 Software Tutorial
Software Tutorial
 Office Software
Office Software
 Array formulas and functions in Excel - examples and guidelines
Array formulas and functions in Excel - examples and guidelines
Array formulas and functions in Excel - examples and guidelines
In this tutorial, you will learn what an Excel array formula is, how to enter it correctly in your worksheets, and how to use array constants and array functions.
Array formulas in Excel are an extremely powerful tool and one of the most difficult to master. A single array formula can perform multiple calculations and replace thousands of usual formulas. And still, 90% of users have never used array functions in their worksheets simply because they are scared to start learning them.
Indeed, array formulas one of the most confusing Excel features to learn. The aim of this tutorial is to make the learning curve as easy and smooth as possible.
What is an array in Excel?
Before we start on array functions and formulas, let's figure out what the term "array" means. Essentially, an array is a collection of items. The items can be text or numbers and they can reside in a single row or column, or in multiple rows and columns.
For example, if you put your weekly grocery list into an Excel array format, it would look like:
{"Milk", "Eggs", "Butter", "Corn flakes"}
Then, if you select cells A1 through D1, enter the above array preceded by an equal sign (=) in the formula bar and press CTRL SHIFT ENTER, you will get the following result:

What you have just done is create a one-dimensional horizontal array. Nothing dreadful so far, right?
What is an array formula in Excel?
The difference between an array formula and a regular formula is that an array formula processes several values instead of just one. In other words, an array formula in Excel evaluates all individual values in an array and performs multiple calculations on one or several items according to the conditions expressed in the formula.
Not only can an array formula deal with several values simultaneously, it can also return several values at a time. So, the results returned by an array formula is also an array.
Array formulas are available in all versions of Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2010, Excel 2007 and lower.
And now, it seems to be the right time for you to create your first array formula.
Simple example of Excel array formula
Suppose you have some items in column B, their prices in column C, and you want to calculate the grand total of all sales.
Of course, nothing prevents you from calculating subtotals in each row first with something as simple as =B2*C2 and then sum those values:

However, an array formula can spare you those extra key strokes since it gets Excel to store intermediate results in memory rather than in an additional column. So, all it takes is a single array formula and 2 quick steps:
- Select an empty cell and enter the following formula in it:
=SUM(B2:B6*C2:C6) - Press the keyboard shortcut CTRL SHIFT ENTER to complete the array formula.
Once you do this, Microsoft Excel surrounds the formula with {curly braces}, which is a visual indication of an array formula.
What the formula does is multiply the values in each individual row of the specified array (cells B2 through C6), add the sub-totals together, and output the grand total:

This simple example shows how powerful an array formula can be. When working with hundreds and thousands of rows of data, just think how much time you can save by entering one array formula in a single cell.
Why use array formulas in Excel?
Excel array formulas are the handiest tool to perform sophisticated calculations and do complex tasks. A single array formula can replace literally hundreds of usual formulas. Array formulas are very good for tasks such as:
- Sum numbers that meet certain conditions, for example sum N largest or smallest values in a range.
- Sum every other row, or every Nth row or column, as demonstrated in this example.
- Count the number of all or certain characters in a specified range. Here is an array formula that counts all chars, and another one that counts any given characters.
How to enter array formula in Excel (Ctrl Shift Enter)
As you already know, the combination of the 3 keys CTRL SHIFT ENTER is a magic touch that turns a regular formula into an array formula.
When entering an array formula in Excel, there are 4 important things to keep in mind:
- Once you've finished typing the formula and simultaneously pressed the keys CTRL SHIFT ENTER, Excel automatically encloses the formula between {curly braces}. When you select such a cell(s), you can see the braces in the formula bar, which gives you a clue that an array formula is in there.
- Manually typing the braces around a formula won't work. You must press the Ctrl Shift Enter shortcut to complete an array formula.
- Every time you edit an array formula, the braces disappear and you must press Ctrl Shift Enter again to save the changes.
- If you forget to press Ctrl Shift Enter, your formula will behave like a usual formula and process only the first value(s) in the specified array(s).
Because all Excel array formulas require pressing Ctrl Shift Enter, they are sometimes called CSE formulas.
Use the F9 key to evaluate portions of an array formula
When working with array formulas in Excel, you can observe how they calculate and store their items (internal arrays) to display the final result you see in a cell. To do this, select one or several arguments within a function's parentheses, and then press the F9 key. To exit the formula evaluation mode, press the Esc key.
In the above example, to see the sub-totals of all products, you select B2:B6*C2:C6, press F9 and get the following result.

