请问谁能给个解释?关于引用“&”
class Test { protected $var = null; function __construct(&$var) { $var['z']=2; $this->var = &$var; $this->var['xx']=2; }}$x=['b'=>2];$d=new Test($x);print_r($x);以上代码如果把$this->var = &$var变成$this->var = $var;
则xx=2这句不生效。$var不是已经是引用了吗?
回复讨论(解决方案)
你修改的是$this->var 但引用的是构造函数的临时变量$var
所以$x不变
$this->var['xx']=2; 再改成$var['xx'] = 2;
你修改的是$this->var 但引用的是构造函数的临时变量$var
所以$x不变
$this->var['xx']=2; 再改成$var['xx'] = 2;
不太明白你的意思。$this->var难道不是指外部变量$x的引用?因为构造中用的是(&$var)这个$var就是引用。而把这个引用给了类中的var
有什么问题吗?很正常啊,是引用地址了。
class Test { protected $var = null; function __construct(&$var) { $var['z']=2; $this->var = &$var; $this->var['xx']=2; }} $x=array('b'=>2);$d=new Test($x);print_r($x);Array
(
[b] => 2
[z] => 2
[xx] => 2
)
$x = array('b'=>2);
$a =& $x; //$a 是 $x 的引用
$a['a'] = 'a'; //所以对 $a 的改变会影响到 $x
$b = $a; //$b 不是 $a 的引用
$b['b'] = 'b'; //所以对 $b 的改变不会影响到 $a,更不会传递到 $x
print_r($x);
http://www.cnblogs.com/thinksasa/p/3334492.html
看看就明白了
$this->var = $var; 不是引用,$this->var修改不?影?$var
$this->var = &$var; 是引用 ,$this->var修改?影?$var
不太明白你的意思。$this->var难道不是指外部变量$x的引用?因为构造中用的是(&$var)这个$var就是引用。而把这个引用给了类中的var
我好像明白你的疑问在哪了
如果$b引用了$a,你再用$b给$c赋值,如果不再次引用$b,$c得到的还是一个新建内存数据,想要使$c引用到$a,那么必须$c = &$b
不太明白你的意思。$this->var难道不是指外部变量$x的引用?因为构造中用的是(&$var)这个$var就是引用。而把这个引用给了类中的var
我好像明白你的疑问在哪了
如果$b引用了$a,你再用$b给$c赋值,如果不再次引用$b,$c得到的还是一个新建内存数据,想要使$c引用到$a,那么必须$c = &$b
看了下手册,貌似php的&与c语言中的&根本不是一个概念。
php 的引用和 c语言 的指针当然不是一回事
但你主贴中的代码的表现和等价c代码的表现是一样的

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1425
1425
 52
52
 1327
1327
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1253
1253
 24
24
 What is the analysis of 2.8k screen?
Jan 02, 2024 pm 12:21 PM
What is the analysis of 2.8k screen?
Jan 02, 2024 pm 12:21 PM
We often see the introduction of how many K screens we have when buying TVs, computers or mobile phones, such as 2.8K screens. At this time, there will be friends who don’t know much about electronic devices and will be curious about what this 2.8K screen means and what the resolution is. What does 2.8k screen mean? Answer: 2.8k screen means that the screen resolution is 2880*18002K, which means the number of horizontal pixels is greater than 2000. For the same size screen, the higher the resolution, the better the picture quality. Introduction to resolution 1. Since the points, lines and surfaces on the screen are all composed of pixels, the more pixels the monitor can display, the finer the picture, and the more information can be displayed in the same screen area. 2. The higher the resolution, the greater the number of pixels, and the sharper the sensed image.
