How to Build an AI Agent using Llama Index and MonsterAPI
AI Agents: The Future of AI, Powered by LlamaIndex and MonsterAPI
AI agents are poised to revolutionize how we interact with technology. These autonomous systems mimic human behavior, performing tasks that require reasoning, decision-making, and real-time interaction – capabilities beyond the reach of traditional LLMs. This article delves into the world of AI agents, showcasing how to build them using LlamaIndex and MonsterAPI. LlamaIndex provides a robust framework for agent development, while MonsterAPI offers convenient access to powerful LLMs.
Learning Objectives:
- Grasp the architecture and functionality of AI agents and their application to real-world problems.
- Understand the key distinctions between LLMs and AI agents in terms of capabilities and applications.
- Learn the core components of an AI agent and how they interact.
- Explore diverse AI agent use cases across various industries.
(This article is part of the Data Science Blogathon.)
Table of Contents:
- What are AI Agents?
- Understanding AI Agent Components
- AI Agent Use Cases
- Building an Agentic RAG System with LlamaIndex and MonsterAPI
- Frequently Asked Questions
What are AI Agents?
AI agents are self-directed systems designed to emulate human actions. They operate within an environment, utilizing LLMs, tools, and memory to accomplish complex tasks. Unlike LLMs, which primarily process and generate text, AI agents engage in perception, action, and decision-making.
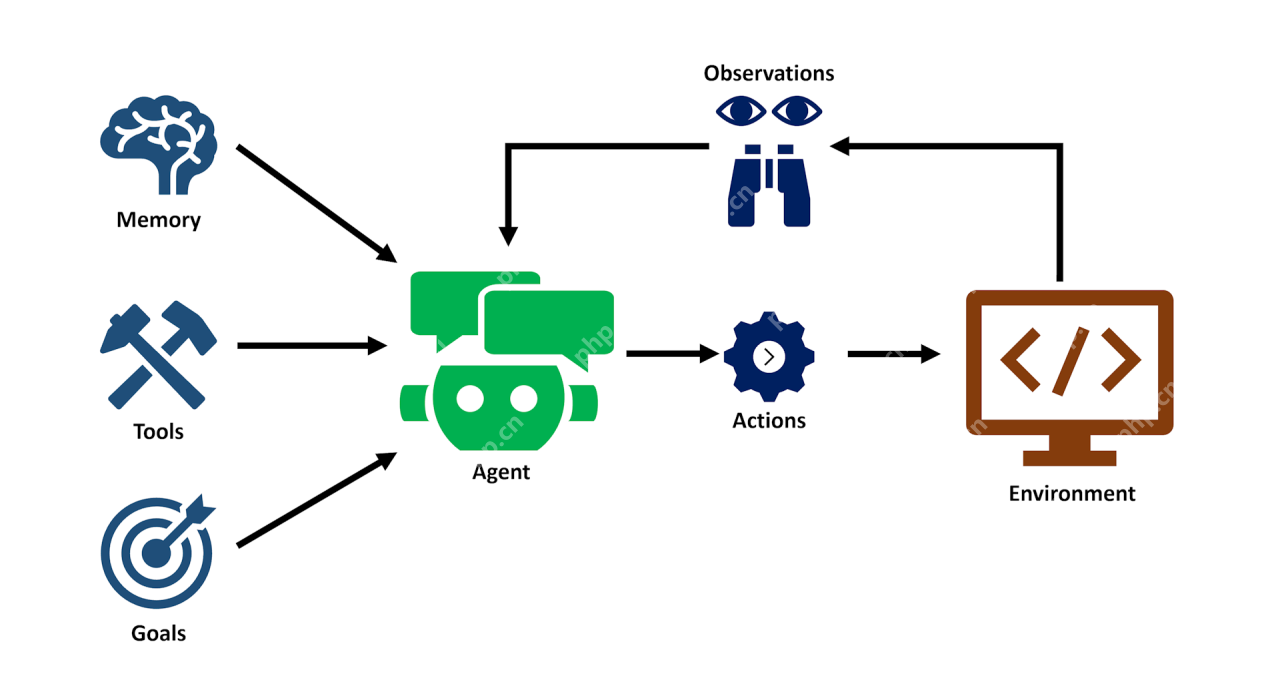
Key characteristics of AI agents include:
- Human-like Thinking: Agents employ tools (search engines, databases, calculators, etc.) to achieve specific outcomes.
- Human-like Action: Agents plan actions and utilize tools strategically to reach goals.
