Node.js event queue explained
Node.js EventEmitter Event Queue
Node.js All asynchronous I/O operations will send an event to the event queue when completed.
Let’s explain the methods and examples of the event queue in detail
Methods:
[code]1.addListener(event, listener) 为指定事件添加一个监听器到监听器数组的尾部。 2.on(event, listener) 为指定事件注册一个监听器,接受一个字符串 event 和一个回调函数。 3.once(event, listener) 为指定事件注册一个单次监听器,即 监听器最多只会触发一次,触发后立刻解除该监听器。 4.removeListener(event, listener) 移除指定事件的某个监听器,监听器 必须是该事件已经注册过的监听器。 5.removeAllListeners([event]) 移除所有事件的所有监听器, 如果指定事件,则移除指定事件的所有监听器 6.setMaxListeners(n) 默认情况下, EventEmitters 如果你添加的监听器超过 10 个就会输出警告信息。 setMaxListeners 函数用于提高监听器的默认限制的数量。 7.listeners(event) 返回指定事件的监听器数组。 8.emit(event, [arg1], [arg2], [...]) 按参数的顺序执行每个监听器,如果事件有注册监听返回 true,否则返回 false。
Class method
[code]1.listenerCount(emitter, event) 返回指定事件的监听器数量。
Event
[code]1.newListener
event - 字符串,事件名称
listener - 处理事件函数
该事件在添加新监听器时被触发
2.removeListener
event - 字符串,事件名称
listener - 处理事件函数
从指定监听器数组中删除一个监听器。需要注意的是,此操作将会改变处于被删监听器之后的那些监听器的索引。event1.js
[code]// 引入 events 模块
var events = require('events');
// 创建 EventEmitter 对象
var eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter();
// 注册监听器
eventEmitter.on('some_event', function () {
console.log('some_event 事件触发');
});
// 计时器
setInterval(function () {
// 触发 some_event 监听器
eventEmitter.emit('some_event');
}, 1000);
Case 2: Pass parameters to the event queue
event2.js
[code]var events = require('events');
var eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter();
eventEmitter.on('listener', function (arg1, arg2) {
console.log('listener1', arg1, arg2);
})
eventEmitter.on('listener', function (arg1, arg2) {
console.log('listener2', arg1, arg2);
});
eventEmitter.emit('listener', 'zhang', 'li');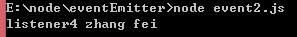
Case 3: Register two event handlers for the same listener
[code]var events = require('events');
var eventEmitter = new events.EventEmitter();
var listener1 = function (arg1, arg2) {
console.log('listener1', arg1, arg2);
};
var listener2 = function (arg1, arg2) {
console.log('listener2', arg1, arg2);
};
// 注册监听器
eventEmitter.on('listener', listener1);
eventEmitter.on('listener', listener2);
// 触发监听器事件
// eventEmitter.emit('listener', 'zhang', 'li');
var listenerLength = require('events').EventEmitter.listenerCount(eventEmitter, 'listener');
eventEmitter.emit('listener', 'zhang', 'li');
console.log('listener 监听器注册 ' + listenerLength + ' 个事件处理函数');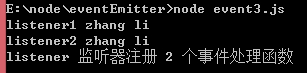
The above is the content of Node.js event queue. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Detailed graphic explanation of the memory and GC of the Node V8 engine
Mar 29, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
Detailed graphic explanation of the memory and GC of the Node V8 engine
Mar 29, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
This article will give you an in-depth understanding of the memory and garbage collector (GC) of the NodeJS V8 engine. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 An article about memory control in Node
Apr 26, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
An article about memory control in Node
Apr 26, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
The Node service built based on non-blocking and event-driven has the advantage of low memory consumption and is very suitable for handling massive network requests. Under the premise of massive requests, issues related to "memory control" need to be considered. 1. V8’s garbage collection mechanism and memory limitations Js is controlled by the garbage collection machine
 Let's talk about how to choose the best Node.js Docker image?
Dec 13, 2022 pm 08:00 PM
Let's talk about how to choose the best Node.js Docker image?
Dec 13, 2022 pm 08:00 PM
Choosing a Docker image for Node may seem like a trivial matter, but the size and potential vulnerabilities of the image can have a significant impact on your CI/CD process and security. So how do we choose the best Node.js Docker image?
 Node.js 19 is officially released, let's talk about its 6 major features!
Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:34 PM
Node.js 19 is officially released, let's talk about its 6 major features!
Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:34 PM
Node 19 has been officially released. This article will give you a detailed explanation of the 6 major features of Node.js 19. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Let's talk in depth about the File module in Node
Apr 24, 2023 pm 05:49 PM
Let's talk in depth about the File module in Node
Apr 24, 2023 pm 05:49 PM
The file module is an encapsulation of underlying file operations, such as file reading/writing/opening/closing/delete adding, etc. The biggest feature of the file module is that all methods provide two versions of **synchronous** and **asynchronous**, with Methods with the sync suffix are all synchronization methods, and those without are all heterogeneous methods.
 Let's talk about the event loop in Node
Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:08 PM
Let's talk about the event loop in Node
Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:08 PM
The event loop is a fundamental part of Node.js and enables asynchronous programming by ensuring that the main thread is not blocked. Understanding the event loop is crucial to building efficient applications. The following article will give you an in-depth understanding of the event loop in Node. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Let's talk about the GC (garbage collection) mechanism in Node.js
Nov 29, 2022 pm 08:44 PM
Let's talk about the GC (garbage collection) mechanism in Node.js
Nov 29, 2022 pm 08:44 PM
How does Node.js do GC (garbage collection)? The following article will take you through it.
 Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
How to package nodejs executable file with pkg? The following article will introduce to you how to use pkg to package a Node project into an executable file. I hope it will be helpful to you!






