Mutable vs Immutable Objects in Python - Analytics Vidhya
Introduction
Python is an object-oriented programming language (or OOPs).In my previous article, we explored its versatile nature. Due to this, Python offers a wide variety of data types, which can be broadly classified into mutable and immutable types. However, as a curious Python developer, I hope you also wonder how theseconcepts impact data. How is data processed and manipulated in memory? How has it affected the quality of the program?This article will provide a comprehensive overview of mutable vs immutable objects in Python and why they are crucial for effective programming. We will explore how mutability and immutability work across different Python objects, such as primitive data types like integers, floats, strings, etc., and built-in datatypes like lists, dictionaries, sets, tuples, etc.
Table of contents
- What is Mutability vs Immutability?
- What are Mutable vs Immutable Objects in Python?
- Comparative Analysis of Python Data Types
- What Happens at the Memory Level?
- How Does Deletion of Objects Work?
- How is the Performance of a Program Determined?
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Mutability vs Immutability?
From a high-level perspective, mutability refers to the ability of any object to be modified, changed, or updated after it is created. This means that if an object is mutable, you can change its state or content without creating a new object.
On the other hand, immutability means that once an object is created, its state cannot be changed/modified/updated. Any change to these objects creates a new object with a different memory allocation rather than altering the existing one.
What are Mutable vs Immutable Objects in Python?
The below image shows that Python’s rich data types can be divided into two categories: Mutable and Immutable objects, which are then further divided.
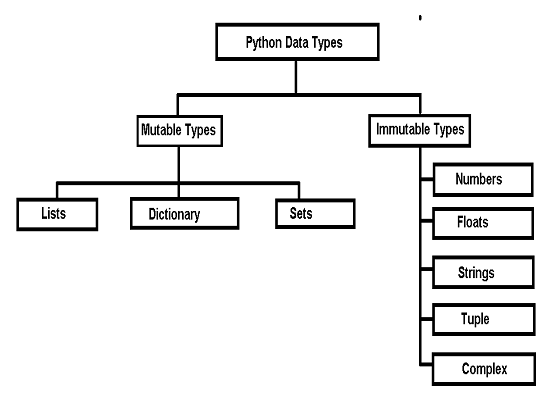
Comparative Analysis of Python Data Types
Let’s have a look over a comparison between all the built-in datatypes:
| Data Type | Mutable/Immutable | Description | Use Case |
| Integers | Immutable | Whole numbers (e.g., 1, -5, 42). | Use when working with numerical data that does not change. |
| Floats | Immutable | Numbers with decimal points (e.g., 3.14, -0.001). | Useful for scientific computations, financial data, etc. |
| Booleans | Immutable | Logical values: True or False. | Conditional checks, logical operations. |
| Strings | Immutable | Sequence of characters (e.g., “hello”, “world”). | Used for text manipulation, document processing, etc. |
| Tuples | Immutable | Ordered collection of items (e.g., (1, 2, 3)). | Suitable for constant data, it can be used as dictionary keys. |
| Frozen Sets | Immutable | An unordered collection of unique items, an immutable version of a set. | Used in cases where the set needs to be constant and hashable. |
| Complex Numbers | Immutable | Numbers with real and imaginary parts (e.g., 1 2j). | Used in scientific computing, signal processing, etc. |
| Lists | Mutable | Ordered collection of items (e.g., [1, 2, 3]). | Use when you need to modify, add, or remove elements frequently. |
| Dictionaries | Mutable | Collection of key-value pairs (e.g., {“name”: “John”, “age”: 30}). | Ideal for mapping relationships, lookups, and data storage. |
| Sets | Mutable | Unordered collection of unique items (e.g., {1, 2, 3}). | Best used for membership testing, removing duplicates, etc. |
| Custom Objects (Classes) | Mutable/Immutable | Behavior depends on how the class is defined (mutable by default). | Tailored behavior based on requirements; can control mutability. |
To understand these concepts in a more Pythonic way, go through these –
- Primitive Datatypes are “Immutable” – Link
- Python Built-in Data Structures are “Mutable” – Link
In these articles, I have discussed the mutability and immutability of these datatypes, the`id`function,shallowanddeep copy,and more, along with codes.
Note: However, I recommend only checking those codes after reading this article. This article enhances your understanding of “What happens inside the memory space?”
What Happens at the Memory Level?
When discussing immutability at the memory level, an immutable object cannot be altered directly. Any operation that seems to modify an immutable object creates a new object with the modified value in memory. Mutable objects share the same memory allocated previously. Changes to these objects occur in place, modifying the existing memory content without new allocation.
Before exploring this further, let’s first understand the two most common concepts about deleting objects from memory.
- Deallocation means that the system frees and makes available for other uses the memory previously occupied by an object.
- Garbage collection is a process in Python that automatically finds and frees up memory that is no longer being used by the program, especially for objects that reference each other in a cycle.
How Does Deletion of Objects Work?
Python’s memory management relies on two major things, reference counting and garbage collectors, to handle the deletion of objects. Let’s understand them one by one:
- Reference Counting: Python tracks the number of references pointing to each object. This is called the reference count.
