va.js—The writing process of Vue form validation plug-in
Foreword
Some time ago, the boss set up the Vue development environment, so we happily came to Vue from JQ. During this period, I was not happy with the form verification. When I saw the plug-in chapter of Vue, I felt that I could write one, so I started writing a form verification plug-in va.js. Of course why not find a plug-in? vue-validator.
I thought about it. One is that form verification is a highly customized thing. In order to take into account the needs of various companies, this kind of plug-in found online adds a lot of functions, which we don’t need. It turns out that vue-validator is 50kb, and the va.js I wrote is only 6kb.
Another thing is that I really think the API of vue-validator is very long. It’s always v-validate:username="['required']", such a long list, and the call I designed is probably like - v-va :Money
Of course, this article only shows how to write a vue form validation plug-in that meets the needs of your company. The following introduces the ideas.
1. The composition of the form validation module
Any form validation module is composed of configuration - verification - error reporting - value collection.
Configuration: Configuration rules and configuration error reporting, as well as priority
Verification: There is verification in the change event, verification when the submit button is clicked, and of course there is also verification in the input event value
Error reporting: The error reporting method is generally points, the error text has a template, and also has a customized
value: Return the verified data to the developer for a call
The following is the request my boss made to me for the company project
Centralized management verification rules and error reporting templates.
The error reporting time is optional
The verified data has been packaged into objects and can be used directly
to allow each page to override the rules, customize the error reporting information, and allow ajax to obtain the data, and then The rules are supplemented
I asked curiously, why is it like this? Then the boss answered me one by one:
The advantage of centralized management rules and error reporting templates is that the rules can be used globally and can be changed once and for all. The boss told me that the regular nickname alone was changed three times. If these regular rules are written on each page, o( ̄ヘ ̄o#) hum, you will have to change N pages
PC and mobile processes are different. Many verifications on PC must be done in the change event or input event. Verification and error reporting, while mobile generally requires going to the submit button for verification. So be prepared when writing a plug-in. Then, the UI used for error reporting must be able to support the layer plug-in we are using now. Of course, the error UI may change in the future, so you understand.
Of course, in the jq era, our public form verification can complete the verification and collect all the data into one object. In this way, there is no need to get the value when using ajax. This plug-in of yours is going to achieve this effect
It turns out that jq’s public script, regular expressions and error reporting are all concentrated in one place, which is very convenient in many places. But it is not flexible enough when some pages need to be changed. Rules like RealName were first configured for a certain page, using the field names on the backend interface. On another payment page, the field name on the back-end interface has been changed to PayUser, but the regular expression is still RealName. It turns out that we need to overwrite RealName. This is not convenient and looks good. The other one, the payment amount, has maximum and minimum limits, which need to be obtained from the backend. You also need to consider this situation. It is necessary to have some flexibility on each page to modify rules, customize error reporting, etc.
After listening to it, I roughly understood it. It turned out that the jq form verification I wrote before had so many uncomfortable points. -_-|||Next, let’s take a look at the good things vue has given me. Let me write
Second, how to write a Vue plug-in
I am a Vue novice, why did I start writing a Vue plug-in? That’s because when I was thinking of a solution, I flipped through the Vue documentation and came here
these things. When I finished writing va.js, I felt that what you wrote was really clear.
Actually, I want to write a command to complete form verification. It turns out that there may be 2-3 instructions, and some methods need to be defined on Vue.prototype so that the rules can be expanded within each sub-instance. So the boss said, this is equivalent to a plug-in. This makes me feel like a whale.
