usage of typedef struct in c language
May 09, 2024 am 10:15 AM
Usage of typedef struct in c language
May 09, 2024 am 10:15 AM
typedef struct is used in C language to create structure type aliases to simplify the use of structures. It aliases a new data type to an existing structure by specifying the structure alias. Benefits include enhanced readability, code reuse, and type checking. Note: The structure must be defined before using an alias. The alias must be unique in the program and only valid within the scope in which it is declared.
 How to solve variable expected in java
May 07, 2024 am 02:48 AM
How to solve variable expected in java
May 07, 2024 am 02:48 AM
Variable expected value exceptions in Java can be solved by: initializing variables; using default values; using null values; using checks and assignments; and knowing the scope of local variables.
 Advantages and disadvantages of closures in js
May 10, 2024 am 04:39 AM
Advantages and disadvantages of closures in js
May 10, 2024 am 04:39 AM
Advantages of JavaScript closures include maintaining variable scope, enabling modular code, deferred execution, and event handling; disadvantages include memory leaks, increased complexity, performance overhead, and scope chain effects.
 What does include mean in c++
May 09, 2024 am 01:45 AM
What does include mean in c++
May 09, 2024 am 01:45 AM
The #include preprocessor directive in C++ inserts the contents of an external source file into the current source file, copying its contents to the corresponding location in the current source file. Mainly used to include header files that contain declarations needed in the code, such as #include <iostream> to include standard input/output functions.
 C++ smart pointers: a comprehensive analysis of their life cycle
May 09, 2024 am 11:06 AM
C++ smart pointers: a comprehensive analysis of their life cycle
May 09, 2024 am 11:06 AM
Life cycle of C++ smart pointers: Creation: Smart pointers are created when memory is allocated. Ownership transfer: Transfer ownership through a move operation. Release: Memory is released when a smart pointer goes out of scope or is explicitly released. Object destruction: When the pointed object is destroyed, the smart pointer becomes an invalid pointer.
 Can the definition and call of functions in C++ be nested?
May 06, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Can the definition and call of functions in C++ be nested?
May 06, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Can. C++ allows nested function definitions and calls. External functions can define built-in functions, and internal functions can be called directly within the scope. Nested functions enhance encapsulation, reusability, and scope control. However, internal functions cannot directly access local variables of external functions, and the return value type must be consistent with the external function declaration. Internal functions cannot be self-recursive.
 Complete collection of excel function formulas
May 07, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
Complete collection of excel function formulas
May 07, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
1. The SUM function is used to sum the numbers in a column or a group of cells, for example: =SUM(A1:J10). 2. The AVERAGE function is used to calculate the average of the numbers in a column or a group of cells, for example: =AVERAGE(A1:A10). 3. COUNT function, used to count the number of numbers or text in a column or a group of cells, for example: =COUNT(A1:A10) 4. IF function, used to make logical judgments based on specified conditions and return the corresponding result.
 The difference between let and var in vue
May 08, 2024 pm 04:21 PM
The difference between let and var in vue
May 08, 2024 pm 04:21 PM
In Vue, there is a difference in scope when declaring variables between let and var: Scope: var has global scope and let has block-level scope. Block-level scope: var does not create a block-level scope, let creates a block-level scope. Redeclaration: var allows redeclaration of variables in the same scope, let does not.



