 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Detailed explanation and example code of JS implementation of calculator (1)
Detailed explanation and example code of JS implementation of calculator (1)
Detailed explanation and example code of JS implementation of calculator (1)
Javascript implements the calculator:
Series of articles:
JS implements the calculator in detail and example code (1)
Javascript implements the calculator time function in detail and examples ( 2)
小javascriptcalculator
The solution I came up with is a clumsy method. Although it is completed, there are still many bugs, and the method used is not the most effective. Basically The function is considered complete, and some small details have been taken into consideration, but there are still other details that need to be dealt with.
The overall design idea is to draw a sketch first -> Design UI -> Write UI code -> Write CSS -> Write JS logic code;
Panel (main-board)
Overall panel size design
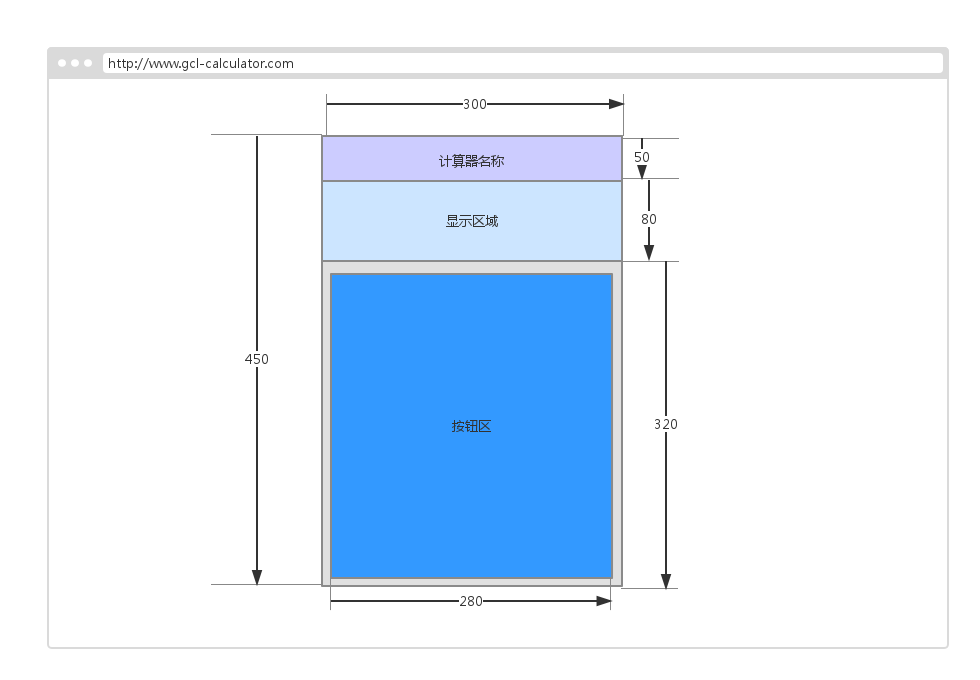
Title bar (board-title)
Font: font: 30px/50px “Comic Sans MS” , "Microsoft Yahei";
Width and height: (100%, 50px);
Screen display area (board-result)
Number display area (result-up ):
Expression display area (result-down):
Button area (board-keys), use the form to complete, and then add onclick event to each td
Complete the interface

Import new font
// main.css
@font-face {
font-family: Lovelo-Black;/×定义font的名字×/
src: url('font/Lovelo Black.otf');/*把下载的字体文件引入进来×/
}
Code analysis
Code organization structure
Calculator object: Calculator;
Calculator properties:
bdResult: DOM object of the screen display area on the calculator panel;
operator: operation Character array, including '+,-,×,÷,=';
digits: valid digit characters, including '0-9' and dot '.';
dot, equal, zero: '.', '=', '0' corresponds to three characters, dot, equal sign, character '0';
digit: the currently input number displayed in the upper layer of the screen display area;
expression: an expression consisting of input numbers and operators displayed in the lower layer of the screen display area;
resSpan: a span object that displays the current number in the upper layer of the screen display area;
resDown: the div object that displays the expression in the lower layer of the screen display area;
last: the last button content entered;
allDigits: all the valid digits in the expression parsed by the expression ;
ops: All operators in the expression parsed with the expression string;
hasEqual: Determine whether the '=' equal sign identifier is pressed;
lastRes: The last calculated result [TODO] has not been used yet and can be continuously calculated to be implemented;
Calculator method:
init: Calculator initialization method;
addTdClick: Add a click event to each td, that is, the calculator button;
calculatorClickEvent: click event;
btnClickHanlder: click event processing function;
showCurrRes: processing The content to be displayed in the upper and lower layers of the screen display area;
showText: display the result processed by showCurrRes;
addZero: add '0' in front of the expression;
calResult: calculation result;
clearData: clear data;
hasOperator: determine whether there is an operator in the expression;
isOperator: determine whether the current character is an operator ;
delHeadZero: Delete the '0' at the beginning of the expression;
Auxiliary method
getResSpan: Get the span object on the upper layer of the screen display;
$tag : Get the tag object based on the tag name;
$: Get the DOM object based on the id;
Code logic
Usage method
Introduce Calculator.js File (based on writing the UI)
Create the object and initialize: new Calculator().init();
Calculator object
// 计算器对象
function Calculator() {
// 私有属性
this.bdResult = $("board-result"); // 计算机面板结果显示区对象
this.operator = ['+', '-', '×', '÷', '='];
this.digits = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '.']; // 组成有效数字的数字数组
this.dot = '.';
this.equal = '=';
this.zero = '0';
this.digit = ""; // 当前输入的数字
this.expression = ""; // 表达式
this.resSpan = getResSpan(); // 数字显示区
this.resDown = $("result-down"); // 表达式显示区
this.last = ""; // 上一次按下的按钮内容
this.allDigits = []; // 从表达式中获取的所有数字组成的数组,将用来和ops中的操作符对应计算出结果
this.ops = []; // 所有操作符组成的数组
this.hasEqual = false; // 判断是否按下了'='键
this.lastRes = 0; // 上一次计算的结果,即上一次按等号后计算出的值
// 私有方法
}
Add a click event (note the reference problem of this in the closure)
// 为td添加点击事件
Calculator.prototype.addTdClick = function () {
var tds = $tag("td");
var that = this; // 需要注意保存this的引用
// 为每个td添加点击事件
for (var i = 0; i < tds.length; i++) {
tds[i].onclick = function (){
