Fundamentals of Python Programming for Beginners - Analytics Vidhya
Introduction
Experienced data professionals have observed a shift in the dominance of certain technical skills, a trend supported by data. Before NumPy's 2005 release, Python was considered slow for numerical analysis. NumPy changed that. Pandas (2008) solidified Python's position as the premier language for data analysis.
The emergence of frameworks like SciKit-Learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch further cemented Python's status as the leading programming language for data science (AI and machine learning).
While a few years ago, the choice between R and Python for data professionals was considered less critical, the rise of AI and LLMs has propelled Python to the forefront. This article presents essential Python tips and tricks to elevate your coding skills, regardless of your experience level.

Learning Objectives
This guide aims to ensure you confidently navigate production-level Python code by:
- Reinforcing your understanding of core Python concepts.
- Enhancing your comprehension of production code functionality.
- Enabling you to reproduce code and write features understood by your team.
A Python notebook containing all code examples is available for download [link to download]. This serves as a handy syntax reference.
Before delving into the details, let's address the key question: Why Python?
Table of Contents
- Why Master Python?
- Python Fundamentals
- Static vs. Dynamic Typing
- Static vs. Dynamic Binding
- Compilation in Programming Languages
- Key Python Keywords
- Identifiers vs. Variables
- Type Conversions
- Immutability in Python
- Memory-Level Considerations
- Primitive Datatypes' Immutability
- Object Deletion and Memory Management
- Efficient Coding Techniques
- Using the
anyOperator Instead ofor
- Using the
- String Manipulation
- The Importance of Unicode Characters
- Strings and Memory Management
- Printing Colored Text
- Opening a Web Browser
- Concatenation without the " " Operator
- The
split()String Method - The
join()String Method - Using the
inOperator for Substrings - Finding Indices with
find() - Using
id()to Get Object Identity - Aliases
- Modifying Print Output with
end - Printing Multiple Elements with Commas
- F-Strings for Formatting
- Returning and Assigning Multiple Values
- Ternary Conditional Operator and List Comprehensions
- Flag Variables
- Removing List Duplicates with Sets
- Using
infor Concise Conditionals
- Debugging Strategies
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Master Python?
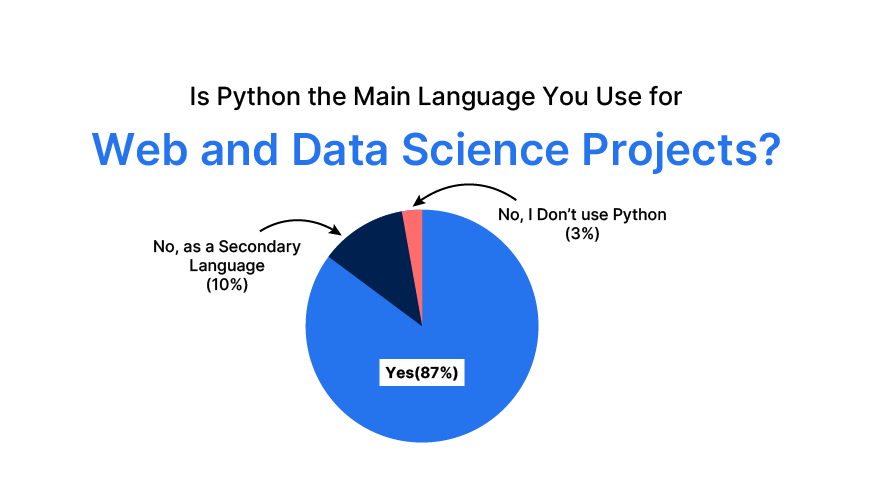
A significant 87% of data scientists use Python for their primary projects, with another 10% using it secondarily. This widespread adoption highlights its importance. Python is extensively used in Gen-AI, deep learning, data science, data analysis, web development, and web scraping. Its popularity in AI and machine learning stems from:
- Ease of Learning: Python boasts a simpler syntax than languages like C or Java, making it beginner-friendly.
-
Rich Libraries: It offers a wealth of built-in functions (e.g.,
print(),list(),str()) and libraries (e.g., NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-Learn) to streamline complex tasks. - Supportive Community: The large and active Python community provides readily available assistance.
Note: Python is case-sensitive. The snake_case convention (lowercase with underscores) is recommended to minimize syntax errors.
Let's explore the core aspects of Python programming.
Python Fundamentals
This section covers fundamental Python concepts:
Static vs. Dynamic Typing
-
Static Typing: Method invocation and property access are determined at compile time, improving type safety and potentially reducing execution time. (Example:
int q = 9;in C ) -
Dynamic Typing: Variable data types are determined at runtime, allowing for flexible type changes. (Example:
a = 1; a = "Hi";in Python)
Static vs. Dynamic Binding
- Static Binding (Early Binding): Method invocation is determined at compile time, leading to faster execution and improved type safety.
