MySQL - CentOS6.5_x64 installation and configuration drbd8.4.2
MySQL——CentOS6.5_x64 installation and configuration drbd8.4.2
1. Host resources:
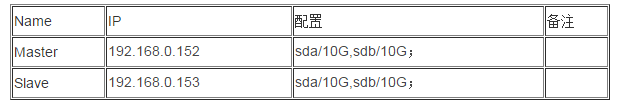
************ *************************************
DRBD download address: http://oss .linbit.com/drbd/
****************************************** *******
2. Basic system configuration
Master and slave are configured as follows.
1. Configure the /etc/hosts file
~]# vi /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 192.168.0.152 master 192.168.0.153 slave
2. Disable selinux:
# sed -i "7s/enforcing/disabled/" /etc/selinux/config
3. Disable or uninstall iptables, here We disable iptables:
1) Turn off the firewall-----service iptables stop
2) Start the firewall-----service iptables start
3) Restart the firewall----- service iptables restart
4) Check the firewall status--service iptables status
5) Permanently turn off the firewall--chkconfig iptables off
6) Enable it after permanent shutdown--chkconfig iptables on
4. Run yum update to upgrade the kernel:
# yum update Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, presto Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.btte.NET ………
5. Format /dev/sdb
#fdisk -l
#fdisk /dev/sdb
6. Restart
reboot
3. Install DRBD 8.4.2 ( The active and standby node configurations are the same)
1. Install the DRBD compilation environment on the active and standby nodes:
# yum -y install gcc flex wget make kernel-devel kernel-headers Git libxslt rpm-build automake autoconf
2. Download the DRBD installation file
# wget http://oss.linbit .com/drbd/8.4/drbd-8.4.2.tar.gz
3. Unzip and install the DRBD file
#tar -zvxf drbd-8.4.2.tar.gz # cd drbd-8.4.2 drbd-8.4.2]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/drbd --with-km drbd-8.4.2]# make KDIR=/usr/src/kernels/`uname -r`/ drbd-8.4.2]# make install
4. Install and configure the DRBD driver module
drbd-8.4.2]# cd drbd drbd-8.4.2]# make clean drbd-8.4.2]# make KDIR=/usr/src/kernels/`uname -r`/ drbd-8.4.2]# cp drbd.ko /lib/modules/`uname -r`/kernel/lib/ drbd-8.4.2]# depmod #创建模块依赖关系的列表 drbd-8.4.2]# cp /usr/local/drbd/etc/rc.d/init.d/drbd /etc/rc.d/init.d/ drbd-8.4.2]# chkconfig --add drbd drbd-8.4.2]# chkconfig drbd on
4. Define the DRBD configuration file (the configuration of the active and backup nodes is the same)
~]# cp /usr/local/drbd/etc/drbd.d/global_common.conf /usr/local/drbd/etc/drbd.d/global_common-bak.conf ~]# vi /usr/local/drbd/etc/drbd.d/global_common.conf
global {
usage-count yes; # 是否参加DRBD使用者统计.默认是yes
# minor-count dialog-refresh disable-ip-verification
}
common {
handlers {
pri-on-incon-degr "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-pri-on-incon-degr.sh; /usr/lib/drbd/notify-emergency-reboot.sh; echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger ; reboot -f";
pri-lost-after-sb "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-pri-lost-after-sb.sh; /usr/lib/drbd/notify-emergency-reboot.sh; echo b > /proc/sysrq-trigger ; reboot -f";
local-io-error "/usr/lib/drbd/notify-io-error.sh; /usr/lib/drbd/notify-emergency-shutdown.sh; echo o > /proc/sysrq-trigger ; halt -f";
}
startup {
wfc-timeout 30;
degr-wfc-timeout 30;
outdated-wfc-timeout 30;
}
options {
# cpu-mask on-no-data-accessible
}
disk {
on-io-error detach;
fencing resource-and-stonith;
resync-rate 50M; # 设置主备节点同步时的网络速率最大值,单位是字节.
}
net {
protocol C; # 使用协议C.表示收到远程主机的写入确认后,则认为写入完成.
cram-hmac-alg sha1; # 设置主备机之间通信使用的信息算法.
