 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C#.Net Tutorial
C#.Net Tutorial
 C# Learning Diary 23---Polymorphism: Operator overloading, method overloading, abstract classes, virtual methods
C# Learning Diary 23---Polymorphism: Operator overloading, method overloading, abstract classes, virtual methods
C# Learning Diary 23---Polymorphism: Operator overloading, method overloading, abstract classes, virtual methods
The definition of polymorphism in C# is: the same operation acts on instances of different classes, different classes perform different interpretations, and finally produce different execution results. In other words, one interface, multiple functions.
C# supports 2 forms of polymorphism: compile-time polymorphism, run-time polymorphism
Compile-time polymorphism:
Compile-time Polymorphism is achieved through overloading
Method overloading
You can have multiple definitions of the same function name in the same scope. Function definitions must differ from each other, either by the type of parameters in the parameter list or by the number of parameters. Function declarations that differ only in return type cannot be overloaded. Write an example
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Test
{
class exchange //定义一个exchange类
{//方法实现交换两参数数据
public void swap(int a, int b)
{
int temp;
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}",a,b);
}
public void swap(string a, string b)
{
string temp;
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}", a, b);
}
}
class program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
exchange exch = new exchange();
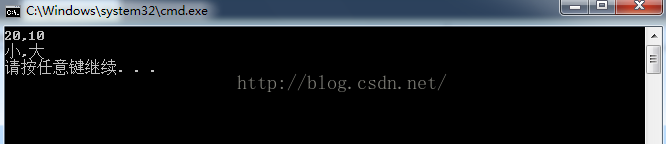
exch.swap(10, 20); //调用 swap(int a,int b)方法
exch.swap("大", "小"); //调用 swap(string a,string b)方法
}
}
}Result:
Operator overloading
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Test
{
class student //定义student类
{
private int Chinese;
private int Math;
public void value(int a, int b) //定义一个赋值的方法,以后学了构造方法就不这么麻烦了
{
Chinese = a;
Math = b;
}
public static student operator + (student a, student b) //运算符重载,实现相加功能
{
student stu = new student();
stu.Chinese = a.Chinese + b.Chinese;
stu.Math = a.Math + b.Math;
return stu;
}
public int getChinese() //获取Chinese 的方法
{
return Chinese;
}
public int getMath() //获取Math 的方法
{
return Math;
}
}
class program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
student a = new student();
student b = new student();
a.value(70,80);
b.value(40, 50);
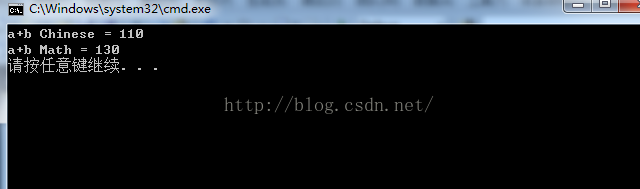
student stu = a + b; //70+40, 80+50
Console.WriteLine("a+b Chinese = {0}\na+b Math = {1}", stu.getChinese(), stu.getMath());
}
}
}Result:
Runtime polymorphism:
Runtime polymorphism means that it is not until the system is running that the actual operation is decided based on the actual situation. Runtime polymorphism in C# is implemented through abstract classes or Implemented using virtual methods.
Abstract classes and abstract methods
C# allows you to use the keyword abstract to create abstract classes or abstract methods. When a derived class inherits from the abstract class, the implementation is complete. Abstract classes contain abstract methods, which can be implemented by derived classes. Derived classes have more specialized functionality. Abstract classes cannot be instantiated.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Test
{//创建抽象类和抽象方法
abstract class score
{
public abstract int Add();
}
//创建子类
class student : score
{
private int Chinese = 80;
private int Math = 90;
public override int Add() //关键字 override 实例方法
{
int sum=Chinese+Math;
return sum;
}
}
class program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
student stu = new student();
Console.WriteLine(stu.Add() ); //结果 170
}
}
}Virtual methods
Virtual methods are declared using the keyword virtual. Virtual methods can have different implementations in different inherited classes. Calls to virtual methods occur at runtime.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Test
{
class score
{
protected int Chinese = 80;
protected int Math = 90;
public virtual int Add() //定义一个虚方法
{
int sum = Chinese + Math;
return sum;
}
}
//定义子类,实现方法
class student : score
{
public override int Add() //关键字 override 实例方法,实现相减操作
{
int sub = Math - Chinese ;
return sub;
}
}
class program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
student stu = new student();
Console.WriteLine(stu.Add() ); //结果 10
}
}
}We can see that the method actually called at runtime is not a virtual method, but the method after the override instance.