va.js mainly uses Vue commands
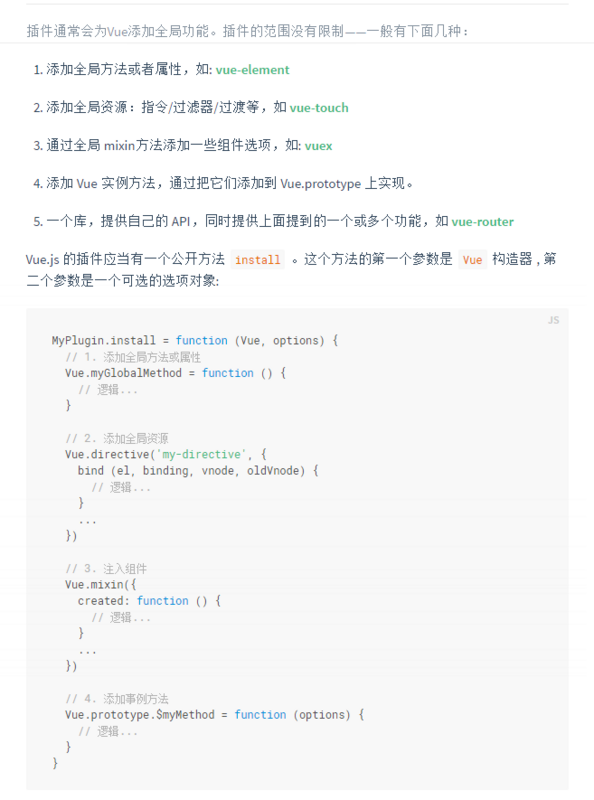
These things, when I finished writing va.js, I felt that what you wrote was really clear.
Actually, I want to write a command to complete the form verification. It turns out that there may be 2-3 instructions, and some methods need to be defined on Vue.prototype so that the rules can be expanded within each sub-instance. So the boss said, this is equivalent to a plug-in. This makes me feel like a whale.
va.js mainly uses Vue instructions
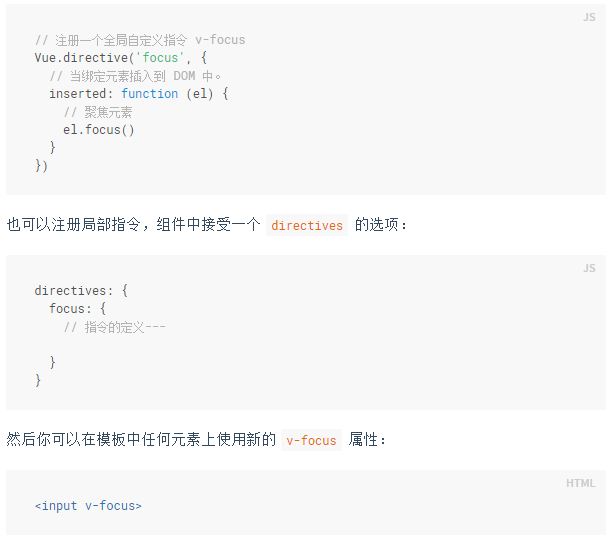

Vue documentation is really written carefully, but let me add one more thing
vnode.context is an instance of Vue
When we are doing projects, we often There are N sub-components hanging on a root component, and N sub-components may be hung on the sub-components. The instance obtained by vnode.context is the instance of the component bound to the instruction. This is quite useful. You can do a lot of things
Of course you also use some Vue.prototype
Vue.prototype.$method is the method that can be called on each component. It can be called using this.$method inside the component

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1665
1665
 14
14
 1424
1424
 52
52
 1322
1322
 25
25
 1270
1270
 29
29
 1249
1249
 24
24
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Different JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.
 JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and Projects
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and Projects
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript's application in the real world includes front-end and back-end development. 1) Display front-end applications by building a TODO list application, involving DOM operations and event processing. 2) Build RESTfulAPI through Node.js and Express to demonstrate back-end applications.
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation Details
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation Details
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and Tools
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and Tools
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Both Python and JavaScript's choices in development environments are important. 1) Python's development environment includes PyCharm, JupyterNotebook and Anaconda, which are suitable for data science and rapid prototyping. 2) The development environment of JavaScript includes Node.js, VSCode and Webpack, which are suitable for front-end and back-end development. Choosing the right tools according to project needs can improve development efficiency and project success rate.




