DSA Day Introduction
Hello everyone!
I will start a blog series focused on data structures and algorithms (DSA). The tutorial content is based on my study and experience.
I will write these tutorials in C and provide introductory tutorials for beginners in C.
Although DSA can be implemented in languages such as C, Java, or Python,
But I chose to use C.
This is a simple introduction, so don’t worry about not being able to understand it. The follow-up article will explain in detail.
This is just a preview of our discussion topic.
C language beginners are advised to learn the basics of C language first. If you are familiar with Java, it is even better.
My blog aims to help everyone learn C and DSA at the same time.
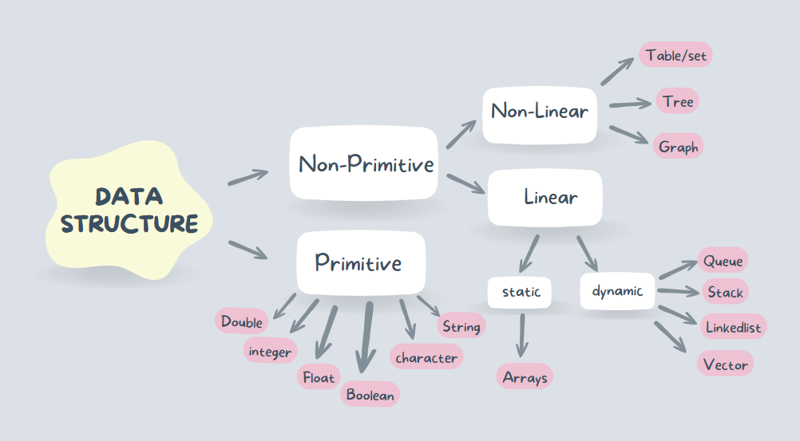
Original data structure
Raw data structures are the most basic data types in programming languages. Common raw data structures include:
- Int: Indicates an integer without a fractional part. For example: -1, 0, 4
- Float, double: represents a real number with a decimal part. For example: 3.14, -0.001, 2.71828
- Character (char): represents a single character, usually enclosed in single quotes. For example: 'a', 'z', '9', '#'
- Boolean value (bool): represents a true or false value, that is, true or false. Used for conditional statements and loops.
- String: Represents a sequence of characters, usually used to store text, enclosed in double quotes. For example: "Hello, world!", "python", "12345"
<code class="c ">#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { // Integer int age = 25; cout </iostream></code>Non-original data structure
A non-primitive data structure, also known as a composite data structure or user-defined data structure, is more complex than the original data structure. They are combined from raw data structures to store and manage more complex data collections.
- Array: an ordered collection of elements of the same type, stored in continuous memory locations.
- Linked list: A collection of elements, each element pointing to the next element, allowing dynamic memory allocation.
- Stack: A linear data structure that follows the principle of last in first out (LIFO). For example: a pile of dishes that can only be added or removed from the top.
- Queue: A linear data structure that follows the first-in first-out (FIFO) principle. For example: wait in line, and the first person who comes will serve first.
- Tree: A hierarchical data structure with root nodes and child nodes, used to represent hierarchical relationships. For example: binary tree, binary search tree.
- Figure: A collection consisting of nodes (vertices) and edges to represent network relationships. For example: social networks, computer networks.
- Hash table: The data structure that stores key-value pairs, and uses a hash function to calculate the storage location.
<code class="c ">// ... (code examples for non-primitive data structures would go here)</code>
The above is the detailed content of DSA Day Introduction. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use the chrono library in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the chrono library in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Using the chrono library in C can allow you to control time and time intervals more accurately. Let's explore the charm of this library. C's chrono library is part of the standard library, which provides a modern way to deal with time and time intervals. For programmers who have suffered from time.h and ctime, chrono is undoubtedly a boon. It not only improves the readability and maintainability of the code, but also provides higher accuracy and flexibility. Let's start with the basics. The chrono library mainly includes the following key components: std::chrono::system_clock: represents the system clock, used to obtain the current time. std::chron
 How to measure thread performance in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to measure thread performance in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Measuring thread performance in C can use the timing tools, performance analysis tools, and custom timers in the standard library. 1. Use the library to measure execution time. 2. Use gprof for performance analysis. The steps include adding the -pg option during compilation, running the program to generate a gmon.out file, and generating a performance report. 3. Use Valgrind's Callgrind module to perform more detailed analysis. The steps include running the program to generate the callgrind.out file and viewing the results using kcachegrind. 4. Custom timers can flexibly measure the execution time of a specific code segment. These methods help to fully understand thread performance and optimize code.
 How to understand ABI compatibility in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to understand ABI compatibility in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
ABI compatibility in C refers to whether binary code generated by different compilers or versions can be compatible without recompilation. 1. Function calling conventions, 2. Name modification, 3. Virtual function table layout, 4. Structure and class layout are the main aspects involved.
 How to optimize code
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:27 PM
How to optimize code
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:27 PM
C code optimization can be achieved through the following strategies: 1. Manually manage memory for optimization use; 2. Write code that complies with compiler optimization rules; 3. Select appropriate algorithms and data structures; 4. Use inline functions to reduce call overhead; 5. Apply template metaprogramming to optimize at compile time; 6. Avoid unnecessary copying, use moving semantics and reference parameters; 7. Use const correctly to help compiler optimization; 8. Select appropriate data structures, such as std::vector.
 How to use string streams in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
How to use string streams in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The main steps and precautions for using string streams in C are as follows: 1. Create an output string stream and convert data, such as converting integers into strings. 2. Apply to serialization of complex data structures, such as converting vector into strings. 3. Pay attention to performance issues and avoid frequent use of string streams when processing large amounts of data. You can consider using the append method of std::string. 4. Pay attention to memory management and avoid frequent creation and destruction of string stream objects. You can reuse or use std::stringstream.
 How to understand the volatile keyword in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:24 PM
How to understand the volatile keyword in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:24 PM
The volatile keyword in C is used to inform the compiler that the value of the variable may be changed outside of code control and therefore cannot be optimized. 1) It is often used to read variables that may be modified by hardware or interrupt service programs, such as sensor state. 2) Volatile cannot guarantee multi-thread safety, and should use mutex locks or atomic operations. 3) Using volatile may cause performance slight to decrease, but ensure program correctness.
 C# vs. C : Choosing the Right Language for Your Project
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:51 AM
C# vs. C : Choosing the Right Language for Your Project
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:51 AM
C# is suitable for projects that require development efficiency and type safety, while C is suitable for projects that require high performance and hardware control. 1) C# provides garbage collection and LINQ, suitable for enterprise applications and Windows development. 2)C is known for its high performance and underlying control, and is widely used in gaming and system programming.
 What is static analysis in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
What is static analysis in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The application of static analysis in C mainly includes discovering memory management problems, checking code logic errors, and improving code security. 1) Static analysis can identify problems such as memory leaks, double releases, and uninitialized pointers. 2) It can detect unused variables, dead code and logical contradictions. 3) Static analysis tools such as Coverity can detect buffer overflow, integer overflow and unsafe API calls to improve code security.