// alert(this.innerText);
var text = this.innerText;
that.calculatorClickEvent(text);
};
}
};
Calculator click event processing entrance
// 计算器按钮事件
Calculator.prototype.calculatorClickEvent = function (btnText) {
// 上一个按键是'='
if (this.hasEqual) {
this.hasEqual = false;
this.clearData();
}
// 结果显示在board-result里
if (btnText != "AC" && btnText != "CE") {
this.btnClickHanlder(btnText);
} else { // AC或CE清零
this.clearData();
}
};
Calculator click event handler
// 计算器的按键事件处理
Calculator.prototype.btnClickHanlder = function (btnText) {
if ((btnText >= '0' && btnText <= '9') || btnText == this.dot) { // 数字键处理
// 如果上一个是操作符,则清空当前数字区
if (this.isOperator(this.last)) {
this.resSpan.innerText = '';
this.digit = '';
} else if ((btnText == this.dot) && (this.last == this.dot)) {
// 如果上一个也是点,则对本次的点按钮不做响应
return;
}
this.digit += btnText;
this.expression += btnText;
} else if (this.isOperator(btnText)) { // 操作符处理
// 如果当前表达式为'0',按'=',不给响应
if ((btnText == this.equal) && (this.resDown.innerText == this.zero || this.resDown.innerText == "")) return;
// 如果上一个是非'='的操作符则不进行处理
if (!this.isOperator(this.last) && btnText == this.equal) { // '='处理
this.showCurrRes(this.zero, this.expression + btnText); // 计算结果显示在表达式区域
return;
} else if (this.isOperator(this.last)) {
// 上一个是操作符,此次的操作符不做记录
return;
} else {
this.expression += btnText;
}
}
this.showCurrRes(this.digit, this.expression);
this.last = btnText;
};
Processes the expression to be displayed and the current input Number
// 显示当前结果的触发方法
Calculator.prototype.showCurrRes = function (digit, expression) {
if (!expression) return;
this.showText(digit, expression);
// 1. 没有'=',表示还没有到计算结果的时候,直接退出
if (expression.indexOf(this.equal) == -1) return;
// 计算出了结果
this.hasEqual = true;
// 2. 处理只按了数字然后直接按了等号的情况,即:'234='则直接返回234
var tmpStr = this.delHeadZero(expression.substr(0, expression.length - 1)); // 去掉最后一个'='
if (!this.hasOperator(tmpStr)) {
this.showText(tmpStr, expression + tmpStr);
return;
}
// 3. 处理表达式字符串,且计算出结果
var start = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < expression.length; i++) {
var c = expression[i];
if (this.isOperator(c)) { // 操作符
this.ops.push(c); // 保存操作符
var numStr = expression.substr(start, i + 1); // 数字字符串
var number = 0;
// 浮点数和整型处理
if (numStr.indexOf(this.dot)) {
number = parseFloat(numStr);
} else {
number = parseInt(numStr);
}
this.allDigits.push(number); // 保存数字
start = i + 1; // 重设数字起始位置,即操作符的下一个字符开始
}
}
// 用allDigits和ops去计算结果
var res = this.calResult();
// 保存此次计算结果,作为下一次计算用 [TODO]
this.lastRes = res;
// 将结果显示出来
this.showText(res + '', expression + res);
};
Display the processing result to the screen display area
// 将表达式和计算结果显示到屏显区
Calculator.prototype.showText = function (digitStr, expression) {
// 先删除开头的'0'
var expStr = this.delHeadZero(expression);
var digStr = this.delHeadZero(digitStr);
// 然后再根据情况决定是否添加'0'
var tmp = expression == this.zero ? expression : this.addZero(expStr);;
var dig = digitStr == this.zero ? digitStr : this.addZero(digStr);
this.resSpan.innerText = dig;
// 如果表达式第一个是操作符,则表示之前按的是'0',则给补上'0',因为前面将开头的'0'都删掉了
if (this.isOperator(tmp[0])) {
tmp = this.zero + tmp;
}
this.resDown.innerText = tmp;
}
Calculation result Function
// 计算结果
Calculator.prototype.calResult = function () {
var first = 0;
var second = 0;
var res = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < this.ops.length; i++) {
first = this.allDigits[i];
second = this.allDigits[i + 1];
switch (this.ops[i]) {
case '+':
res = first + second;
break;
case '-':
res = first - second;
break;
case '×':
res = first * second;
break;
case '÷':
res = first / second;
break;
default:
break;
}
this.allDigits[i + 1] = res;
}
return res;
};
Clear data
// 计算完一次,清空所有数据,以备下次计算使用
Calculator.prototype.clearData = function () {
this.allDigits = [];
this.ops = [];
this.expression = this.zero;
this.digit = '';
this.resSpan.innerText = this.zero;
this.resDown.innerText = this.zero;
};
Auxiliary function
Processing The '0' problem at the beginning of the expression (the first button is the 0 key or the first is a floating point number less than 1, the expression needs to be filled with zeros;)
// 开头添加'0',防止重复出现或者没有'0'情况
Calculator.prototype.addZero = function (expression) {
if (!expression) return this.zero;
if (expression[0] == this.dot) { // 浮点数
return this.zero + expression;
} else {
return expression;
}
};
Remove zero function at the beginning
// 去开头的零
Calculator.prototype.delHeadZero = function (str) {
// 先把开头的‘0'都删掉
var tmp = "";
tmp = str.replace(/^[0]+/gi, "");
if (tmp[0] == this.dot) { // 浮点数重新补上'0'
tmp = this.zero + tmp;
}
return tmp;
};
Determine whether the string contains an operator
// 判断表达式中是否含有操作符