- Human-like Observation: Agents utilize planning frameworks to react, adapt, and take appropriate actions based on input and stored memory.
Here's a comparison of LLMs and AI agents:
| Feature | LLMs | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Core Capability | Text processing and generation | Perception, action, decision-making |
| Interaction | Text-based | Real-world or simulated environment |
| Applications | Chatbots, content generation, translation | Virtual assistants, automation, robotics |
| Limitations | Limited real-time interaction, potential for inaccuracies | Resource-intensive, complex development |
Understanding AI Agent Components
AI agents consist of interconnected components:
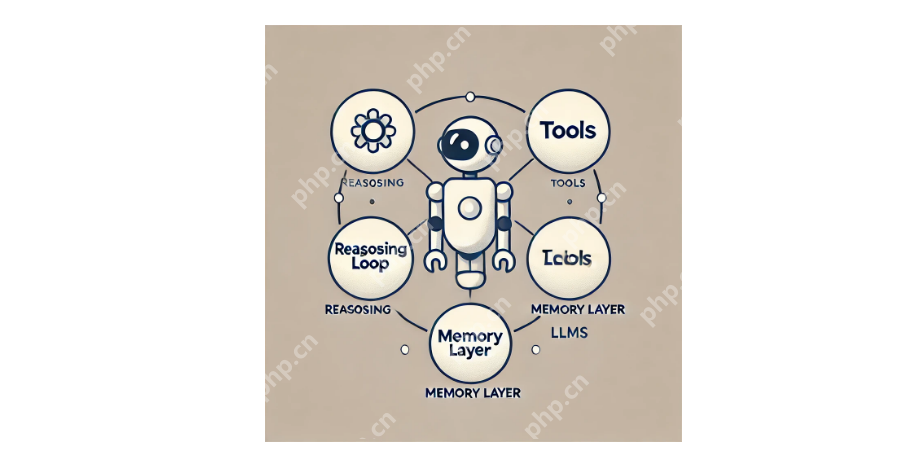
- Reasoning Loop: The core decision-making engine, planning actions and refining outputs.
- Memory Layer: Stores past actions and information, enabling efficient task completion (short-term and long-term memory).
- Models: LLMs that synthesize and generate human-understandable results.
- Tools: External functions (APIs, databases, calculators) that perform specific tasks.
These components interact dynamically. The reasoning loop uses model outputs to guide decisions, while tools execute those decisions. This closed-loop system enables seamless information processing, decision-making, and action.
LlamaIndex's Role in Agent Development
LlamaIndex simplifies agent development by providing high-level tools and classes. Its reasoning loop mechanisms (function-calling agents, ReAct agents) seamlessly integrate with LLMs, vector stores, and other components. A typical LlamaIndex agent setup looks like this:
from llama_index.agent.openai import OpenAIAgent from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI # import and define tools # Define functions and tools to interact with agent # initialize llm llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0613") # initialize openai agent agent = OpenAIAgent.from_tools(tools, llm=llm, verbose=True)
AI Agent Use Cases
AI agents find applications across diverse fields:
- Agentic RAG: Context-aware systems leveraging business data for enhanced query responses.
- SQL Agents: Translate natural language into SQL queries for database interaction.
- Workflow Assistants: Integrate with calendars, weather APIs, and other tools.
- Code Assistants: Aid in code review, writing, and improvement.
- Content Curation: Suggest and summarize articles and blog posts.
- Automated Trading: Analyze market data and execute trades.
- Threat Detection: Monitor network traffic and respond to cyber threats.
Building an Agentic RAG System with LlamaIndex and MonsterAPI
This section demonstrates building a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) agent using LlamaIndex and MonsterAPI. MonsterAPI simplifies LLM deployment and management, offering cost-effective access to models like Meta's Llama-3-8B-Instruct.
Step 1: Setup
Install necessary libraries and obtain a MonsterAPI key.
# install necessary libraries (replace with your actual commands) # ... import os from llama_index.llms.monsterapi import MonsterLLM from llama_index.core.embeddings import resolve_embed_model from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader import fitz # PyMuPDF # set up your FREE MonsterAPI key to access to models os.environ["MONSTER_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY"
Step 2: MonsterAPI Model Setup
Initialize the Llama-3-8B-Instruct model via MonsterAPI.
model = "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct"
llm = MonsterLLM(model=model, temperature=0.75)
result = llm.complete("What's the difference between AI and ML?") # Test the modelStep 3: Data Loading and Vector Store
Load documents, create a vector store index, and set up a query engine.