- Cyclic References —Garbage Collection: Python also has a garbage collector that handles cyclic references. Sometimes, objects reference each other in a loop. When the reference count drops to zero, the memory occupied by the object is deallocated. For example, object A references object B and object B references object A. Even if no other part of the program needs these objects, their reference counts never drop to zero because they reference each other. This is where the garbage collector steps in.
How is the Performance of a Program Determined?
In terms of performance implications, mutability and immutability have significant differences. Immutable data types are generally faster to access and process. Python can optimize memory usage by reusing immutable objects, mainly if you’re working with small integers and strings across the program.
Mutable data types are more flexible but can incur additional overhead due to the need for dynamic memory space resizing. For instance, lists in Python are dynamic arrays because they are stored in a way that allows them to grow and shrink in size while performing operations such as adding or deleting elements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between mutable and immutable objects is crucial for writing efficient and reliable code in Python. For example, immutability offers safety where data should not change, such as in key-value mappings or concurrent programming.
Conversely, mutability is helpful in scenarios where dynamic updates to data structures are necessary for that particular part of the program. Knowing when to use what is essential to understanding the trade-offs in performance and complexity, ultimately leading to writing maintainable programs.
Also Read: Comprehensive Guide to Python Built-in Data Structures
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the difference between mutable vs immutable objects in Python?A. Mutable objects, like lists or dictionaries, offer the flexibility of in-place modification after their creation. Meanwhile, immutable objects, such as tuples or strings, cannot be altered after creation in the same memory allocation.
Q2. Why are strings immutable in Python?A. Strings are immutable to optimize memory usage and allow safe sharing across different program parts. This reduces memory usage for frequently used strings and simplifies reasoning about string handling in multi-threaded environments.
Q3. How does immutability affect performance in Python?A. Immutable objects can lead to faster performance because they are easier to manage in memory. Python can reuse immutable objects, reducing the overhead of creating new objects repeatedly. This adds insight into memory management benefits.
The above is the detailed content of Mutable vs Immutable Objects in Python - Analytics Vidhya. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Meta's Llama 3.2: A Leap Forward in Multimodal and Mobile AI Meta recently unveiled Llama 3.2, a significant advancement in AI featuring powerful vision capabilities and lightweight text models optimized for mobile devices. Building on the success o
 10 Generative AI Coding Extensions in VS Code You Must Explore
Apr 13, 2025 am 01:14 AM
10 Generative AI Coding Extensions in VS Code You Must Explore
Apr 13, 2025 am 01:14 AM
Hey there, Coding ninja! What coding-related tasks do you have planned for the day? Before you dive further into this blog, I want you to think about all your coding-related woes—better list those down. Done? – Let’
 AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
This week's AI landscape: A whirlwind of advancements, ethical considerations, and regulatory debates. Major players like OpenAI, Google, Meta, and Microsoft have unleashed a torrent of updates, from groundbreaking new models to crucial shifts in le
 Selling AI Strategy To Employees: Shopify CEO's Manifesto
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Selling AI Strategy To Employees: Shopify CEO's Manifesto
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Shopify CEO Tobi Lütke's recent memo boldly declares AI proficiency a fundamental expectation for every employee, marking a significant cultural shift within the company. This isn't a fleeting trend; it's a new operational paradigm integrated into p
 A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AM
A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Introduction Imagine walking through an art gallery, surrounded by vivid paintings and sculptures. Now, what if you could ask each piece a question and get a meaningful answer? You might ask, “What story are you telling?
 GPT-4o vs OpenAI o1: Is the New OpenAI Model Worth the Hype?
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
GPT-4o vs OpenAI o1: Is the New OpenAI Model Worth the Hype?
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
Introduction OpenAI has released its new model based on the much-anticipated “strawberry” architecture. This innovative model, known as o1, enhances reasoning capabilities, allowing it to think through problems mor
 Reading The AI Index 2025: Is AI Your Friend, Foe, Or Co-Pilot?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:13 PM
Reading The AI Index 2025: Is AI Your Friend, Foe, Or Co-Pilot?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:13 PM
The 2025 Artificial Intelligence Index Report released by the Stanford University Institute for Human-Oriented Artificial Intelligence provides a good overview of the ongoing artificial intelligence revolution. Let’s interpret it in four simple concepts: cognition (understand what is happening), appreciation (seeing benefits), acceptance (face challenges), and responsibility (find our responsibilities). Cognition: Artificial intelligence is everywhere and is developing rapidly We need to be keenly aware of how quickly artificial intelligence is developing and spreading. Artificial intelligence systems are constantly improving, achieving excellent results in math and complex thinking tests, and just a year ago they failed miserably in these tests. Imagine AI solving complex coding problems or graduate-level scientific problems – since 2023
 How to Add a Column in SQL? - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:43 AM
How to Add a Column in SQL? - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:43 AM
SQL's ALTER TABLE Statement: Dynamically Adding Columns to Your Database In data management, SQL's adaptability is crucial. Need to adjust your database structure on the fly? The ALTER TABLE statement is your solution. This guide details adding colu