The above is C# Learning Diary 23---Polymorphism Operator Overloading , method overloading, abstract classes, and virtual methods. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1655
1655
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1306
1306
 25
25
 1252
1252
 29
29
 1226
1226
 24
24
 How do inheritance and polymorphism affect class coupling in C++?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 02:33 PM
How do inheritance and polymorphism affect class coupling in C++?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 02:33 PM
Inheritance and polymorphism affect the coupling of classes: Inheritance increases coupling because the derived class depends on the base class. Polymorphism reduces coupling because objects can respond to messages in a consistent manner through virtual functions and base class pointers. Best practices include using inheritance sparingly, defining public interfaces, avoiding adding data members to base classes, and decoupling classes through dependency injection. A practical example showing how to use polymorphism and dependency injection to reduce coupling in a bank account application.
 What are the advantages and disadvantages of polymorphism in C++?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 08:08 PM
What are the advantages and disadvantages of polymorphism in C++?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 08:08 PM
Advantages and Disadvantages of C++ Polymorphism: Advantages: Code Reusability: Common code can handle different object types. Extensibility: Easily add new classes without modifying existing code. Flexibility and maintainability: separation of behavior and type improves code flexibility. Disadvantages: Runtime overhead: Virtual function dispatch leads to increased overhead. Code Complexity: Multiple inheritance hierarchies add complexity. Binary size: Virtual function usage increases binary file size. Practical case: In the animal class hierarchy, polymorphism enables different animal objects to make sounds through Animal pointers.
 Java Interfaces and Abstract Classes: The Road to Programming Heaven
Mar 04, 2024 am 09:13 AM
Java Interfaces and Abstract Classes: The Road to Programming Heaven
Mar 04, 2024 am 09:13 AM
Interface: An implementationless contract interface defines a set of method signatures in Java but does not provide any concrete implementation. It acts as a contract that forces classes that implement the interface to implement its specified methods. The methods in the interface are abstract methods and have no method body. Code example: publicinterfaceAnimal{voideat();voidsleep();} Abstract class: Partially implemented blueprint An abstract class is a parent class that provides a partial implementation that can be inherited by its subclasses. Unlike interfaces, abstract classes can contain concrete implementations and abstract methods. Abstract methods are declared with the abstract keyword and must be overridden by subclasses. Code example: publicabstractcla
 What role does destructor play in polymorphism in C++?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:30 PM
What role does destructor play in polymorphism in C++?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:30 PM
Destructors are crucial in C++ polymorphism, ensuring that derived class objects properly clean up memory when they are destroyed. Polymorphism allows objects of different types to respond to the same method call. The destructor is automatically called when an object is destroyed to release its memory. The derived class destructor calls the base class destructor to ensure that the base class memory is released.
 The role of C++ function return value types in polymorphism
Apr 13, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
The role of C++ function return value types in polymorphism
Apr 13, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
In polymorphism, the function return value type specifies the specific object type returned when a derived class overrides a base class method. The return value type of a derived class method can be the same as the base class or more specific, allowing more derived types to be returned, thereby increasing flexibility.
 How does C++ function overloading achieve polymorphism?
Apr 13, 2024 pm 12:21 PM
How does C++ function overloading achieve polymorphism?
Apr 13, 2024 pm 12:21 PM
Function overloading can be used to achieve polymorphism, where a derived class method is called through a base class pointer and the compiler selects the overloaded version based on the actual parameter types. In the example, the Animal class defines a virtual makeSound() function, and the Dog and Cat classes rewrite this function. When makeSound() is called through the Animal* pointer, the compiler will call the corresponding rewritten version based on the pointed object type, thus achieving polymorphism. sex.
 How does polymorphism support object-oriented development in C++?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 10:37 PM
How does polymorphism support object-oriented development in C++?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 10:37 PM
Polymorphism is a concept in object-oriented programming that allows objects to exist in multiple forms, making code more flexible, scalable, and maintainable. Polymorphism in C++ leverages virtual functions and inheritance, as well as pure virtual functions and abstract classes to implement dynamic binding, allowing us to create class hierarchies that change behavior based on the actual type of the object. In practice, polymorphism allows us to create base class pointers to different derived class objects and call the appropriate functions based on the actual type of the object.
 Polymorphism of function overriding and inheritance: the art of realizing flexible calls between objects
May 02, 2024 am 10:30 AM
Polymorphism of function overriding and inheritance: the art of realizing flexible calls between objects
May 02, 2024 am 10:30 AM
Function rewriting and inheritance polymorphism are two key concepts in OOP to achieve flexible object calling: Function rewriting: the derived class redefines the function of the same name in the base class, and executes the specific implementation in the derived class when called. Polymorphism of inheritance: A derived class can be used in the same way as a base class, and when a method is called through a base class reference, its implementation in the derived class is executed.