Note. Please pay attention that you must select some part of the formula prior to pressing F9, otherwise the F9 key will simply replace your formula with the calculated value(s).
Single-cell and multi-cell array formulas in Excel
Excel array formula can return a result in a single cell or in multiple cells. An array formula entered in a range of cells is called a multi-cell formula. An array formula residing in a single cell is called a single-cell formula.
There exist a few Excel array functions that are designed to return multi-cell arrays, for example TRANSPOSE, TREND, FREQUENCY, LINEST, etc.
Other functions, such as SUM, AVERAGE, AGGREGATE, MAX, MIN, can calculate array expressions when entered into a single cell by using Ctrl Shift Enter.
The following examples demonstrate how to use a single-cell and multi-cell array formula.
Example 1. A single-cell array formula
Suppose you have two columns listing the number of items sold in 2 different months, say columns B and C, and you want to find the maximum sales increase.
Normally, you would add an additional column, say column D, that calculates the sales change for each product using a formula like =C2-B2, and then find the maximum value in that additional column =MAX(D:D).
An array formula does not need an additional column since it perfectly stores intermediate results in memory. So, you just enter the following formula and press Ctrl Shift Enter:
=MAX(C2:C6-B2:B6)

Example 2. A multi-cell array formula in Excel
In the previous SUM example, suppose you have to pay 10% tax from each sale and you want to calculate the tax amount for each product with one formula.
Select the range of empty cells, say D2:D6, and enter the following formula in the formula bar:
=B2:B6 * C2:C6 * 0.1
Once you press Ctrl Shift Enter, Excel will place an instance of your array formula in each cell of the selected range, and you will get the following result:

Example 3. Using an Excel array function to return a multi-cell array
As already mentioned, Microsoft Excel provides a few so called "array functions" that are specially designed to work with multi-cell arrays. TRANSPOSE is one of such functions and we are going to utilize it to transpose the above table, i.e. convert rows to columns.
- Select an empty range of cells where you want to output the transposed table. Since we are converting rows to columns, be sure to select the same number of rows and columns as your source table has columns and rows, respectively. In this example, we are selecting 6 columns and 4 rows.
- Press F2 to enter the edit mode.
- Enter the formula and press Ctrl Shift Enter.
In our example, the formula is:
=TRANSPOSE($A$1:$D$6)
The result is going to look similar to this:

This is how you use TRANSPOSE as a CSE array formula in Excel 2019 and earlier. In Dynamic Array Excel, this also works as a regular formula. To learn other ways to transpose in Excel, please check out this tutorial: How to switch columns and rows in Excel.
How to work with multi-cell array formulas
When working with multi-cell array formulas in Excel, be sure to follow these rules to get the correct results:
- Select the range of cells where you want to output the results before entering the formula.
- To delete a multi-cell array formula, either select all the cells containing it and press DELETE, or select the entire formula in the formula bar, press DELETE, and then press Ctrl Shift Enter.
- You cannot edit or move the contents of an individual cell in an array formula, nor can you insert new cells into or delete existing cells from a multi-cell array formula. Whenever you try doing this, Microsoft Excel will throw the warning "You cannot change part of an array".
- To shrink an array formula, i.e. to apply it to fewer cells, you need to delete the existing formula first and then enter a new one.
- To expand an array formula, i.e. apply it to more cells, select all cells containing the current formula plus empty cells where you want to have it, press F2 to switch to the edit mode, adjust the references in the formula and press Ctrl Shift Enter to update it.
- You cannot use multi-cell array formulas in Excel tables.
- You should enter a multi-cell array formula in a range of cells of the same size as the resulting array returned by the formula. If your Excel array formula produces an array larger than the selected range, the excess values won't appear on the worksheet. If an array returned by the formula is smaller than the selected range, #N/A errors will appear in extra cells.
If your formula may return an array with a variable number of elements, enter it in a range equal to or larger than the maximum array returned by the formula and wrap your formula in the IFERROR function, as demonstrated in this example.
Excel array constants
In Microsoft Excel, an array constant is simply a set of static values. These values never change when you copy a formula to other cells or values.
You already saw an example of an array constant created from a grocery list in the very beginning of this tutorial. Now, let's see what other array types exist and how you create them.
There exist 3 types of array constants:
1. Horizontal array constant
A horizontal array constant resides in a row. To create a row array constant, type the values separated by commas and enclose then in braces, for example {1,2,3,4}.
Note. When creating an array constant, you should type the opening and closing braces manually.
To enter a horizontal array in a spreadsheet, select the corresponding number of blank cells in a row, type the formula ={1,2,3,4} in the formula bar, and press Ctrl Shift Enter. The result will be similar to this:

As you see in the screenshot, Excel wraps an array constant in another set of braces, exactly like it does when you are entering an array formula.
2. Vertical array constant
A vertical array constant resides in a column. You create it in the same way as a horizontal array with the only difference that you delimit the items with semicolons, for example:
={11; 22; 33; 44}

3. Two-dimensional array constant
To create a two-dimensional array, you separate each row by a semicolon and each column of data by a comma.
={"a", "b", "c"; 1, 2, 3}

Working with Excel array constants
Array constants are one of the cornerstones of an Excel array formula. The following information and tips might help you use them in the most efficient way.
-
Elements of an array constant
An array constant can contain numbers, text values, Booleans (TRUE and FALSE) and error values, separated by commas or semicolons.
You can enter a numerical value as an integer, decimal, or in scientific notation. If you use text values, they should be surrounded in double quotes (") like in any Excel formula.
An array constant cannot include other arrays, cell references, ranges, dates, defined names, formulas, or functions.
-
Naming array constants
To make an array constant easier to use, give it a name:
- Switch to the Formulas tab > Defined Names group and click Define Name. Alternatively, press Ctrl F3 and click New.
- Type the name in the Name
- In the Refers to box, enter the items of your array constant surrounded in braces with the preceding equality sign (=). For example:
={"Su", "Mo", "Tu", "We", "Th", "Fr", "Sa"}
- Click OK to save your named array and close the window.
To enter the named array constant in a sheet, select as many cells in a row or column as there are items in your array, type the array's name in the formula bar preceded with the = sign and press Ctrl Shift Enter.
The result should resemble this:

-
Preventing errors
If your array constant does not work correctly, check for the following problems:
- Delimit the elements of your array constant with the proper character - comma in horizontal array constants and semicolon in vertical ones.
- Selected a range of cells that exactly matches the number of items in your array constant. If you select more cells, each extra cell will have the #N/A error. If you select fewer cells, only a part of the array will be inserted.
Using array constants in Excel formulas
Now that you are familiar with the concept of array constants, let's see how you can use arrays informulas to solve your practical tasks.
Example 1. Sum N largest / smallest numbers in a range
You start by creating a vertical array constant containing as many numbers as you want to sum. For example, if you want to add up 3 smallest or largest numbers in a range, the array constant is {1,2,3}.
Then, you take either LARGE or SMALL function, specify entire range of cells in the first parameter and include the array constant in the second. Finally, embed it in the SUM function, like this:
Sum the largest 3 numbers: =SUM(LARGE(range, {1,2,3}))
Sum the smallest 3 numbers: =SUM(SMALL(range, {1,2,3}))
Don't forget to press Ctrl Shift Enter since you are entering an array formula, and you will get the following result:

In a similar fashion, you can calculate the average of N smallest or largest values in a range:
Average of the top 3 numbers: =AVERAGE(LARGE(range, {1,2,3}))
Average of the bottom 3 numbers: =AVERAGE(SMALL(range, {1,2,3}))
Example 2. Array formula to count cells with multiple conditions
Suppose, you have a list of orders and you want to know how many times a given seller has sold given products.
The easiest way would be using a COUNTIFS formula with multiple conditions. However, if you want to include many products, your COUNTIFS formula may grow too big in size. To make it more compact, you can use COUNTIFS together with SUM and include an array constant in one or several arguments, for example:
=SUM(COUNTIFS(range1, "criteria1", range2, {"criteria1", "criteria2"}))
The real formula may look as follows:
=SUM(COUNTIFS(B2:B9, "sally", C2:C9, {"apples", "lemons"}))

Our sample array consists of only two elements since the goal is to demonstrate the approach. In your real array formulas, you may include as many elements as your business logic requires, provided that the total length of the formula does not exceed 8,192 characters in Excel 2019 - 2007 (1,024 characters in Excel 2003 and lower) and your computer is powerful enough to process large arrays. Please see the limitations of array formulas for more details.
And here is an advanced array formula example that finds the sum of all matching values in a table: SUM and VLOOKUP with an array constant.
AND and OR operators in Excel array formulas
An array operator tells the formula how you want to process the arrays - using AND or OR logic.
- AND operator is the asterisk (*) which is the multiplication symbol. It instructs Excel to return TRUE if ALL of the conditions evaluate to TRUE.
- OR operator is the plus sign ( ). It returns TRUE if ANY of the conditions in a given expression evaluates to TRUE.
Array formula with the AND operator
In this example, we find the sum of sales where the sales person is Mike AND the product is Apples:
=SUM((A2:A9="Mike") * (B2:B9="Apples") * (C2:C9))
Or
=SUM(IF(((A2:A9="Mike") * (B2:B9="Apples")), (C2:C9)))