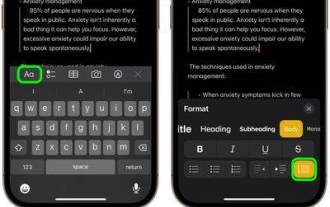 How to use block quotes in Apple Notes
Oct 12, 2023 pm 11:49 PM
How to use block quotes in Apple Notes
Oct 12, 2023 pm 11:49 PM
In iOS 17 and macOS Sonoma, Apple has added new formatting options for Apple Notes, including block quotes and a new Monostyle style. Here's how to use them. With additional formatting options in Apple Notes, you can now add block quotes to your notes. The block quote format makes it easy to visually offset sections of writing using the quote bar to the left of the text. Just tap/click the "Aa" format button and select the block quote option before typing or when you are on the line you want to convert to a block quote. This option applies to all text types, style options, and lists, including checklists. In the same Format menu you can find the new Single Style option. This is a revision of the previous "equal-width"
 C++ compilation error: undefined reference, how to solve it?
Aug 21, 2023 pm 08:52 PM
C++ compilation error: undefined reference, how to solve it?
Aug 21, 2023 pm 08:52 PM
C++ is a popular programming language, but during use, the compilation error "undefined reference" often occurs, which brings a lot of trouble to program development. This article will discuss the solution to the "undefined reference" error from both the cause and the solution. 1. Cause of error When the C++ compiler compiles a source file, it will be divided into two stages: the compilation stage and the link stage. The compilation phase converts the source code in the source files into assembly code, while the linking phase combines different source files into an executable file.
 What are the benefits of C++ functions returning reference types?
Apr 20, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
What are the benefits of C++ functions returning reference types?
Apr 20, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
The benefits of functions returning reference types in C++ include: Performance improvements: Passing by reference avoids object copying, thus saving memory and time. Direct modification: The caller can directly modify the returned reference object without reassigning it. Code simplicity: Passing by reference simplifies the code and requires no additional assignment operations.
 How to use C++ reference and pointer parameter passing?
Apr 12, 2024 pm 10:21 PM
How to use C++ reference and pointer parameter passing?
Apr 12, 2024 pm 10:21 PM
References and pointers in C++ are both methods of passing function parameters, but there are differences. A reference is an alias for a variable. Modifying the reference will modify the original variable, while the pointer stores the address of the variable. Modifying the pointer value will not modify the original variable. When choosing to use a reference or a pointer, you need to consider factors such as whether the original variable needs to be modified, whether a null value needs to be passed, and performance considerations.
 C++ syntax error: When a function returns a pointer or reference, it cannot return a local variable or temporary object. What should I do?
Aug 22, 2023 am 09:22 AM
C++ syntax error: When a function returns a pointer or reference, it cannot return a local variable or temporary object. What should I do?
Aug 22, 2023 am 09:22 AM
C++ is an object-oriented programming language, and its flexibility and power often provide programmers with great help. However, precisely because of its flexibility, it is difficult to avoid various small errors when programming. One of the most common mistakes is that when a function returns a pointer or reference, it cannot return a local variable or temporary object. So how to deal with this problem? This article will introduce the relevant content in detail. The cause of the problem is that in the C++ language, local variables and temporary objects are dynamically allocated during the running of the function. When the function ends, these local variables and temporary
 In-depth analysis of pointers and references in C++ to optimize memory usage
Jun 02, 2024 pm 07:50 PM
In-depth analysis of pointers and references in C++ to optimize memory usage
Jun 02, 2024 pm 07:50 PM
By using pointers and references, memory usage in C++ can be optimized: Pointers: store addresses of other variables and can point to different variables, saving memory, but may generate wild pointers. Reference: Aliased to another variable, always points to the same variable, does not generate wild pointers, and is suitable for function parameters. Optimizing memory usage can improve code efficiency and performance by avoiding unnecessary copies, reducing memory allocations, and saving space.
 Things to note when passing C++ function constant reference parameters
Apr 21, 2024 am 08:30 AM
Things to note when passing C++ function constant reference parameters
Apr 21, 2024 am 08:30 AM
Constant reference parameter passing ensures parameter immutability within a function and has the following advantages: Parameter immutability: A function cannot modify constant reference parameters. Improved efficiency: no need to create copies of parameters. Error detection: Attempting to modify a constant reference parameter triggers a compile-time error.




