Learn javascript through jQuery source code (2)_jquery
Clever 1: Function
Function is a rare talent in JavaScript code.
♥ It can place code segments and encapsulate relatively independent functions.
♥ It can also implement classes and inject OOP ideas.
jQuery is a function, you can also think of it as a class (haha, it is a class in itself).
(function(){
var jQuery = function() {
// Function body
}
window.jQuery = window.$ = jQuery;
})();
console.log(jQuery);
The empty function above is the so-called constructor. The constructor is a basic method of a class in object-oriented languages.
Clever 2: Extended Prototype
What is a prototype object? I will give you a blog post that you can read about http://www.jb51.net/article/32857.htm.
JavaScript binds a prototype attribute to all functions, and this attribute points to a prototype object. We define the inherited properties and methods of the class in the prototype object.
The prototype object is the basic mechanism for JavaScript to implement inheritance.
(function(){
var jQuery = function () {
// Function body
}
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
// Extended prototype object
jquery: "1.8.3",
test: function() {
console.log('test');
}
}
window.jQuery = window.$ = jQuery;
})();
(new jQuery()).test();
Clever 3: Use the factory method to create an instance
The above method must be called using the following method, so A lot of objects will be generated, thus wasting memory consumption.
(new jQuery()).test();
The jQuery source code uses a very soft method, which is also a familiar factory method, for calling.
(function(){
var jQuery = function () {
// Function body
return jQuery.fn.init();
}
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
// Extended prototype object
jquery : "1.8.3",
init: function() {
return this;
},
test: function() {
console.log('test');
}
}
window.jQuery = window.$ = jQuery;
})();
jQuery().test();

(function(){
var jQuery = function() {
return this;
}
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
//Extended prototype object
jquery: "1.8.3",
test: function() {
console.log('test');
}
}
window.jQuery = window.$ = jQuery;
})();
console.log(jQuery());
Output Result
Imagination 2: Let the jQuery function body directly return an instance of the class.
(function(){
var jQuery = function() {
return new jQuery();
}
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
// Extended prototype object
jquery: "1.8.3",
test: function() {
console.log('test');
}
}
window.jQuery = window.$ = jQuery;
})();
console.log(jQuery());
Output results
Clever 4: Separate scopes
Thinking 1: What is the this scope returned by the init() method?
(function(){
var jQuery = function() {
// Function body
return jQuery.fn.init();
}
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
// Extended prototype object
jquery: "1.8.3",
init: function() {
this.init_jquery = '2.0';
return this ;
}
}
window.jQuery = window.$ = jQuery;
})();
console.log(jQuery().jquery);
console.log (jQuery().init_jquery);
Output result

This scope in the init() method: the this keyword refers to the init() function The object where the scope is located can also access the function of the upper-level object jQuery.fn object. ——This kind of thinking will destroy the independence of scope, which is likely to have a negative impact on the jQuery framework.
Thought 2: How to separate this in init() from the jQuery.fn object? ——Instantiate the init initialization type.
(function(){
var jQuery = function () {
// Function body
return new jQuery.fn.init();
}
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
// Extended prototype object
jquery: "1.8.3",
init: function() {
this.init_jquery = '2.0';
return this;
}
}
window.jQuery = window .$ = jQuery;
})();
console.log(jQuery().jquery);
console.log(jQuery().init_jquery);
The output result
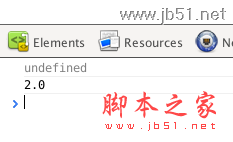
is initialized by instantiating the init() type, limiting this in the init() method, only active within the init() function, and preventing it from going out of scope.
Ingenious 5: Prototype passing
Thinking 1: In Ingenious 4, we separate this in init() from the jquery.fn object. So how can we ensure "Smart 4" and still access the jQuery prototype object? ——Prototype transfer.
Let jQuery’s prototype object override the prototype object of the init() constructor.
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn;
All codes:
(function(){
var jQuery = function() {
// Function body
return new jQuery.fn.init();
}
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype = {
// Extended prototype object
jquery: "1.8.3",
init: function() {
this.init_jquery = '2.0';
return this;
}
}
jQuery.fn.init.prototype = jQuery.fn;
window.jQuery = window.$ = jQuery;
})();
console.log(jQuery() .jquery);
console.log(jQuery().init_jquery);
Output result
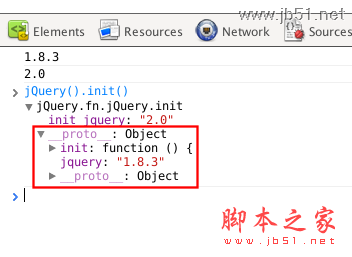
Point the prototype pointer of the init() object to jQuery.fn. ——In this way, this in init() inherits the methods and properties defined by the jQuery.fn prototype object.
Summary
Thank you bloggers for your messages, especially puni, who introduced me to a good book. It would be great if you could add some more.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1248
1248
 24
24
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Different JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript is the core language of modern web development and is widely used for its diversity and flexibility. 1) Front-end development: build dynamic web pages and single-page applications through DOM operations and modern frameworks (such as React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Server-side development: Node.js uses a non-blocking I/O model to handle high concurrency and real-time applications. 3) Mobile and desktop application development: cross-platform development is realized through ReactNative and Electron to improve development efficiency.
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
This article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
I built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.




