COUNT and COUNTA functions to count cells in Excel
This tutorial provides a concise overview of Excel's COUNT and COUNTA functions, illustrating their use with practical examples. You'll also learn how to leverage COUNTIF and COUNTIFS for counting cells based on specific criteria.
Excel excels at numerical manipulation, but often requires counting cells containing values—any value, or specific value types. This might involve counting inventory items or list entries. Excel offers COUNT and COUNTA functions for this purpose.
Let's explore these core functions and then delve into formulas for counting cells meeting particular conditions, highlighting nuances in counting various value types.
Excel COUNT Function: Counting Numerical Cells
The COUNT function tallies cells containing numerical values. Its syntax is:
COUNT(value1, [value2], ...)
where value1, value2, etc., represent cell references or ranges. Excel 365-2007 supports up to 255 arguments; earlier versions handle up to 30.
For example, =COUNT(A1:A100) counts numeric cells in A1:A100. Importantly, dates and times (stored as serial numbers) are also counted.
Key COUNT Function Considerations:
- For cell references/ranges, only numbers, dates, and times are counted. Blanks and non-numeric entries are ignored.
- When directly inputting values, numbers, dates, times, TRUE/FALSE booleans, and numeric text (e.g., "5") are counted.
For instance, =COUNT(1, "apples", "2", 1/1/2016, TRUE) returns 4.
COUNT Function Examples:
- Counting numeric cells in a single range:
=COUNT(A2:A10) - Counting across multiple non-contiguous ranges:
=COUNT(B2:B7, D2:D7)


Tips: Use COUNTIF or COUNTIFS for counting numbers meeting specific criteria. For counting cells with text, logical values, and errors, use COUNTA.
Excel COUNTA Function: Counting Non-Blank Cells
COUNTA counts cells containing any value (non-empty cells). Its syntax mirrors COUNT's:
COUNTA(value1, [value2], ...)
=COUNTA(A1:A100) counts non-empty cells in A1:A100. Multiple non-adjacent ranges are also supported: =COUNTA(B2:B10, D2:D20, E2:F10).
COUNTA counts: numbers, dates/times, text, TRUE/FALSE, error values, and even empty text strings (""). However, it does not count truly empty cells. Cells appearing empty but containing spaces or formulas returning "" will be counted.

The Excel status bar provides a quick count of non-blank cells in a selected range.

Advanced Cell Counting Techniques
Beyond COUNT and COUNTA, Excel offers functions for more complex counting scenarios.
Counting Cells Meeting One Condition (COUNTIF)
COUNTIF counts cells meeting a specified criterion:
COUNTIF(range, criteria)
=COUNTIF(A2:A15, "apples") counts "apples" in A2:A15. Cell references can also be used for the criteria.

Counting Cells Matching Multiple Criteria (COUNTIFS)
COUNTIFS extends COUNTIF to handle multiple ranges and criteria:
COUNTIFS(criteria_range1, criteria1, [criteria_range2, criteria2]...)
=COUNTIFS(A2:A15,"apples", B2:B15,">=200") counts "apples" with sales ≥ $200. Cell references can be used for criteria.

Determining Total Cells in a Range
Use ROWS and COLUMNS to find the total number of cells in a rectangular range:
=ROWS(range)*COLUMNS(range)
=ROWS(A1:D7)*COLUMNS(A1:D7) calculates the total cells in A1:D7.