- Dynamic Binding (Late Binding): Method invocation is determined at runtime, offering greater flexibility and polymorphism.
Compilation in Programming Languages
Compilation transforms high-level code into machine-executable binary code. This is done using:
- Compilers: (e.g., Java, C , C) translate the entire code at once before execution.
- Interpreters: (e.g., Python, PHP) translate code line by line during execution.
Key Python Keywords
[Image of key Python keywords]
Identifiers vs. Variables
Identifiers are names used to uniquely identify objects (variables, functions, classes, etc.), while variables are names associated with memory locations storing values. Python identifier rules include:
- Cannot begin with a digit.
- Can contain uppercase/lowercase letters, digits, and underscores.
- Cannot be keywords.
Type Conversions
Type conversion (or type casting) changes an object's data type. Python supports:
- Implicit Type Conversion: The interpreter automatically handles type conversion to minimize data loss.
-
Explicit Type Conversion: Using functions like
int(),float(), andstr()to explicitly convert types. Caution is needed to avoid data loss.
Immutability in Python
-
Immutable objects:
int,float,complex,str,tuple,frozenset. Their values cannot be changed after creation. -
Mutable objects:
list,dict,set,bytearray. Their values can be modified in place.
Memory-Level Considerations
Immutable object modifications create new objects in memory, while mutable object changes occur within the existing memory allocation.
Primitive Datatypes' Immutability
The id() function reveals the unique memory address of an object. This demonstrates that modifying an immutable object creates a new object with a different memory address.
Object Deletion and Memory Management
Python's memory management uses:
- Reference Counting: Each object tracks its references. When the count reaches zero, the memory is freed.
- Cyclic Garbage Collection: Handles situations where objects circularly reference each other, preventing memory leaks.
Efficient Coding Techniques
[Continue with the remaining sections, adapting the style and content as shown in the previous examples.]
The above is the detailed content of Fundamentals of Python Programming for Beginners - Analytics Vidhya. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Meta's Llama 3.2: A Leap Forward in Multimodal and Mobile AI Meta recently unveiled Llama 3.2, a significant advancement in AI featuring powerful vision capabilities and lightweight text models optimized for mobile devices. Building on the success o
 10 Generative AI Coding Extensions in VS Code You Must Explore
Apr 13, 2025 am 01:14 AM
10 Generative AI Coding Extensions in VS Code You Must Explore
Apr 13, 2025 am 01:14 AM
Hey there, Coding ninja! What coding-related tasks do you have planned for the day? Before you dive further into this blog, I want you to think about all your coding-related woes—better list those down. Done? – Let’
 AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
This week's AI landscape: A whirlwind of advancements, ethical considerations, and regulatory debates. Major players like OpenAI, Google, Meta, and Microsoft have unleashed a torrent of updates, from groundbreaking new models to crucial shifts in le
 Selling AI Strategy To Employees: Shopify CEO's Manifesto
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Selling AI Strategy To Employees: Shopify CEO's Manifesto
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Shopify CEO Tobi Lütke's recent memo boldly declares AI proficiency a fundamental expectation for every employee, marking a significant cultural shift within the company. This isn't a fleeting trend; it's a new operational paradigm integrated into p
 A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AM
A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Introduction Imagine walking through an art gallery, surrounded by vivid paintings and sculptures. Now, what if you could ask each piece a question and get a meaningful answer? You might ask, “What story are you telling?
 GPT-4o vs OpenAI o1: Is the New OpenAI Model Worth the Hype?
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
GPT-4o vs OpenAI o1: Is the New OpenAI Model Worth the Hype?
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
Introduction OpenAI has released its new model based on the much-anticipated “strawberry” architecture. This innovative model, known as o1, enhances reasoning capabilities, allowing it to think through problems mor
 Reading The AI Index 2025: Is AI Your Friend, Foe, Or Co-Pilot?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:13 PM
Reading The AI Index 2025: Is AI Your Friend, Foe, Or Co-Pilot?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:13 PM
The 2025 Artificial Intelligence Index Report released by the Stanford University Institute for Human-Oriented Artificial Intelligence provides a good overview of the ongoing artificial intelligence revolution. Let’s interpret it in four simple concepts: cognition (understand what is happening), appreciation (seeing benefits), acceptance (face challenges), and responsibility (find our responsibilities). Cognition: Artificial intelligence is everywhere and is developing rapidly We need to be keenly aware of how quickly artificial intelligence is developing and spreading. Artificial intelligence systems are constantly improving, achieving excellent results in math and complex thinking tests, and just a year ago they failed miserably in these tests. Imagine AI solving complex coding problems or graduate-level scientific problems – since 2023
 How to Add a Column in SQL? - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:43 AM
How to Add a Column in SQL? - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:43 AM
SQL's ALTER TABLE Statement: Dynamically Adding Columns to Your Database In data management, SQL's adaptability is crucial. Need to adjust your database structure on the fly? The ALTER TABLE statement is your solution. This guide details adding colu