Technically, this formula multiplies the elements of the three arrays in the same positions. The first two arrays are represented by TRUE and FALSE values which are the results of comparing A2:A9 to Mike" and B2:B9 to "Apples". The third array contains the sales numbers from the range C2:C9. Like any math operation, multiplication converts TRUE and FALSE to 1 and 0, respectively. And because multiplying by 0 always gives zero, the resulting array has 0 when either or both conditions are not met. If both conditions are met, the corresponding element from the third array gets into the final array (e.g. 1*1*C2 = 10). So, the result of multiplication is this array: {10;0;0;30;0;0;0;0}. Finally, the SUM function adds up the array's elements and return a result of 40.
Excel array formula with the OR operator
The following array formula with the OR operator ( ) adds up all sales where the sales person is Mike OR product is Apples:
=SUM(IF(((A2:A9="Mike") (B2:B9="Apples")), (C2:C9)))

In this formula, you add up the elements of the first two arrays (which are the conditions you want to test), and get TRUE (>0) if at least one condition evaluates to TRUE; FALSE (0) when all the conditions evaluates to FALSE. Then, IF checks if the result of addition is greater than 0, and if it is, SUM adds up a corresponding element of the third array (C2:C9).
Tip. In modern versions of Excel, there is no need to use an array formula for this kind of tasks - a simple SUMIFS formula handles them perfectly. Nevertheless, the AND and OR operators in array formulas may prove helpful in more complex scenarios, let alone a very good gymnastics of mind : )
Double unary operator in Excel array formulas
If you've ever worked with array formulas in Excel, chances are you came across a few ones containing a double dash (--) and you may have wondered what it was used for.
A double dash, which is technically called the double unary operator or double negative, is used to convert non-numeric Boolean values (TRUE / FALSE) returned by some expressions into 1 and 0 that an array function can understand.
The following example will hopefully make things easier to understand. Suppose you have a list of dates in column A and you want to know how many dates occur in January, regardless of the year.
The following formula will work a treat:
=SUM(--(MONTH(A2:A10)=1))
Since this is an Excel array formula, remember to press Ctrl Shift Enter to complete it.
If you are interested in some other month, replace 1 with a corresponding number. For example, 2 stands for February, 3 means March, and so on. To make the formula more flexible, you can specify the month number in some cell, like demonstrated in the screenshot:

And now, let's analyze how this array formula works. The MONTH function returns the month of each date in cells A2 through A10 represented by a serial number, which producing the array {2;1;4;2;12;1;2;12;1}.
After that, each element of the array is compared to the value in cell D1, which is number 1 in this example. The result of this comparison is an array of Boolean values TRUE and FALSE. As you remember, you can select a certain portion of an array formula and press F9 to see what that part equates to:

Finally, you have to convert these Boolean values to 1's and 0's that the SUM function can understand. And this is what the double negative sign is needed for. The first unary coerces TRUE/FALSE to -1/0, respectively. The second one negates the values, i.e. reverses the sign, turning them into 1 and 0, which most of Excel functions can understand and work with. If you remove the double unary from the above formula, it won't work.
I am hopeful this short tutorial has proved helpful on your road to mastering Excel array formulas. Next week, we are going to continue with Excel arrays by focusing on advanced formula examples. Please stay tuned and thank you for reading!
The above is the detailed content of Array formulas and functions in Excel - examples and guidelines. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1668
1668
 14
14
 1426
1426
 52
52
 1328
1328
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1255
1255
 24
24
 If You Don't Rename Tables in Excel, Today's the Day to Start
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:58 AM
If You Don't Rename Tables in Excel, Today's the Day to Start
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:58 AM
Quick link Why should tables be named in Excel How to name a table in Excel Excel table naming rules and techniques By default, tables in Excel are named Table1, Table2, Table3, and so on. However, you don't have to stick to these tags. In fact, it would be better if you don't! In this quick guide, I will explain why you should always rename tables in Excel and show you how to do this. Why should tables be named in Excel While it may take some time to develop the habit of naming tables in Excel (if you don't usually do this), the following reasons illustrate today
 How to change Excel table styles and remove table formatting
Apr 19, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to change Excel table styles and remove table formatting
Apr 19, 2025 am 11:45 AM
This tutorial shows you how to quickly apply, modify, and remove Excel table styles while preserving all table functionalities. Want to make your Excel tables look exactly how you want? Read on! After creating an Excel table, the first step is usual
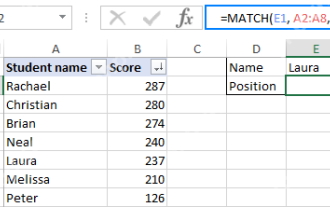 Excel MATCH function with formula examples
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Excel MATCH function with formula examples
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
This tutorial explains how to use MATCH function in Excel with formula examples. It also shows how to improve your lookup formulas by a making dynamic formula with VLOOKUP and MATCH. In Microsoft Excel, there are many different lookup/ref
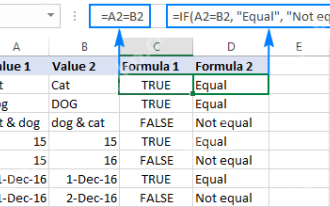 Excel: Compare strings in two cells for matches (case-insensitive or exact)
Apr 16, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Excel: Compare strings in two cells for matches (case-insensitive or exact)
Apr 16, 2025 am 11:26 AM
The tutorial shows how to compare text strings in Excel for case-insensitive and exact match. You will learn a number of formulas to compare two cells by their values, string length, or the number of occurrences of a specific character, a
 How to Make Your Excel Spreadsheet Accessible to All
Apr 18, 2025 am 01:06 AM
How to Make Your Excel Spreadsheet Accessible to All
Apr 18, 2025 am 01:06 AM
Improve the accessibility of Excel tables: A practical guide When creating a Microsoft Excel workbook, be sure to take the necessary steps to make sure everyone has access to it, especially if you plan to share the workbook with others. This guide will share some practical tips to help you achieve this. Use a descriptive worksheet name One way to improve accessibility of Excel workbooks is to change the name of the worksheet. By default, Excel worksheets are named Sheet1, Sheet2, Sheet3, etc. This non-descriptive numbering system will continue when you click " " to add a new worksheet. There are multiple benefits to changing the worksheet name to make it more accurate to describe the worksheet content: carry
 Don't Ignore the Power of F4 in Microsoft Excel
Apr 24, 2025 am 06:07 AM
Don't Ignore the Power of F4 in Microsoft Excel
Apr 24, 2025 am 06:07 AM
A must-have for Excel experts: the wonderful use of the F4 key, a secret weapon to improve efficiency! This article will reveal the powerful functions of the F4 key in Microsoft Excel under Windows system, helping you quickly master this shortcut key to improve productivity. 1. Switching formula reference type Reference types in Excel include relative references, absolute references, and mixed references. The F4 keys can be conveniently switched between these types, especially when creating formulas. Suppose you need to calculate the price of seven products and add a 20% tax. In cell E2, you may enter the following formula: =SUM(D2 (D2*A2)) After pressing Enter, the price containing 20% tax can be calculated. But,
 I Always Name Ranges in Excel, and You Should Too
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:56 AM
I Always Name Ranges in Excel, and You Should Too
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:56 AM
Improve Excel efficiency: Make good use of named regions By default, Microsoft Excel cells are named after column-row coordinates, such as A1 or B2. However, you can assign more specific names to a cell or cell range, improving navigation, making formulas clearer, and ultimately saving time. Why always name regions in Excel? You may be familiar with bookmarks in Microsoft Word, which are invisible signposts for the specified locations in your document, and you can jump to where you want at any time. Microsoft Excel has a bit of a unimaginative alternative to this time-saving tool called "names" and is accessible via the name box in the upper left corner of the workbook. Related content #
 5 Open-Source Alternatives to Microsoft Excel
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:56 AM
5 Open-Source Alternatives to Microsoft Excel
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:56 AM
Excel remains popular in the business world, thanks to its familiar interfaces, data tools and a wide range of feature sets. Open source alternatives such as LibreOffice Calc and Gnumeric are compatible with Excel files. OnlyOffice and Grist provide cloud-based spreadsheet editors with collaboration capabilities. Looking for open source alternatives to Microsoft Excel depends on what you want to achieve: Are you tracking your monthly grocery list, or are you looking for tools that can support your business processes? Here are some spreadsheet editors for a variety of use cases. Excel remains a giant in the business world Microsoft Ex