shared-secret "123456";
}
}~]# vi /usr/local/drbd/etc/drbd.d/Redis.res
resource redis{
on master {
device /dev/drbd1; #逻辑设备的路径
disk /dev/sdb; #物理设备
address 192.168.0.152:7788; #IP和监听端口
meta-disk internal;
}
on slave {
device /dev/drbd1;
disk /dev/sdb;
address 192.168.0.153:7788;
meta-disk internal;
}~]# modprobe drbd #载入DRBD模块 ~]# lsmod |grep drbd #确认DRBD模块载入成功
drbd 314184 0 libcrc32c 1246 1 drbd
~]# drbdadm create-md redis #创建元数据
--== Thank you for participating in the global usage survey ==-- The server's response is: you are the 4070th user to install this version md_offset 10737414144 al_offset 10737381376 bm_offset 10737053696 Found some data ==> This might destroy existing data! <== Do you want to proceed? [need to type 'yes' to confirm] yes Writing meta data... initializing activity log NOT initializing bitmap New drbd meta data block successfully created. success
~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/drbd/var/run/drbd ~]# drbdadm up redis #启用资源
Device '1' is configured! Command 'drbdmeta 1 v08 /dev/sdb internal apply-al' terminated with exit code 20
~]# cat /proc/drbd #查看DRBD状态
version: 8.4.2 (api:1/proto:86-101) GIT-hash: 7ad5f850d711223713d6dcadc3dd48860321070c build by , 2012-12-31 20:26:02 1: cs:Connected ro:Secondary/Secondary ds:Inconsistent/Inconsistent C r----- ns:0 nr:0 dw:0 dr:0 al:0 bm:0 lo:0 pe:0 ua:0 ap:0 ep:1 wo:f oos:10485404
~]# mkdir /drbd #为DRBD分区挂载创建路径
**************************** *************************************************** ************************************
5. Settings Primary node Primary node (master configuration)
~]# drbdadm primary --force redis #设置master角色为Primary ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/drbd1 #格式化drbd1(逻辑设备)
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
文件系统标签=
操作系统:Linux
块大小=4096 (log=2)
分块大小=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
655360 inodes, 2621351 blocks
131067 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
第一个数据块=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=2684354560
80 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632
正在写入inode表: 完成
Creating journal (32768 blocks):
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: 完成
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 36 mounts or 180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.~]# mount /dev/drbd1 /drbd #挂载DRBD分区 ~]# df -h
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用%% 挂载点 /dev/sda3 8.7G 1.1G 7.3G 13% / tmpfs 497M 0 497M 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 194M 64M 120M 35% /boot /dev/drbd1 9.9G 151M 9.2G 2% /drbd
6. Synchronization test:
mater operation:
~]# ls anaconda-ks.cfg drbd-8.4.2 drbd-8.4.2.tar.gz install.log install.log.syslog ~]# cp drbd-8.4.2.tar.gz /drbd ~]# ll /drbd 总用量 676 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 675803 10月 15 21:14 drbd-8.4.2.tar.gz drwx------ 2 root root 16384 10月 15 21:07 lost+found ~]# umount /dev/drbd1 #卸载挂载的DRBD分区 ~]# drbdadm secondary redis #主节点角色降级
slave operation:
~]# drbdadm primary redis #备节点设置成primary角色 ~]# mount /dev/drbd1 /drbd #备节点挂载DRBD分区 ~]# df -h
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用%% 挂载点 /dev/sda3 8.7G 1.1G 7.3G 13% / tmpfs 497M 0 497M 0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 194M 64M 120M 35% /boot /dev/drbd1 9.9G 152M 9.2G 2% /drbd
~]# ll /drbd 总用量 676 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 675803 10月 15 21:14 drbd-8.4.2.tar.gz drwx------ 2 root root 16384 10月 15 21:07 lost+found
Test completed~!
The above is the content of MySQL-CentOS6.5_x64 installation and configuration drbd8.4.2. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1653
1653
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1304
1304
 25
25
 1251
1251
 29
29
 1224
1224
 24
24
 MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main role of MySQL in web applications is to store and manage data. 1.MySQL efficiently processes user information, product catalogs, transaction records and other data. 2. Through SQL query, developers can extract information from the database to generate dynamic content. 3.MySQL works based on the client-server model to ensure acceptable query speed.
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
I encountered a tricky problem when developing a small application: the need to quickly integrate a lightweight database operation library. After trying multiple libraries, I found that they either have too much functionality or are not very compatible. Eventually, I found minii/db, a simplified version based on Yii2 that solved my problem perfectly.
 Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Article summary: This article provides detailed step-by-step instructions to guide readers on how to easily install the Laravel framework. Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that speeds up the development process of web applications. This tutorial covers the installation process from system requirements to configuring databases and setting up routing. By following these steps, readers can quickly and efficiently lay a solid foundation for their Laravel project.
 How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
The key to installing MySQL elegantly is to add the official MySQL repository. The specific steps are as follows: Download the MySQL official GPG key to prevent phishing attacks. Add MySQL repository file: rpm -Uvh https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm Update yum repository cache: yum update installation MySQL: yum install mysql-server startup MySQL service: systemctl start mysqld set up booting
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Installing MySQL on CentOS involves the following steps: Adding the appropriate MySQL yum source. Execute the yum install mysql-server command to install the MySQL server. Use the mysql_secure_installation command to make security settings, such as setting the root user password. Customize the MySQL configuration file as needed. Tune MySQL parameters and optimize databases for performance.