# ... (Document loading and processing using SimpleDirectoryReader, SentenceSplitter, and embedding model) ...
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents, transformations=[splitter], embed_model=embed_model)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine(llm=llm)
response = query_engine.query("What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation?")
This RAG agent leverages custom data via LlamaIndex's vector store and MonsterAPI's LLM.
Conclusion
AI agents represent a significant advancement in AI, enabling autonomous task completion and human-like interaction. LlamaIndex and MonsterAPI provide powerful tools for building sophisticated agents. As these technologies mature, the potential for creating increasingly intelligent and autonomous applications will only grow.
Key Takeaways:
- Learned about the functionality and architecture of AI agents.
- Understood the differences between LLMs and AI agents.
- Explored the core components of AI agents.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1: Does LlamaIndex support agent development? A1: Yes, LlamaIndex offers built-in tools for creating AI agents.
- Q2: What is an LLM agent in LlamaIndex? A2: A semi-autonomous system using LLMs and tools to achieve user goals.
- Q3: What's the main difference between LLMs and AI agents? A3: LLMs primarily process text, while AI agents interact with the environment and use tools.
(Note: Images used are assumed to be appropriately licensed for use in this context.)
The above is the detailed content of How to Build an AI Agent using Llama Index and MonsterAPI. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Meta's Llama 3.2: A Leap Forward in Multimodal and Mobile AI Meta recently unveiled Llama 3.2, a significant advancement in AI featuring powerful vision capabilities and lightweight text models optimized for mobile devices. Building on the success o
 10 Generative AI Coding Extensions in VS Code You Must Explore
Apr 13, 2025 am 01:14 AM
10 Generative AI Coding Extensions in VS Code You Must Explore
Apr 13, 2025 am 01:14 AM
Hey there, Coding ninja! What coding-related tasks do you have planned for the day? Before you dive further into this blog, I want you to think about all your coding-related woes—better list those down. Done? – Let’
 AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
This week's AI landscape: A whirlwind of advancements, ethical considerations, and regulatory debates. Major players like OpenAI, Google, Meta, and Microsoft have unleashed a torrent of updates, from groundbreaking new models to crucial shifts in le
 Selling AI Strategy To Employees: Shopify CEO's Manifesto
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Selling AI Strategy To Employees: Shopify CEO's Manifesto
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Shopify CEO Tobi Lütke's recent memo boldly declares AI proficiency a fundamental expectation for every employee, marking a significant cultural shift within the company. This isn't a fleeting trend; it's a new operational paradigm integrated into p
 A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AM
A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Introduction Imagine walking through an art gallery, surrounded by vivid paintings and sculptures. Now, what if you could ask each piece a question and get a meaningful answer? You might ask, “What story are you telling?
 GPT-4o vs OpenAI o1: Is the New OpenAI Model Worth the Hype?
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
GPT-4o vs OpenAI o1: Is the New OpenAI Model Worth the Hype?
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
Introduction OpenAI has released its new model based on the much-anticipated “strawberry” architecture. This innovative model, known as o1, enhances reasoning capabilities, allowing it to think through problems mor
 How to Add a Column in SQL? - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:43 AM
How to Add a Column in SQL? - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:43 AM
SQL's ALTER TABLE Statement: Dynamically Adding Columns to Your Database In data management, SQL's adaptability is crucial. Need to adjust your database structure on the fly? The ALTER TABLE statement is your solution. This guide details adding colu
 Reading The AI Index 2025: Is AI Your Friend, Foe, Or Co-Pilot?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:13 PM
Reading The AI Index 2025: Is AI Your Friend, Foe, Or Co-Pilot?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:13 PM
The 2025 Artificial Intelligence Index Report released by the Stanford University Institute for Human-Oriented Artificial Intelligence provides a good overview of the ongoing artificial intelligence revolution. Let’s interpret it in four simple concepts: cognition (understand what is happening), appreciation (seeing benefits), acceptance (face challenges), and responsibility (find our responsibilities). Cognition: Artificial intelligence is everywhere and is developing rapidly We need to be keenly aware of how quickly artificial intelligence is developing and spreading. Artificial intelligence systems are constantly improving, achieving excellent results in math and complex thinking tests, and just a year ago they failed miserably in these tests. Imagine AI solving complex coding problems or graduate-level scientific problems – since 2023