Calculator.prototype.hasOperator = function (str) {
if (!str) return;
for (var i = 0; i < this.operator.length; i++) {
if (str.indexOf(this.operator[i]) >= 0) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
Other functions
// 获取输入的数字显示区对象
function getResSpan() {
return $("result-up").getElementsByTagName("span")[0];
}
// 根据标签名获取DOM对象
function $tag(tagName) {
return document.getElementsByTagName(tagName);
}
// 根据ID获取DOM对象
function $(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
Problem
The bottom of the text is displayed: processed by setting the row height;
Through one-time When parsing an expression, you need to consider whether '0' needs to exist at the beginning of the expression;
Thank you for reading, I hope it can help everyone, thank you for your support of this site!
For more detailed explanations and example codes of JS calculator implementation (1), please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website for related articles!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1677
1677
 14
14
 1431
1431
 52
52
 1334
1334
 25
25
 1279
1279
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.
 JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and Projects
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and Projects
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript's application in the real world includes front-end and back-end development. 1) Display front-end applications by building a TODO list application, involving DOM operations and event processing. 2) Build RESTfulAPI through Node.js and Express to demonstrate back-end applications.
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation Details
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation Details
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and Tools
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and Tools
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Both Python and JavaScript's choices in development environments are important. 1) Python's development environment includes PyCharm, JupyterNotebook and Anaconda, which are suitable for data science and rapid prototyping. 2) The development environment of JavaScript includes Node.js, VSCode and Webpack, which are suitable for front-end and back-end development. Choosing the right tools according to project needs can improve development efficiency and project success rate.
 The Role of C/C in JavaScript Interpreters and Compilers
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Role of C/C in JavaScript Interpreters and Compilers
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C and C play a vital role in the JavaScript engine, mainly used to implement interpreters and JIT compilers. 1) C is used to parse JavaScript source code and generate an abstract syntax tree. 2) C is responsible for generating and executing bytecode. 3) C implements the JIT compiler, optimizes and compiles hot-spot code at runtime, and significantly improves the execution efficiency of JavaScript.
 From Websites to Apps: The Diverse Applications of JavaScript
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AM
From Websites to Apps: The Diverse Applications of JavaScript
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:02 AM
JavaScript is widely used in websites, mobile applications, desktop applications and server-side programming. 1) In website development, JavaScript operates DOM together with HTML and CSS to achieve dynamic effects and supports frameworks such as jQuery and React. 2) Through ReactNative and Ionic, JavaScript is used to develop cross-platform mobile applications. 3) The Electron framework enables JavaScript to build desktop applications. 4) Node.js allows JavaScript to run on the server side and supports high concurrent requests.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Use Cases and Applications Compared
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Use Cases and Applications Compared
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python is more suitable for data science and automation, while JavaScript is more suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 1. Python performs well in data science and machine learning, using libraries such as NumPy and Pandas for data processing and modeling. 2. Python is concise and efficient in automation and scripting. 3. JavaScript is indispensable in front-end development and is used to build dynamic web pages and single-page applications. 4. JavaScript plays a role in back-end development through Node.js and supports full-stack development.