This tutorial covers the fundamentals of Excel's COUNT and COUNTA functions, providing a solid foundation for efficient cell counting.
The above is the detailed content of COUNT and COUNTA functions to count cells in Excel. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1675
1675
 14
14
 1429
1429
 52
52
 1333
1333
 25
25
 1278
1278
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 If You Don't Rename Tables in Excel, Today's the Day to Start
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:58 AM
If You Don't Rename Tables in Excel, Today's the Day to Start
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:58 AM
Quick link Why should tables be named in Excel How to name a table in Excel Excel table naming rules and techniques By default, tables in Excel are named Table1, Table2, Table3, and so on. However, you don't have to stick to these tags. In fact, it would be better if you don't! In this quick guide, I will explain why you should always rename tables in Excel and show you how to do this. Why should tables be named in Excel While it may take some time to develop the habit of naming tables in Excel (if you don't usually do this), the following reasons illustrate today
 How to change Excel table styles and remove table formatting
Apr 19, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to change Excel table styles and remove table formatting
Apr 19, 2025 am 11:45 AM
This tutorial shows you how to quickly apply, modify, and remove Excel table styles while preserving all table functionalities. Want to make your Excel tables look exactly how you want? Read on! After creating an Excel table, the first step is usual
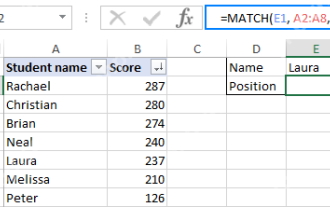 Excel MATCH function with formula examples
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Excel MATCH function with formula examples
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
This tutorial explains how to use MATCH function in Excel with formula examples. It also shows how to improve your lookup formulas by a making dynamic formula with VLOOKUP and MATCH. In Microsoft Excel, there are many different lookup/ref
 How to Make Your Excel Spreadsheet Accessible to All
Apr 18, 2025 am 01:06 AM
How to Make Your Excel Spreadsheet Accessible to All
Apr 18, 2025 am 01:06 AM
Improve the accessibility of Excel tables: A practical guide When creating a Microsoft Excel workbook, be sure to take the necessary steps to make sure everyone has access to it, especially if you plan to share the workbook with others. This guide will share some practical tips to help you achieve this. Use a descriptive worksheet name One way to improve accessibility of Excel workbooks is to change the name of the worksheet. By default, Excel worksheets are named Sheet1, Sheet2, Sheet3, etc. This non-descriptive numbering system will continue when you click " " to add a new worksheet. There are multiple benefits to changing the worksheet name to make it more accurate to describe the worksheet content: carry
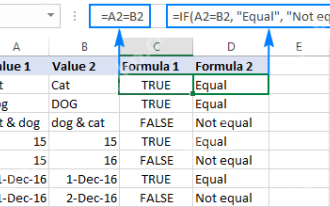 Excel: Compare strings in two cells for matches (case-insensitive or exact)
Apr 16, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Excel: Compare strings in two cells for matches (case-insensitive or exact)
Apr 16, 2025 am 11:26 AM
The tutorial shows how to compare text strings in Excel for case-insensitive and exact match. You will learn a number of formulas to compare two cells by their values, string length, or the number of occurrences of a specific character, a
 Don't Ignore the Power of F4 in Microsoft Excel
Apr 24, 2025 am 06:07 AM
Don't Ignore the Power of F4 in Microsoft Excel
Apr 24, 2025 am 06:07 AM
A must-have for Excel experts: the wonderful use of the F4 key, a secret weapon to improve efficiency! This article will reveal the powerful functions of the F4 key in Microsoft Excel under Windows system, helping you quickly master this shortcut key to improve productivity. 1. Switching formula reference type Reference types in Excel include relative references, absolute references, and mixed references. The F4 keys can be conveniently switched between these types, especially when creating formulas. Suppose you need to calculate the price of seven products and add a 20% tax. In cell E2, you may enter the following formula: =SUM(D2 (D2*A2)) After pressing Enter, the price containing 20% tax can be calculated. But,
 5 Open-Source Alternatives to Microsoft Excel
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:56 AM
5 Open-Source Alternatives to Microsoft Excel
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:56 AM
Excel remains popular in the business world, thanks to its familiar interfaces, data tools and a wide range of feature sets. Open source alternatives such as LibreOffice Calc and Gnumeric are compatible with Excel files. OnlyOffice and Grist provide cloud-based spreadsheet editors with collaboration capabilities. Looking for open source alternatives to Microsoft Excel depends on what you want to achieve: Are you tracking your monthly grocery list, or are you looking for tools that can support your business processes? Here are some spreadsheet editors for a variety of use cases. Excel remains a giant in the business world Microsoft Ex
 I Always Name Ranges in Excel, and You Should Too
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:56 AM
I Always Name Ranges in Excel, and You Should Too
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:56 AM
Improve Excel efficiency: Make good use of named regions By default, Microsoft Excel cells are named after column-row coordinates, such as A1 or B2. However, you can assign more specific names to a cell or cell range, improving navigation, making formulas clearer, and ultimately saving time. Why always name regions in Excel? You may be familiar with bookmarks in Microsoft Word, which are invisible signposts for the specified locations in your document, and you can jump to where you want at any time. Microsoft Excel has a bit of a unimaginative alternative to this time-saving tool called "names" and is accessible via the name box in the upper left corner of the workbook. Related content #




